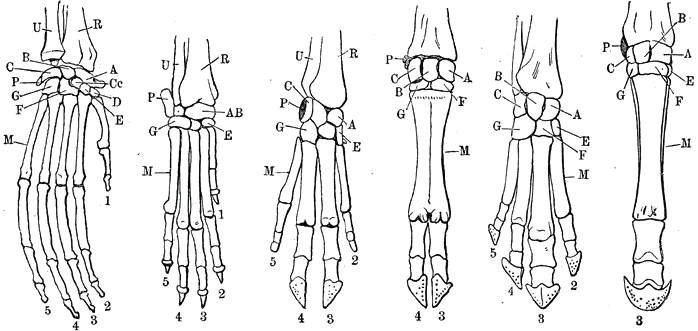|
Poikilopleuron
''Poekilopleuron'' (meaning "varied ribs") is a genus of carnosaurian theropod dinosaur, which lived during the middle Bathonian of the Jurassic, about 168 to 166 million years ago. The genus has been used under many different spelling variants, although only one, ''Poekilopleuron'', is valid. The type species is ''P. bucklandii'', named after William Buckland, and many junior synonyms of it have also been erected. Little material is currently known, as the holotype was destroyed in World War II, although many casts of the material still exist. Discovery and naming ''Poekilopleuron'' is a genus of theropod with a long and complex history. The holotype was discovered in July 1835 near La Maladrerie and the genus was named and first described by Jacques Amand Eudes-Deslongchamps in a report published in 1836, based on holotype material that is now destroyed. In 1837, Eudes-Deslongchamps published a more detailed account of this discovery in a monographEudes-Deslongchamps J.-A. (18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathonian
In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age (geology), age and stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.2 ±1.2 annum, Ma to around 165.3 ±1.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds the Bajocian Age and precedes the Callovian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The Bathonian Stage takes its name from Bath, Somerset, Bath, a spa town in England built on Jurassic limestone (the Latinized form of the town name is ''Bathonium''). The name was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist Jean Baptiste Julien d'Omalius d'Halloy, d'Omalius d'Halloy in 1843. The original type locality (geology), type locality was located near Bath. The French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny was in 1852 the first to define the exact length of the stage. The base of the Bathonian is at the first appearance of ammonite species ''Parkinsonia (ammonite), Parkinsonia (Gonolkites) convergens'' in the stratigraphic column. The global referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnosauria
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Carnosauria as clade including both Allosauroidea and Megalosauroidea (which is sometimes recovered as paraphyletic with respect to Allosauroidea), and thus including the majority of non- coelurosaurian members of theropod clade Tetanurae. Other researchers have found Allosauroidea and Megalosauroidea to be unrelated groups.Cau A. (2024)A Unified Framework for Predatory Dinosaur Macroevolution Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana, 63(1): 1-19. Distinctive characteristics of carnosaurs include large eye sockets, a long narrow skull and modifications of the legs and pelvis such as the thigh (femur) being longer than the shin ( tibia). Carnosaurs first appeared in the Middle Jurassic around , and the last definitive carnosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages ( limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some other primates), the term ''upper limb'' is often used. A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle or of a dolphin, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them. Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and hallux, big toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is Anatomical terms of locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastralia
Gastralia (: gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptiles, gastralia provide support for the abdomen and attachment sites for abdominal muscles. The possession of gastralia may be ancestral for Tetrapoda and were possibly derived from the ventral scales found in animals like rhipidistians, labyrinthodonts, and ''Acanthostega'', and may be related to ventral elements of turtle plastrons. Similar, but not homologous cartilagenous elements, are found in the ventral body walls of lizards and anurans. These structures have been referred to as inscriptional ribs, based on their alleged association with the inscriptiones tendinae (the tendons that form the six pack in humans). However, the terminology for these gastral-like structures remains confused. Both types, along with sternal ribs (ossified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falaise En Normandie , December 1174 between the captive William I, King of Scots, and the English King Henry II
{{disambig, geo ...
Falaise may refer to: Places * Falaise, Ardennes, commune in France * Falaise, Calvados, commune in France ** The Falaise pocket, site of a battle in the Second World War * La Falaise, commune in the Yvelines ''département'', France * The Falaise escarpment in Quebec City, Canada * Falaise, home of Harry Guggenheim at Sands Point, New York * ''Falaise de Bandiagara'', French name of the Bandiagara Escarpment in Mali Other * Treaty of Falaise The Treaty of Falaise was a forced written agreement made in December 1174 between the captive William I, King of Scots, and Henry II, King of England. During the Revolt of 1173-1174, William joined the rebels and was captured at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called '' Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank – for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Buckland
William Buckland Doctor of Divinity, DD, Royal Society, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian, geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist. His work in the early 1820s proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire had been a prehistoric hyena den, for which he was awarded the Copley Medal. It was praised as an example of how scientific analysis could reconstruct events in the distant past. He pioneered the use of fossilised Feces, faeces in reconstructing ecosystems, coining the term coprolites. Buckland also wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named ''Megalosaurus'' in 1824. Buckland followed the Gap creationism, Gap Theory in interpreting the biblical account of ''Genesis'' as two widely separated episodes of creation. It had emerged as a way to reconcile the scriptural account with discoveries in geology suggesting the earth was very old. Early in his career Buckland believed he had found evidence of the Deluge myth, bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |