|
Plum Curculio
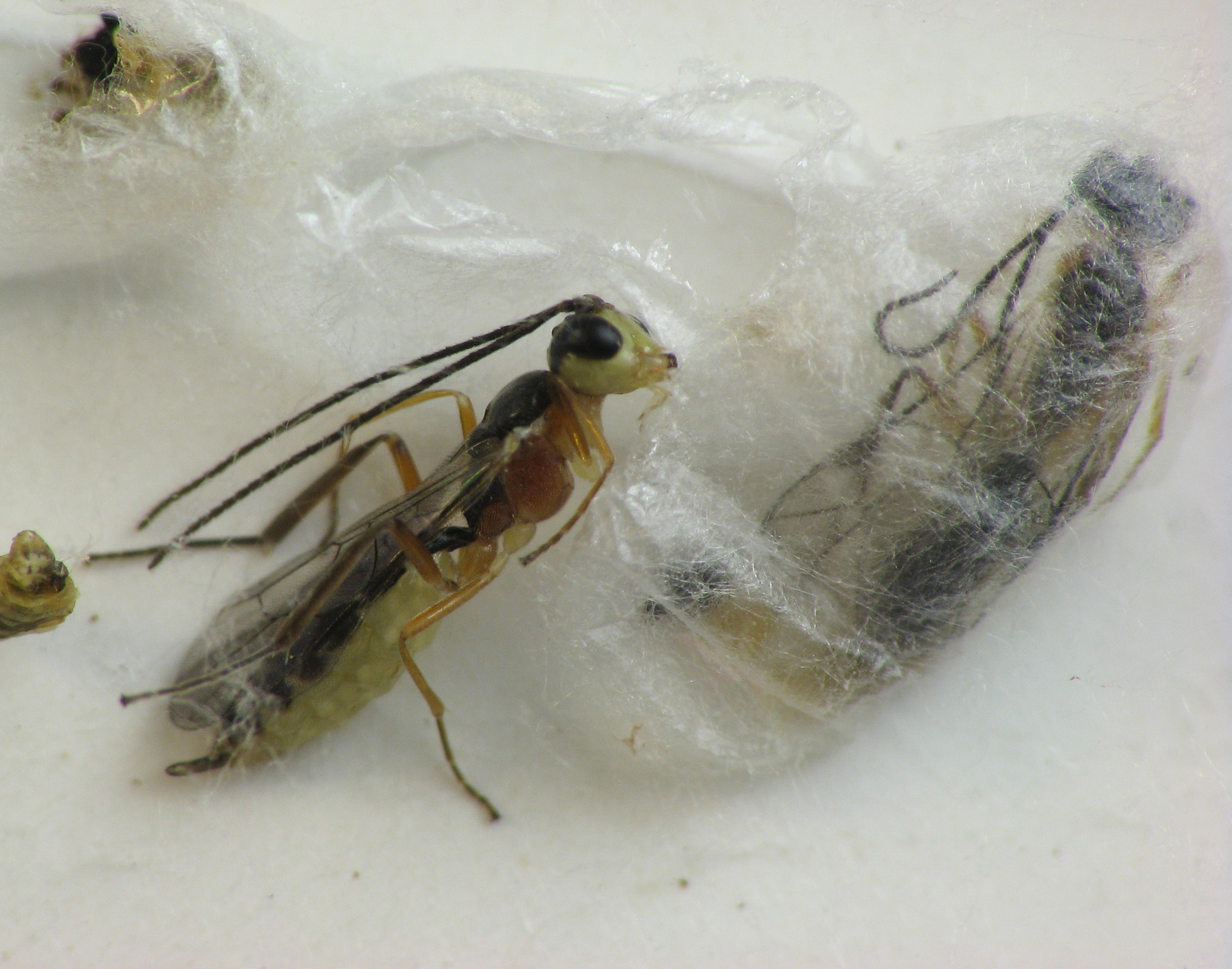
The plum curculio (''Conotrachelus nenuphar'') is a true weevil native to the regions east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. It is notorious for destroying fruits if left uncontrolled. Life stages A female curculio uses a number of hosts to lay her eggs in, including plums, peaches, apples, pears, and other pome and stone fruits as well as blueberries. After the female has chosen a suitable host, she will build an egg chamber under the fruit skin to receive the egg. She then turns around and places the egg in the cavity. Next, she slices a curved slit underneath the egg cavity, leaving the egg in a flap of flesh and causing a crescent-shaped scar on the outside of the fruit. Without this curved slit, eggs are killed by pressure from the growth of the host fruit. There are four larval instars. There is a univoltine "northern strain" and multivoltine "southern strain" of plum curculio, with the two strains being largely reproductively incompatible due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conotrachelus Nenuphar
The plum curculio (''Conotrachelus nenuphar'') is a true weevil native to the regions east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. It is notorious for destroying fruits if left uncontrolled. Life stages A female curculio uses a number of hosts to lay her eggs in, including plums, peaches, apples, pears, and other pome and stone fruits as well as blueberries. After the female has chosen a suitable host, she will build an egg chamber under the fruit skin to receive the egg. She then turns around and places the egg in the cavity. Next, she slices a curved slit underneath the egg cavity, leaving the egg in a flap of flesh and causing a crescent-shaped scar on the outside of the fruit. Without this curved slit, eggs are killed by pressure from the growth of the host fruit. There are four larval instars. There is a univoltine "northern strain" and multivoltine "southern strain" of plum curculio, with the two strains being largely reproductively incompatible due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plum Curculio
The plum curculio (''Conotrachelus nenuphar'') is a true weevil native to the regions east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. It is notorious for destroying fruits if left uncontrolled. Life stages A female curculio uses a number of hosts to lay her eggs in, including plums, peaches, apples, pears, and other pome and stone fruits as well as blueberries. After the female has chosen a suitable host, she will build an egg chamber under the fruit skin to receive the egg. She then turns around and places the egg in the cavity. Next, she slices a curved slit underneath the egg cavity, leaving the egg in a flap of flesh and causing a crescent-shaped scar on the outside of the fruit. Without this curved slit, eggs are killed by pressure from the growth of the host fruit. There are four larval instars. There is a univoltine "northern strain" and multivoltine "southern strain" of plum curculio, with the two strains being largely reproductively incompatible due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Herbst
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Herbst (1 November 1743 – 5 November 1807) was a German natural history, naturalist and entomologist from Petershagen, Minden-Ravensberg. He served as a chaplain in the Prussian army. His marriage in Berlin, 1770, with Euphrosyne Luise Sophie (1742–1805), daughter of the Prussian ''Hofrat'' Libert Waldschmidt, seems to have been childless. He was the joint editor, with Carl Gustav Jablonsky, of ''Naturgeschichte der in- und ausländischen Insekten'' (1785–1806, 10 volumes), which was one of the first attempts at a complete survey of the order Coleoptera. Herbst's ''Naturgeschichte der Krabben und Krebse'', released in installments, was the first full survey of crustaceans. Herbst's other works included ''Anleitung zur Kenntnis der Insekten'' (1784–86, 3 volumes), ''Naturgeschichte de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria infecting many species of arthropods and filarial nematodes. The symbiotic relationship ranges from parasitism to obligate mutualism. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes of arthropods, and is possibly the most widespread reproductive parasite bacterium in the biosphere. Its interactions with hosts are complex and highly diverse across different host species. Some host species cannot reproduce, or even survive, without ''Wolbachia'' colonisation. One study concluded that more than 16% of neotropical insect species carry bacteria of this genus, and as many as 25 to 70% of all insect species are estimated to be potential hosts. History The first organism classified as ''Wolbachia'' was discovered in 1924 by Marshall Hertig and Simeon Burt Wolbach in the common house mosquito. They described it as "a somewhat pleomorphic, rodlike, Gram-negative, intracellular organism hatapparently infects only the ovaries and te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crataegus
''Crataegus'' (), commonly called hawthorn, quickthorn, thornapple, Voss, E. G. 1985. ''Michigan Flora: A guide to the identification and occurrence of the native and naturalized seed-plants of the state. Part II: Dicots (Saururaceae–Cornaceae)''. Cranbrook Institute of Science and University of Michigan Herbarium, Ann Arbor, Michigan. May-tree,Graves, Robert. ''The White Goddess: A Historical Grammar of Poetic Myth'', 1948, amended and enlarged 1966, New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. whitethorn, Mayflower or hawberry, is a genus of several hundred species of shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere in Europe, Asia, North Africa and North America. The name "hawthorn" was originally applied to the species native to northern Europe, especially the common hawthorn ''C. monogyna'', and the unmodified name is often so used in Britain and Ireland. The name is now also applied to the entire genus and to the related Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
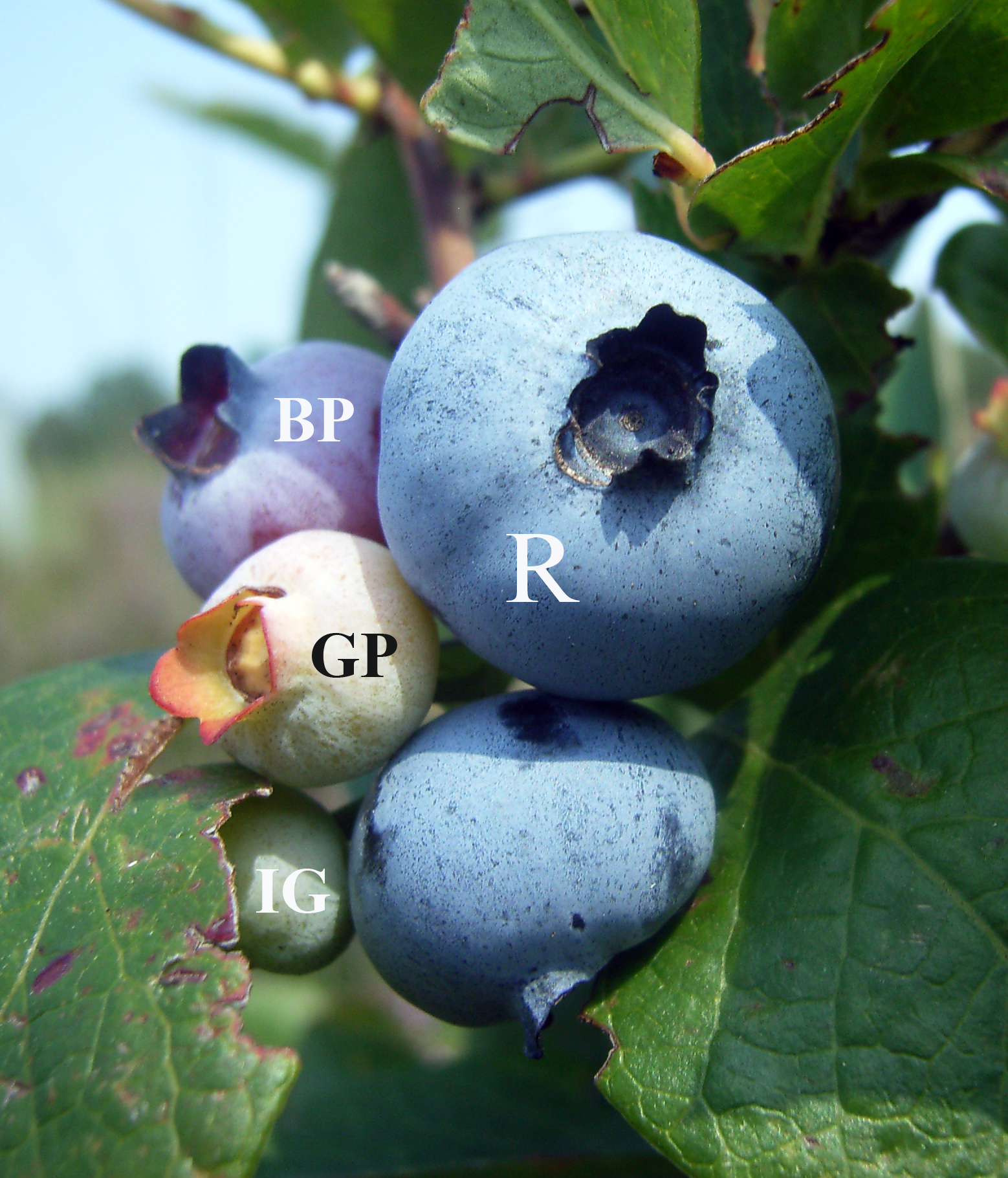
Blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' with the genus ''Vaccinium''. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In the commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world's supply of highbush blueberries. Description Many species of blueberries grow wild in North America, including '' Vaccinium myrtilloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quince
The quince (; ''Cydonia oblonga'') is the sole member of the genus ''Cydonia'' in the Malinae subtribe (which contains apples, pears, and other fruits) of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yellow pome fruit, similar in appearance to a pear. Ripe quince fruits are hard, tart, and astringent. They are eaten raw or processed into jam, quince cheese, or alcoholic drinks. The quince tree is sometimes grown as an ornamental plant for its attractive pale pink blossoms and as a miniature bonsai plant. In ancient Greece, the word for quince was used ribaldly by poets such as Aristophanes to signify teenage breasts. Description Quinces are shrubs or small trees up to tall and wide. Young twigs are covered in a grey down. The leaves are oval, and are downy on the underside. The solitary flowers, produced in late spring after the leaves, are white or pink. The ripe fruit is aromatic but remains hard; gritty stone cells are disperse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''. Usually an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also called apricots. In 2022, world production of apricots was 3.9 million tonnes, led by Turkey with 21% of the total. Etymology ''Apricot'' first appeared in English in the 16th century as ''abrecock'' from the Middle French or later , from Spanish '' albaricoque'' and Catalan , in turn from Arabic (, ), from Byzantine Greek (, ), derived from late Greek (, ) from Latin () (, ). Description The apricot is a small tree, tall, with a trunk up to in diameter and a dense, spreading canopy. The leaves are ovate, long, and wide, with a rounded base, a pointed tip, and a finely serrated margin. The flowers are in diameter, with five white to pinkish petals; they are produced singly or in pairs in early spring before the leaves. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit). Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The name 'cherry' also refers to the cherry tree and its wood, and is sometimes applied to almonds and visually similar flowering trees in the genus ''Prunus'', as in " ornamental cherry" or " cherry blossom". Wild cherry may refer to any of the cherry species growing outside cultivation, although ''Prunus avium'' is often referred to specifically by the name "wild cherry" in the British Isles. Botany True cherries ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus'' contains species that are typically called cherries. They are known as true cherries and distinguished by having a single winter bud per axil, by having the flowers in small corymbs or umbels of several together (occasionally solitary, e.g. ''P. serrula''; some species with short racemes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectarine
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called nectarines. Peaches and nectarines are the same species, though they are regarded commercially as different fruits. The tree is regarded as handsome and is planted in gardens for its springtime blooms in addition to fruit production. The peach tree is relatively short lived, usually not exceeding twenty years of age. However, the peach fruit is regarded as a symbol of longevity in several East Asian cultures. The specific name ''persica'' refers to its widespread cultivation in Persia (modern-day Iran), from where it was transplanted to Europe and in the 16th century to the Americas. It belongs to the genus ''Prunus'', which also includes the cherry, apricot, almond, and plum, and which is part of the rose family. The peach is very popular; only the ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Wing
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insect flight, insects to fly. They are found on the second and third Thorax (insect anatomy), thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the Odonata, dragonflies and Neuroptera, lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family (biology), family or even genus level in many order (biology), orders of insects. Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pupa
A pupa (; : pupae) is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages thereof being egg, larva, pupa, and imago. The processes of entering and completing the pupal stage are controlled by the insect's hormones, especially juvenile hormone, prothoracicotropic hormone, and ecdysone. The act of becoming a pupa is called pupation, and the act of emerging from the pupal case is called eclosion or emergence. The pupae of different groups of insects have different names such as ''chrysalis'' for the pupae of butterflies and ''tumbler'' for those of the mosquito family. Pupae may further be enclosed in other structures such as cocoons, nests, or shells. Position in life cycle The pupal stage follows the larval stage, or in some cases a prepupal stage, and precedes adulthood ('' imago'') in insects with compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |