|
Pigment Yellow 13
Pigment Yellow 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 12, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by phenyl and to Pigment Yellow 14 where the xylyl groups are replaced by o-tolyl. It is often depicted as an azo (-N=N-) structure, but according to X-ray crystallography closely related compounds exist as the keto-hydrazide tautomer In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the reloca ...s.{{cite journal, doi=10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00068-2 , title=The crystal and molecular structures of three diarylide yellow pigments, C. I. Pigments Yellow 13, 14 and 63 , date=2002 , last1=Barrow , first1=M. , journal=Dyes and Pigme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
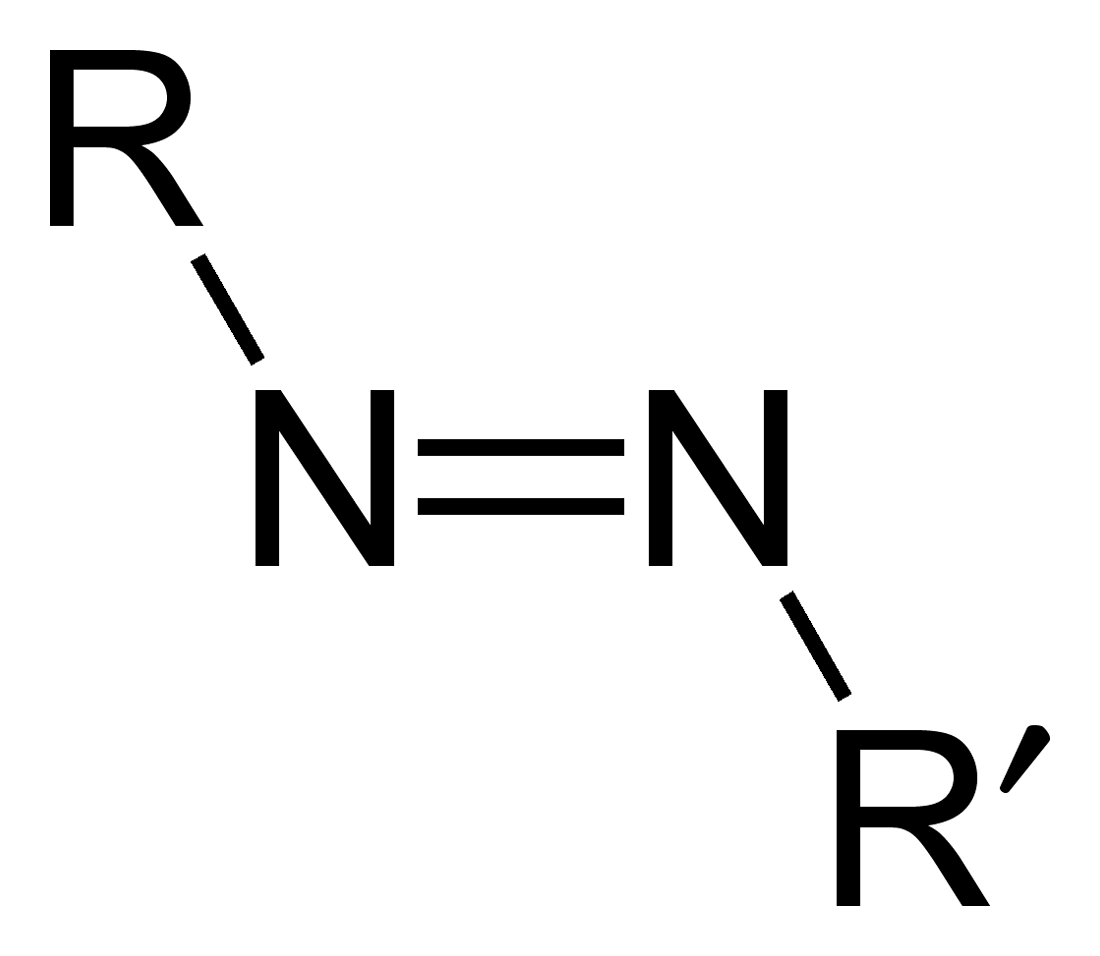
Azo Compound
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarylide Pigment
Diarylide pigments are organic compounds that are used as pigments in inks and related materials. They often are yellow or yellow-green. To some extent, these organic compounds have displaced cadmium sulfide from the market. Being pigments, these compounds exist as (yellow) powders of low solubility in water. They are similar to the simpler monoazo pigments called arylide yellows.K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. Production and properties The formation of diarylide pigments involves the reaction of doubly diazotized aromatic diamines (derivatives of benzidine) with acetoacetanilide. By varying both of these components, several useful pigments have been produced. A related family of organic pigments are the simpler arylides, which arise from the coupling of ''mono''-diazonium salts with the same coupling partners. The pigments' colors can range from yellow to yellow-green. One common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine
3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity. Preparation and reactions 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is prepared in two steps from 2-nitrochlorobenzene. The first step involves reduction with zinc in base to afford 2,2'-dichlorodiphenylhydrazine. This intermediate undergoes the benzidine rearrangement to afford 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. Aqueous solutions of 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine degrade in light to monochloro derivative. It undergoes chlorination (for example in water treatment plants) to give the tetrachloro derivative. The most widely practiced reaction of 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine is its double diazoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment Yellow 12
Diarylide pigments are organic compounds that are used as pigments in inks and related materials. They often are yellow or yellow-green. To some extent, these organic compounds have displaced cadmium sulfide from the market. Being pigments, these compounds exist as (yellow) powders of low solubility in water. They are similar to the simpler monoazo pigments called arylide yellows.K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. Production and properties The formation of diarylide pigments involves the reaction of doubly diazotized aromatic diamines (derivatives of benzidine) with acetoacetanilide. By varying both of these components, several useful pigments have been produced. A related family of organic pigments are the simpler arylides, which arise from the coupling of ''mono''-diazonium salts with the same coupling partners. The pigments' colors can range from yellow to yellow-green. One common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment Yellow 14
Pigment Yellow 14 is an organic compound classified as an azo compound. It is a commercial yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 13, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by an ortho tolyl. It is often depicted as an azo (-N=N-) structure, but according to X-ray crystallography closely related compounds exist as the keto-hydrazide tautomer In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the reloca ...s.{{cite journal, doi=10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00068-2 , title=The crystal and molecular structures of three diarylide yellow pigments, C. I. Pigments Yellow 13, 14 and 63 , date=2002 , last1=Barrow , first1=M. , journal=Dyes and Pigments , volume=55 , issue=2–3 , pages=79–89 Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure (valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is a quantum superposition, essentially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigments
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Pigments
Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product of decay, or is composed of organic compounds * Organic compound, a compound that contains carbon ** Organic chemistry, chemistry involving organic compounds Farming, certification and products * Organic farming, agriculture conducted according to certain standards, especially the use of stated methods of fertilization and pest control * Organic certification, accreditation process for producers of organically-farmed products * Organic horticulture, the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture * Organic products, "organics": ** Organic food, food produced from organic farming methods and often certified organic according to organic farming stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shades Of Yellow
Varieties of the color yellow may differ in hue, chroma (also called saturation, intensity, or colorfulness) or lightness (or value, tone, or brightness), or in two or three of these qualities. Variations in value are also called tints and shades, a tint being a yellow or other hue mixed with white, a shade being mixed with black. A large selection of these various colors is shown below. Web colors Yellow (RGB) (X11 yellow) (color wheel yellow) The color box at right shows the most intense yellow representable in 8-bit RGB color model; yellow is a ''secondary'' color in an additive RGB space. This color is also called color wheel yellow. It is at precisely 60 degrees on the HSV color wheel, also known as the RGB color wheel. Its complementary color is blue. Yellow (CMYK) (process yellow) (canary yellow) Process yellow (also called pigment yellow or printer's yellow), also known as canary yellow, is one of the three colors typically used as subtractive primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |