|
Photon Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
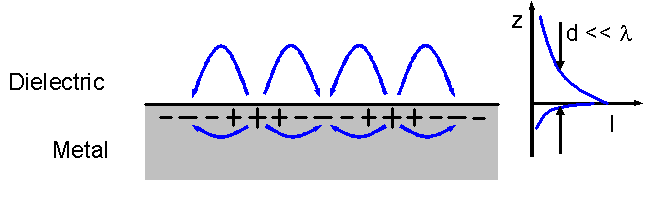
The operation of a photon scanning tunneling microscope (PSTM) is analogous to the operation of an electron scanning tunneling microscope, with the primary distinction being that PSTM involves tunneling of photons instead of electrons from the sample surface to the probe tip. A beam of light is focused on a prism at an angle greater than the critical angle of the refractive medium in order to induce total internal reflection within the prism. Although the beam of light is not propagated through the surface of the refractive prism under total internal reflection, an evanescent field of light is still present at the surface. The evanescent field is a standing wave which propagates along the surface of the medium and decays exponentially with increasing distance from the surface. The surface wave is modified by the topography of the sample, which is placed on the surface of the prism. By placing a sharpened, optically conducting probe tip very close to the surface (at a distance <λ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of scanning probe microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. STM senses the surface by using an extremely sharp conducting tip that can distinguish features smaller than 0.1 nm with a 0.01 nm (10 pm) depth resolution. This means that individual atoms can routinely be imaged and manipulated. Most scanning tunneling microscopes are built for use in ultra-high vacuum at temperatures approaching absolute zero, but variants exist for studies in air, water and other environments, and for temperatures over 1000 °C. STM is based on the concept of quantum tunneling. When the tip is brought very near to the surface to be examined, a bias voltage applied between the two allows electrons to tunnel through the vacuum separating them. The resulting ''tunneling current'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Internal Reflection
In physics, total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (boundary) from one medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely reflected back into the first ("internal") medium. It occurs when the second medium has a higher wave speed (i.e., lower refractive index) than the first, and the waves are incident at a sufficiently oblique angle on the interface. For example, the water-to-air surface in a typical fish tank, when viewed obliquely from below, reflects the underwater scene like a mirror with no loss of brightness (Fig.1). TIR occurs not only with electromagnetic waves such as light and microwaves, but also with other types of waves, including sound and water waves. If the waves are capable of forming a narrow beam (Fig.2), the reflection tends to be described in terms of " rays" rather than waves; in a medium whose properties are independent of direction, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Topography
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly flat ideal (a true plane). Surface texture is one of the important factors that control friction and transfer layer formation during sliding. Considerable efforts have been made to study the influence of surface texture on friction and wear during sliding conditions. Surface textures can be isotropic or anisotropic. Sometimes, stick-slip friction phenomena can be observed during sliding, depending on surface texture. Each manufacturing process (such as the many kinds of machining) produces a surface texture. The process is usually optimized to ensure that the resulting texture is usable. If necessary, an additional process will be added to modify the initial texture. The latter process may be grinding (abrasive cutting), polis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoluminescence
Photoluminescence (abbreviated as PL) is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). It is one of many forms of luminescence (light emission) and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photons that excite electrons to a higher energy level in an atom), hence the prefix ''photo-''. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductorsHayes, G.R.; Deveaud, B. (2002). "Is Luminescence from Quantum Wells Due to Excitons?". ''Physica Status Solidi A'' 190 (3): 637–640doi:10.1002/1521-396X(200204)190:33.0.CO;2-7/ref> up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours. Observation of photoluminescence at a certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect of the absorption of electromagnetic radiation is attenuation of the radiation; attenuation is the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible spectrum, visible, near infrared, or ultraviolet, near ultraviolet range is used, although X-ray Raman scattering, X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Time-resolved spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evanescent Field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting Antenna (radio), antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process: materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an applied electric field. For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measurable piezoelectricity when their static structure is deformed by about 0.1% of the original dimension. Conversely, those same crystals will change about 0.1% of their static dimension when an external electric field is applied. The inverse piezoelectric effect is used in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that Energy transformation, converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, Measuring instrument, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
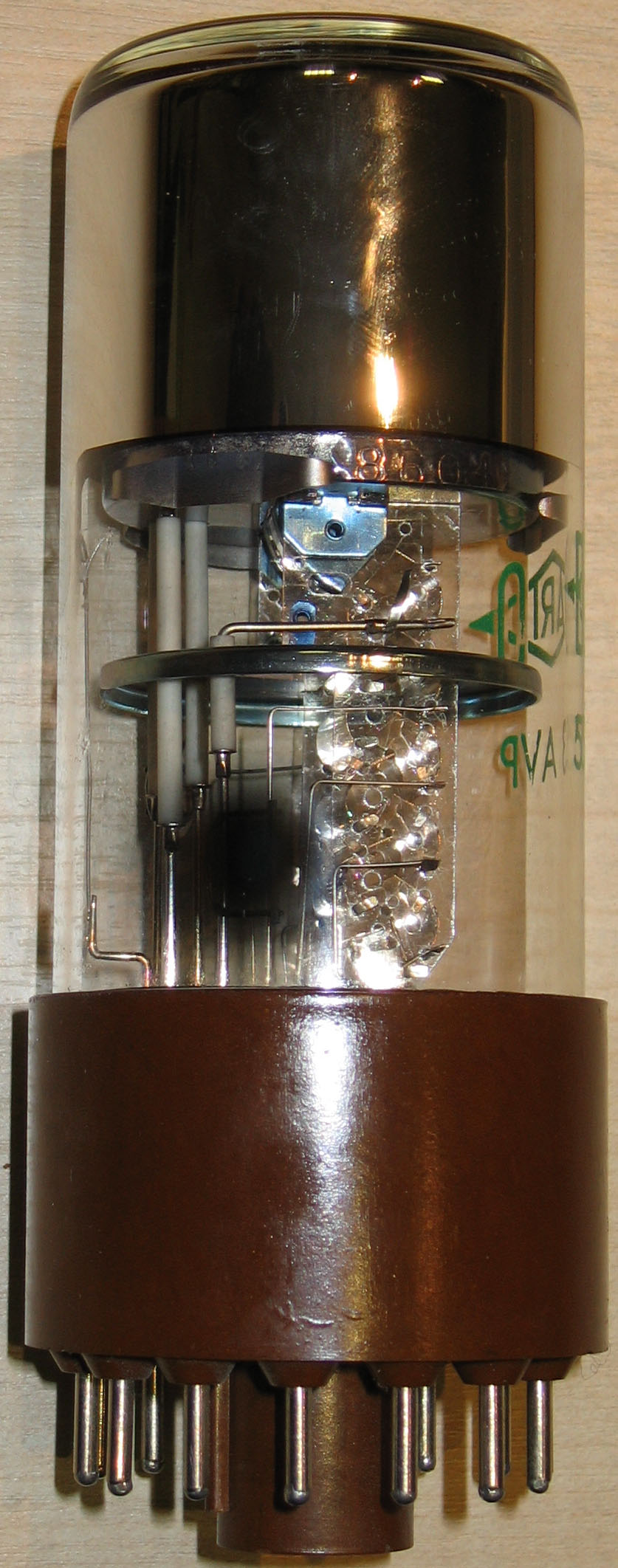
Photomultiplier Tube
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible light, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 108 (i.e., 160 decibel, dB),Decibels are power ratios. Power is proportional to I2 (current squared). Thus a current gain of 108 produces a power gain of 1016, or 160 decibel, dB in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. The combination of high Gain (electronics), gain, low Noise (electronics), noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in Spectroscopy, low light level spectroscopy, confocal microscopy, Raman spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in the form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Even though photonics is a commonly used term, there is no widespread agreement on a clear definition of the term or on the difference between photonics and related fields, such as optics. Photonics is closely related to quantum electronics, where quantum electronics deals with the theoretical part of it while photonics deal with its engineering applications. Though covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum, most photonic applications are in the range of visible and near-infrared light. The term ''photonics'' developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s. History The word 'Photonics' is derived from the Greek w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |