|
Plestiodon Barbouri
''Plestiodon barbouri'', also known commonly as Barbour's blue-tailed skink and Barbour's eyelid skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Japan. Etymology The specific name, ''barbouri'', is in honor of American herpetologist Thomas Barbour. Beolens B, Watkins M, Grayson M (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Eumeces barbouri'', p. 16). Geographic range ''P. barbouri'' is found on the Amami Islands and the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. Habitat The preferred natural habitats of ''P. barbouri'' are forest and shrubland. Reproduction The mode of reproduction of ''P. barbouri'' is unknown. References Further reading * Schmitz A, Mausfeld P, Embert D (2004). "Molecular studies on the genus ''Eumeces'' Wiegmann 1834: phylogenetic relationships and taxonomic imlications". ''Hamadryad'' 28 (1–2): 73–89. (''Plestiodon barbouri'', new combination). * Van Denburgh J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Van Denburgh
John Van Denburgh (August 23, 1872 – October 24, 1924) was an American herpetologist from California (who also used the name Van Denburgh in publications, hence this name is used below). Biography Van Denburgh was born in San Francisco and enrolled at Stanford University in 1891. As of 1895, he organized the herpetology department of the California Academy of Sciences. In 1897, he received a Ph.D. from Stanford University and earned a M.D. from Johns Hopkins in 1902. Subsequently, he practiced medicine in San Francisco, while again serving as curator of the herpetological collections of the California Academy of Sciences. After the San Francisco earthquake of 1906 he was instrumental in rebuilding the lost herpetology collections through new expeditions and also acquisitions of other collections. In 1922, he published the two-volume ''The Reptiles of Western North America''. He died in 1924 while on vacation in Honolulu, Hawaii. Taxa named by and in honor of Van Denburgh V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Watkins (zoologist)
Michael or Mike Watkins may refer to: * Michael D. Watkins, American author * Michael M. Watkins, American engineer and scientist * Michael W. Watkins Michael W. Watkins (often credited as Michael Watkins) is an American cinematographer, television director and television producer. He has worked on ''Smallville'', ''Boomtown'', ''The X-Files'', and '' Lois & Clark: The New Adventures of Super ..., American television producer * Mike Watkins (rugby union) (born 1952), Welsh rugby union player * Mike Watkins (basketball) (born 1995), American basketball player * Mike Watkins (American football) (born 1978), American football player * Mike K. Watkins (1947–1998), British explosive ordnance disposal expert commemorated at the Canadian National Vimy Memorial {{hndis, Watkins, Michael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Japan
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 31 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plestiodon
''Plestiodon'' is a genus of lizards in the family Scincidae (skinks). The genus contains many species formerly classified under the genus '' Eumeces'', except those now placed in '' Mesoscincus''. They are secretive, agile animals with a cylindrical body covered with smooth, shiny scales. They are distributed from East Asia to throughout North America from southern Canada south to Mexico, including oceanic islands such as Bermuda. Defensive mechanism The conspicuous coloring of species of ''Plestiodon'' is a survival trait: it attracts a predator's attention to the tail of the animal, which will break off when grabbed. A skink thus often manages to escape and hide under some rock, log, or fallen leaves while the predator still contemplates the wildly thrashing severed tail. (This is an instance of what is called autotomy: voluntarily shedding a body part in order to escape, and later re generating the body part.) After the tail regenerates, it usually has the same color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the island a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
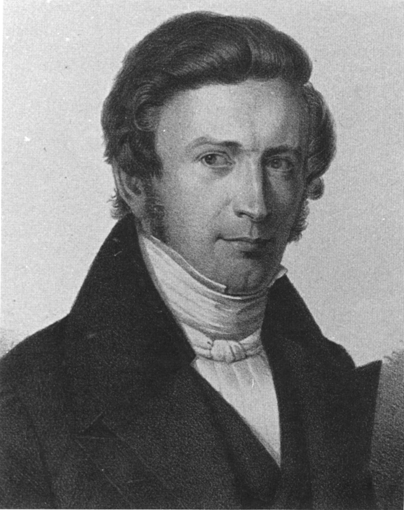
Arend Friedrich August Wiegmann
Arend Friedrich August Wiegmann (2 June 1802 – 15 January 1841) was a German zoologist and herpetologist born in Braunschweig. He studied medicine and philology at the University of Leipzig, and afterwards was an assistant to Martin Lichtenstein (1780–1857) in Berlin. In 1828 he became a professor at Cologne, and two years later was an extraordinary professor at the Humboldt University in Berlin. Wiegmann specialized in the study of herpetology and mammalogy. In 1835, he founded, together with other scholars, the zoological periodical '' Archiv für Naturgeschichte'', also known as "Wiegmann's Archive". With Johann Friedrich Ruthe (1788–1859) he wrote an important textbook of zoology called ''Handbuch der Zoologie'', and in 1834 Wiegmann published ''Herpetologia Mexicana'', a monograph on the reptiles of Mexico. In 1841 he died of tuberculosis at the age of 38 in Berlin. His father Arend Friedrich Wiegmann (1771–1853) a German researcher in botany. Species describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modes Of Reproduction
Animals make use of a variety of modes of reproduction to produce their young. Traditionally this variety was classified into three modes, oviparity (embryos in eggs), viviparity (young born live), and ovoviviparity (intermediate between the first two). However, each of those so-called traditional modes covered a wide range of diverse reproductive strategies. The biologist Thierry Lodé has accordingly proposed five modes of reproduction based on the relationship between the zygote (the fertilised egg) and the parents. His revised modes are ovuliparity, with external fertilisation; oviparity, with internal fertilisation of large eggs containing a substantial nutritive yolk; ovo-viviparity, that is oviparity where the zygotes are retained for a time in a parent's body, but without any sort of feeding by the parent; histotrophic viviparity, where the zygotes develop in the female's oviducts, but are fed on other tissues; and hemotrophic viviparity, where the developing embryos are fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It may be the mature vegetation type in a particular region and remain stable over time, or a transitional community that occurs temporarily as the result of a disturbance, such as fire. A stable state may be maintained by regular natural disturbance such as fire or browsing. Shrubland may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the danger of fire. The term was coined in 1903. Shrubland species generally show a wide range of adaptations to fire, such as heavy seed production, lignotubers, and fire-induced germination. Botanical structural form In botany and ecology a shrub is defined as a much-branched woody plant less than 8 m high and usually with many stems. Tall shrubs are mostly 2–8 m high, small shrubs 1–2 m high an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
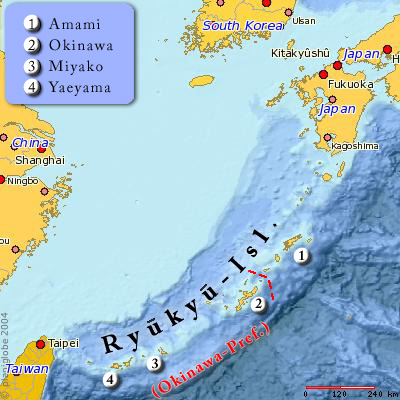
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yonaguni the westernmost. The larger are mostly high islands and the smaller mostly coral. The largest is Okinawa Island. The climate of the islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south. Precipitation is very high and is affected by the rainy season and typhoons. Except the outlying Daitō Islands, the island chain has two major geologic boundaries, the Tokara Strait (between the Tokara and Amami Islands) and the Kerama Gap (between the Okinawa and Miyako Islands). The islands beyond the Tokara Strait are characterized by their coral reefs. The Ōsumi and Tokara Islands, the northernmost of the isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest of Kyushu. Administratively, the group belongs to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. The Geospatial Information Authority of Japan and the Japan Coast Guard agreed on February 15, 2010, to use the name of for the Amami Islands. Prior to that, was also used. The name of Amami is probably cognate with , the goddess of creation in the Ryukyuan creation myth. Geography The Amami Islands are limestone islands of coralline origin and have a total area of approximately , of which constitute the city (''-shi'') of Amami, and constitute the district (''-gun'') of Oshima. The highest elevation is ''Yuwandake'' with a height of on Amami Ōshima. The climate is a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') with very warm su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)