|
Pluteus Brunneidiscus
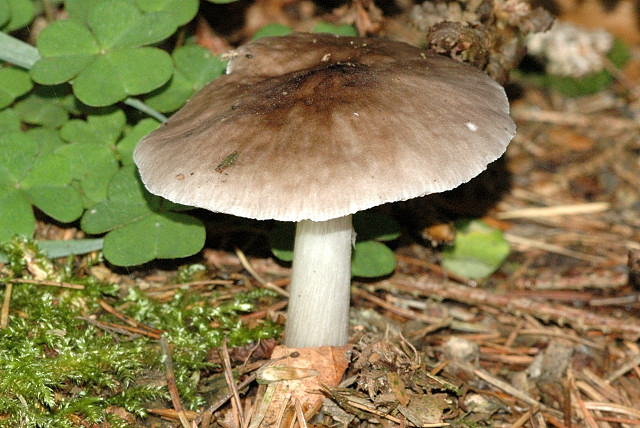
''Pluteus brunneidiscus'' is a species of agaric fungus in the family Pluteaceae. It was first described scientifically by American mycologist William Alphonso Murrill in 1917. It is found in Europe (Spain) and North America. Description Pileus and stipe without blue-green tinges. Specimens are small to medium-sized and have a brown pileus which is usually darker at the center. Habitat and distribution Solitary, on wood of broad-leaved trees. Found in the U.S. and in Spain from June to November. Chemistry These mushrooms contain psilocybin Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&n ....Justo, A. & M.L. Castro. (2007). "Observations in ''Pluteus'' section Pluteus in Spain: Two new records for Europe". ''Mycotaxon'' 102: 209–220. See also * List of ''Pluteus'' species Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alphonso Murrill
William Alphonso Murrill (October 13, 1869 – December 25, 1957) was an American mycologist, known for his contributions to the knowledge of the Agaricales and Polyporaceae. In 1904, he became the assistant Curator at the New York Botanical Garden (NYBG). He, along with the NYBG, founded the journal ''Mycologia'' and was its first editor for 16 years. Murrill was known to travel extensively to describe the mycota of Europe and the Americas. He traveled along the East Coast, Pacific Coast, Mexico and the Caribbean. Although Murrill was a very influential person at the NYBG, having worked his way up to become assistant director in 1908, his rather eccentric personality caused problems with his job. He went on annual collecting trips to Mexico, the Caribbean, Europe, and South America, sometimes, without informing any of his colleagues prior. These trips resulted in a cumulative total of 70,000 specimens, 1,400 of which are deposited in the NYBG.William Alphonso Murrill Records ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaric
An agaric () is a type of fungus fruiting body characterized by the presence of a pileus (cap) that is clearly differentiated from the stipe (stalk), with lamellae (gills) on the underside of the pileus. In the UK, agarics are called "mushrooms" or "toadstools". In North America they are typically called "gilled mushrooms". "Agaric" can also refer to a basidiomycete species characterized by an agaric-type fruiting body. Archaically, agaric meant 'tree-fungus' (after Latin ''agaricum''); however, that changed with the Linnaean interpretation in 1753 when Linnaeus used the generic name '' Agaricus'' for gilled mushrooms. Most species of agaricus belong to the order Agaricales in the subphylum Agaricomycotina. The exceptions, where agarics have evolved independently, feature largely in the orders Russulales, Boletales, Hymenochaetales, and several other groups of basidiomycetes. Old systems of classification placed all agarics in the Agaricales and some (mostly older) sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluteaceae
The Pluteaceae are a family of small to medium-sized mushrooms which have free gill attachment and pink spores. Members of Pluteaceae can be mistaken for members of Entolomataceae, but can be distinguished by the angled spores and attached gills of the Entolomataceae. The four genera in the Pluteaceae comprise the widely distributed ''Volvariella'' and ''Pluteus'', the rare '' Chamaeota'', and '' Volvopluteus'', which was newly described in 2011 as a result of molecular analysis. The ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008) estimates there are 364 species in the family. Selected species * ''Pluteus cervinus'', synonym ''Pluteus atricapillus'', or deer mushroom * ''Pluteus concentricus'' * '' Pluteus leoninus'' * ''Pluteus murinus'' * '' Pluteus salicinus'', or the knackers crumpet (hallucinogenic) * ''Volvariella volvacea'' * '' Volvopluteus gloiocephalus'' See also *List of Agaricales families The Agaricales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes (divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from about a dozen other genera. Psilocybin is itself biologically inactive but is quickly converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar, in some aspects, to those of LSD, mescaline, and DMT. In general, the effects include euphoria, visual and mental hallucinations, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time, and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Imagery found on prehistoric murals and rock paintings of modern-day Spain and Algeria suggests that human usage of psilocybin mushrooms predates recorded history. In Mesoamerica, the mushrooms had long been consumed in spiritual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pluteus Species
This is an incomplete list of species in the agaric genus ''Pluteus''. Species of ''Pluteus'' are commonly found growing on woody substrates including stumps, logs, fallen branches, woody debris such as sawdust, and buried wood. Three sections are widely accepted in ''Pluteus'', including ''Pluteus'', ''Hispidoderma'' Fayod, and ''Celluloderma'' Fayod. Section ''Pluteus'' is characterized by fruit bodies with a filamentous cap cuticle (pileipellis) and thick-walled pleurocystidia A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar .... Section ''Hispidoderma'' consists of species with a filamentous pileipellis and thin-walled pleurocystidia. Section ''Celluloderma'' is defined by a cystoderm pileipellis composed of ellipsoid to saccate-pyriform to vesiculose cells with or without cysti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1917
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of Europe
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluteus
''Pluteus'' is a large genus of fungi with over 300 species. They are wood rotting saprobes with pink spore prints and gills that are free from the stem. The Latin word ''Pluteus'' means ''shed or penthouse''. Characteristics of the genus Characteristics of the ''Pluteus'' genus are: #These fungi grow on wood or wood remains. #The spore powder is deep pink, soon giving a pink tint to the initially pale gills. #The gills are free from the stipe. #There is no volva or ring (exception: the rare recently reclassified North American species ''P. mammillatus'', previously ''Chamaeota sphaerospora''). #Microscopically, they often have abundant, distinctive cystidia. The spores are smooth and roughly egg-shaped. ''Pluteus'' is separated from ''Volvariella'' due to the lack of a volva, and from '' Entoloma'' by growing on wood and by microscopic features (''Entolomas'' have angular spores). Naming The name ''Pluteus'' was established in 1837 by the founding mycologist Elias Mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
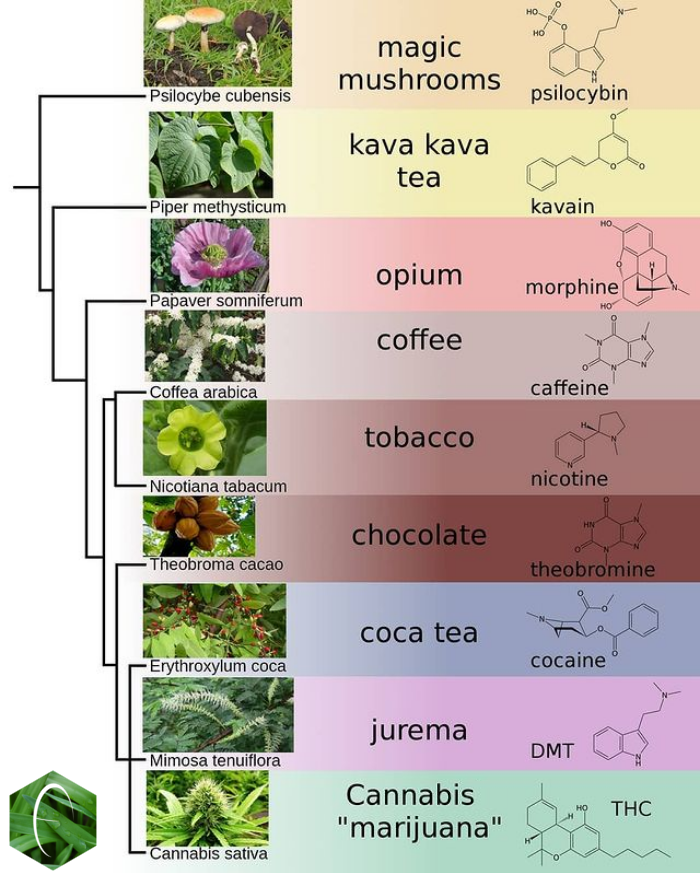
Psychoactive Fungi
This is a list of psychoactive plants, fungi, and animals. Plants Psychoactive plants include, but are not limited to, the following examples: * ''Cannabis'': cannabinoids * Tobacco: nicotine and beta-carboline alkaloids * Coca: cocaine * Opium Poppy: morphine, codeine, thebaine, papaverine, noscapine, and narceine * ''Salvia divinorum'': salvinorin A * Khat: cathine and cathinone * Kava: kavalactones * Nutmeg: myristicin * Nightshade (''Solanaceae'') plants containing hyoscyamine, atropine, and scopolamine: ** ''Datura'' ** Deadly nightshade (''Atropa belladonna'') ** Henbane (''Hyoscyamus niger'') ** Mandrake (''Mandragora officinarum'') ** Other ''Solanaceae'' * Psychoactive cacti, which contain mainly mescaline: ** Peyote ** Other '' Lophophora'' ** Peruvian Torch cactus ** San Pedro cactus ** Other '' Echinopsis'' * Minimally psychoactive plants that contain mainly caffeine and theobromine: ** Coffee ** Tea (also contains theanine) ** Guarana ** Yerba Mate ** Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |