|
Phytoprogestogen
Phytoprogestogens, also known as phytoprogestins, are phytochemicals (that is, naturally occurring, plant-derived chemicals) with progestogenic effects. Relative to their phytoestrogen counterparts, phytoprogestogens are rare. However, a number have been identified, including kaempferol, diosgenin (found in yam), apigenin (found in chasteberry), naringenin, and syringic acid, among others. In addition, 3,8-dihydrodiligustilide from ''Ligusticum chuanxiong'' is a potent progestogen ( EC50 = 90 nM), whereas riligustilide Riligustilide is a nonsteroidal phytoprogestogen that is found in ''Ligusticum chuanxiong''. It is a very weak agonist of the progesterone receptor (EC50 ≈ 81 μM). Another compound in the plant, 3,8-dihydrodiligustilide, is also a phytop ... is a weak progestogen (EC50 ≈ 81 μM). References Progestogens {{pharmacology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riligustilide
Riligustilide is a nonsteroidal phytoprogestogen that is found in ''Ligusticum chuanxiong''. It is a very weak agonist of the progesterone receptor (EC50 ≈ 81 μM). Another compound in the plant, 3,8-dihydrodiligustilide, is also a phytoprogestogen, but is almost 1,000-fold more potent in comparison ( EC50 = 90 nM). See also * Kaempferol * Tanaproget Tanaproget (INN; developmental code names NSP-989, WAY-166989) is an investigational nonsteroidal progestin. It is a high affinity, high efficacy, and very selective agonist of the progesterone receptor (PR). Due to its much more selective b ... References Progestogens Cyclobutanes Lactones Alkene derivatives Spiro compounds {{genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligusticum Chuanxiong
''Ligusticum striatum'' (syn. ''L. wallichii'') is a flowering plant native to India, Kashmir, and Nepal in the carrot family best known for its use in traditional Chinese medicine where it is considered one of the 50 fundamental herbs. It is known by the common name Szechuan lovage. It contains the phytoprogestogens 3,8-dihydrodiligustilide and riligustilide. Uses Along with ''Ligusticum wallichii'', L. striatum is one of the possible herbs used to make the Chinese Traditional Medicine ''chuānxiōng'' () It is used in China, with portions of other plants and herbs (such as monkshood and '' Rosa banksiae'') to make a liniment to treat a painful swelling of the joints. It can be used to treat ischemic strokes, improve brain microcirculation and inhibit thrombus formation and platelet aggregation. References striatum The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the foreb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytochemical
Phytochemicals are chemical compounds produced by plants, generally to help them resist fungi, bacteria and plant virus infections, and also consumption by insects and other animals. The name comes . Some phytochemicals have been used as poisons and others as traditional medicine. As a term, ''phytochemicals'' is generally used to describe plant compounds that are under research with unestablished effects on health, and are not scientifically defined as essential nutrients. Regulatory agencies governing food labeling in Europe and the United States have provided guidance for industry to limit or prevent health claims about phytochemicals on food product or nutrition labels. Definition Phytochemicals are chemicals of plant origin. Phytochemicals (from Greek ''phyto'', meaning "plant") are chemicals produced by plants through primary or secondary metabolism. They generally have biological activity in the plant host and play a role in plant growth or defense against competitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy (i.e., ''progestational''), although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles. The progestogens are one of three types of sex hormones, the others being estrogens like estradiol and androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone. In addition, they are one of the five major classes of steroid hormones, the others being the androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids, as well as the neurosteroids. All endogenous progestogens are characterized by their basic 21-carbon skeleton, called a pregnane skeleton (C21). In similar manner, the estrogens possess an estrane skeleton (C18), and androgens, an androstane skeleton ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
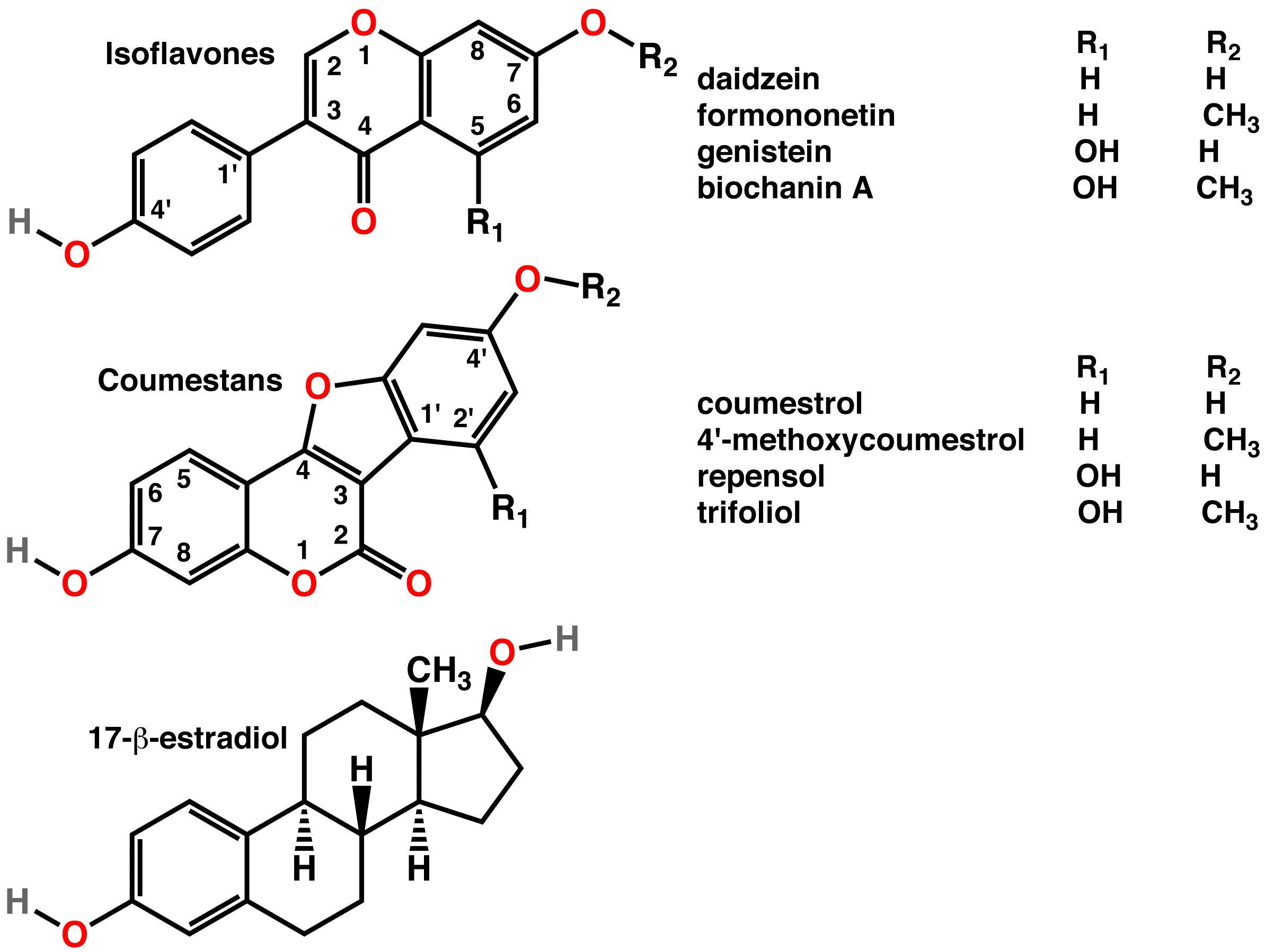
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaempferol
Kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonol, a type of flavonoid, found in a variety of plants and plant-derived foods including kale, beans, tea, spinach, and broccoli. Kaempferol is a yellow crystalline solid with a melting point of . It is slightly soluble in water and highly soluble in hot ethanol, ethers, and DMSO. Kaempferol is named for 17th-century German naturalist Engelbert Kaempfer.Kaempferol at .com; retrieved October 20, 2017 Natural occurrence Kaempferol is a secondary metabolite found in many plants, plant-derived foods, and traditional medicines. Its flavor is considered bitter. In plants and food< ...
|
Diosgenin
Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of ''Dioscorea'' wild yam species, such as the Kokoro. The sugar-free (aglycone) product of such hydrolysis, diosgenin is used for the commercial synthesis of cortisone, pregnenolone, progesterone, and other steroid products. Sources It is present in detectable amounts in '' Costus speciosus'', ''Smilax menispermoidea'', ''Helicteres isora'', species of ''Paris'', '' Aletris'', '' Trigonella'', and ''Trillium'', and in extractable amounts from many species of ''Dioscorea'' – '' D. althaeoides'', '' D. colletti'', '' D. composita'', '' D. floribunda'', '' D. futschauensis'', '' D. gracillima'', '' D. hispida'', '' D. hypoglauca'', '' D. mexicana'', '' D. nipponica'', '' D. panthaica'', '' D. parviflora'', '' D. septemloba'', and '' D. zingiberensis''. Industrial uses Diosgenin is a precursor for several hormones, starting with the Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yam (vegetable)
Yam is the common name for some plant species in the genus ''Dioscorea'' (family Dioscoreaceae) that form edible tubers. Yams are perennial herbaceous vines cultivated for the consumption of their starchy tubers in many temperate and tropical regions, especially in West Africa, South America and the Caribbean, Asia, and Oceania. The tubers themselves, also called "yams", come in a variety of forms owing to numerous cultivars and related species. Yams were independently domesticated on three different continents: Africa ('' Dioscorea rotundata''), Asia ('' Dioscorea alata''), and the Americas ('' Dioscorea trifida''). Etymology The name "yam" appears to derive from Portuguese ''inhame'' or Canarian (Spain) ''ñame'', which derived from West African languages during trade. However in both languages, this name commonly refers to the taro plant (''Colocasia esculenta'') from the genus '' Colocasia'', as opposed to ''Dioscorea''. The main derivations borrow from verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apigenin
Apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone), found in many plants, is a natural product belonging to the flavone class that is the aglycone of several naturally occurring glycosides. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool. Sources in nature Apigenin is found in many fruits and vegetables, but parsley, celery, celeriac, and chamomile tea are the most common sources. Apigenin is particularly abundant in the flowers of chamomile plants, constituting 68% of total flavonoids. Dried parsley can contain about 45 mg apigenin/gram of the herb, and dried chamomile flower about 3-5 mg/gram. The apigenin content of fresh parsley is reportedly 215.5 mg/100 grams, which is much higher than the next highest food source, green celery hearts providing 19.1 mg/100 grams. Biosynthesis Apigenin is biosynthetically derived from the general phenylpropanoid pathway and the flavone synthesis pathway. The phenylpropanoid pathway starts from the aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasteberry
''Vitex agnus-castus'', also called vitex, chaste tree (or chastetree), chasteberry, Abraham's balm, lilac chastetree, or monk's pepper, is a native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of '' Vitex'', which is on the whole a genus of tropical and sub-tropical flowering plants.David J. Mabberley. 2008. ''Mabberley's Plant-Book'' third edition (2008). Cambridge University Press: UK. Theophrastus mentioned the shrub several times, as ''agnos'' (άγνος) in ''Enquiry into Plants''. It has been long believed to be an anaphrodisiac – leading to its name as ''chaste tree'' – but its effectiveness for such action remains unproven. Vitex is a cross-pollinating plant, but its self-pollination has been recorded.Verein für Arznei- und Gewürzpflanzen Saluplanta. 2013. ''Handbuch des Arznei- und Gewürzpflanzenbaus'' volume 5 Arznei- und Gewürzpflanzen L-Z, pages 192-199. Verein für Arznei- und Gewürzpflanzen Saluplanta: Bernburg, Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs. Structure Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydroxy groups at the 4', 5, and 7 carbons. It may be found both in the aglycol form, naringenin, or in its glycosidic form, naringin, which has the addition of the disaccharide neohesperidose attached via a glycosidic linkage at carbon 7. Like the majority of flavanones, naringenin has a single chiral center at carbon 2, although the optical purity is variable. Racemization of S(-)-naringenin has been shown to occur fairly quickly. Sources and bioavailability Naringenin and its glycoside has been found in a variety of herbs and fruits, including grapefruit, bergamot, sour orange, tart cherries, tomatoes, cocoa, Greek oregano, water mint, as well as in beans. Ratios of naringenin to naringin vary among sources, as do enantiomeric ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringic Acid
Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compound and dimethoxybenzene that is commonly found as a plant metabolite. Natural occurrence Syringic acid can be found in several plants including '' Ardisia elliptica'' and ''Schumannianthus dichotomus''. Synthesis Syringic acid can be prepared by selectively hydrolyzing ( demethylating) eudesmic acid with 20% sulfuric acid. Presence in food Syringic acid can be found in several fruits including olives, dates, spices, pumpkin, grapes, acai palm, honey, red wine, among others. Its presence in the ancient Egyptian drink shedeh could confirm it was made out of grape, as syringic acid is released by the breakdown of the compound malvidin, also found in red wine. It is also found in vinegar. Applications Various studies have found syringic acid to exhibit useful pharmaceutical properties such as anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic. Syringic acid can be enzymatically pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |