|
Phoenicianism
Phoenicianism is a form of Lebanese nationalism that apprizes and presents Phoenicia, ancient Phoenicia as the chief ethno-cultural foundation of the Lebanese people. It is juxtaposed with Arab migrations to the Levant following the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century, which resulted in the region's Arabization. As such, this perspective opposes pan-Arabism and pan-Islamism, and also seeks to resist Lebanon–Syria relations, Syrian influence on the Lebanese political and cultural spheres. Within Lebanon, the Phoenicianist ideology has most notably garnered support among Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians, especially the Maronites. Adopted by Christian intellectuals upon the creation of the French Third Republic, French-administered Greater Lebanon, State of Greater Lebanon, Phoenicianism has been endorsed by a number of prominent Lebanese figures, such as the Maronite poet Said Akl, Saïd Akl, and by political organizations like the Lebanese Renewal Party, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Renewal Party
The Lebanese Renewal Party – LRP (Arabic: حزب التجدد اللبناني transliteration ''Hezb al-Tajaddud al-Lubnani'') or Parti de la Renovation Libanaise (PRL) in French, was a political party in Lebanon formed in 1972 by a number of staunch Lebanese nationalists including activist Etienne Saqr, poet Said Akl and writer May Murr. Its ideology was based on Phoenicianism and the idea that the Lebanese nation is an independent non-Arab entity and is not part of the Arab World. This orientation also warned against pan-Arabism, leftist ideology and the Palestinian military presence in Lebanon. History It was formed by right-wing activists opposed to the presence of the Palestinian refugees in Lebanon. The refugee population also included a substantial element of Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) fighters, especially after the 1970 Black September events in Jordan. This created severe tension in Lebanon, and is believed by many to have been a driving factor behind t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Said Akl
Said Akl (; 4 July 1911 – 28 November 2014) was a Lebanese poet, linguist, philosopher, writer, playwright and language reformer. He is considered one of the most important Lebanese poets of the modern era. He is most famous for his advocacy on behalf of codifying the spoken Lebanese Arabic language as competency distinct from Standard Arabic, to be written in a modern modified Roman script consisting of 36 symbols that he deemed an evolution of the Phoenician alphabet. Despite this, he contributed to several literary movements (primarily, symbolism (arts), symbolism) in Modern Standard Arabic, producing some of the masterpieces of modern Arabic Belles-lettres, belle lettres. Akl aligned himself with Lebanese nationalism, and was one of the founding members of the Lebanese Renewal Party in 1972. The party, characterized by its Phoenicianism, pro-Phoenicianism stance, aimed to distance Lebanon from Pan-Arabism. His views found support within the Guardians of the Cedars movement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maronites
Maronites (; ) are a Syriac Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant (particularly Lebanon) whose members belong to the Maronite Church. The largest concentration has traditionally resided near Mount Lebanon in modern Lebanon. The Maronite Church is an Eastern Catholic particular church in full communion with the pope and the rest of the Catholic Church. The Maronites derive their name from Saint Maron, (350-410 AD. ), a monk who migrated with his followers from Antioch to the Lebanese Mountains and founded the Maronite church. The spread of Christianity was very slow in the Lebanese region, in the 5th century AD in the highlands they were still pagan. St. Maron sent the apostle Abraham of Cyrrhus known as the "Apostle of Lebanon" with a mandate to convert the pagan inhabitants of Lebanon to Christianity. After their conversion, the inhabitants of the region renamed the Adonis River to the Abrahamic River in honor of the Saint who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guardians Of The Cedars
The Guardians of the Cedars (GoC; ; ''Ḥurrās al-Arz) was'' a Lebanese nationalist party and former militia in Lebanon. It was formed by Étienne Saqr (also known with the kunya "Abu Arz" or "Father of the Cedars") and others along with the Lebanese Renewal Party in the early 1970s. It operated in the Lebanese Civil War under the slogan: ''Lebanon, at your service.'' The militia was explicitly anti-Palestinian, and gained a reputation for brutality against Palestinian fighters. Creation The Guardians of the Cedars started to form a militia in the years leading up to the Lebanese Civil War and commenced military operations in April 1975. In September 1975, Communiqué No. 1 was issued to denounce advocates of the partition of Lebanon. The second communiqué contained a bitter attack on the Palestinians. The third articulated the party's stance on the issue of Lebanese identity: Lebanon should dissociate itself from Arabism. The party spread its messages by means of graffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Nationalism
Lebanese nationalism is a nationalist ideology which considers the Lebanese people as a separate nation independent from the Arab world and strives to maintain Lebanon as an independent nation-state. The ideology may consider the Lebanese people to be direct descendants of the Phoenicians, a concept associated with Phoenicianism. The ideology is highly controversial and has been criticized for disuniting the Lebanese people rather than uniting them. While Lebanese nationalism appeals to the Lebanese Maronite community, it is generally unpopular among Lebanese Muslims, who often support Pan-Arabism and Pan-Islamism, as well as among Greek Orthodox Christians. History The Druze and Maronite community in Lebanon played an important role in the formation of the modern state of Lebanon in the early 18th century, through a governing and social system known as the " Maronite-Druze dualism" in Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate This ideology is rooted in the 19th-century sectarian war betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west; Cyprus lies a short distance from the coastline. Lebanon has a population of more than five million and an area of . Beirut is the country's capital and largest city. Human habitation in Lebanon dates to 5000 BC. From 3200 to 539 BC, it was part of Phoenicia, a maritime civilization that spanned the Mediterranean Basin. In 64 BC, the region became part of the Roman Empire and the subsequent Byzantine Empire. After the seventh century, it Muslim conquest of the Levant, came under the rule of different Islamic caliphates, including the Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun, Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid. The 11th century saw the establishment of Christian Crusader states, which fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Christian Militias
The Lebanese Front was a coalition of mainly right-wing Lebanese Nationalist parties formed in 1976 by majority Christian groups during the Lebanese Civil War. It was intended to act as a reaction force to the Lebanese National Movement (LNM) of Kamal Jumblatt and other left-wing allies. History The Lebanese Front was presided by the former president of Lebanon, Camille Chamoun, and its main participants were Pierre Gemayel, the founder and leader of the then-largest political party in Lebanon, the Kataeb Party, president Suleiman Frangieh, who had just finished his presidential years in office. It also included first class intellectuals, such as distinguished professor of philosophy and eminent diplomat Charles Malik who had been president of the United Nations General Assembly in 1958, and Fouad Frem al-Boustani, the president of the Lebanese University. The front also included religious figures such as Father Charbel Qassis, who was later replaced by Father Bulus Naaman the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Maritime Expansions Across The Mediterranean
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient civilization in the north of Canaan in parts of Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine. Phoenicia may also refer to: Historical places *Phoenice (Roman province), a province of the Roman Empire encompassing the reg ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian coast. They developed a Maritime history, maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula, evidenced by thousands of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Phoenician inscriptions. The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions after the decline of most major Mediterranean basin cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. They called themselves Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Islamism
Pan-Islamism () is a political movement which advocates the unity of Muslims under one Islamic country or state – often a caliphate – or an international organization with Islamic principles. Historically, after Ottomanism, which aimed at the unity of all Ottoman citizens, Pan-Islamism was promoted in the Ottoman Empire during the last quarter of the 19th century by Sultan Abdul Hamid II for the purpose of preventing secession movements of the Muslim peoples in the empire. Pan-Islamism differentiates itself from pan-nationalistic ideologies, for example Pan-Arabism, by focusing on religion and not ethnicity and race. It sees the ummah (Muslim community) as the focus of allegiance and mobilization, including the Tawhid belief by the guidance of Quran and Sunnah's teachings. The major leaders of the Pan-Islamist movement were the triad of Jamal al-Din Afghani (1839–1897), Muhammad Abduh (1849–1905) and Sayyid Rashid Rida (1865–1935), who were active in anti-colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernacular
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken language, spoken form of language, particularly when perceptual dialectology, perceived as having lower social status or less Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige than standard language, which is more codification (linguistics), codified, institutionally promoted, literary language, literary, or formal. More narrowly, a particular language variety that does not hold a widespread high-status perception, and sometimes even carries social stigma, is also called a vernacular, vernacular dialect, nonstandard dialect, etc. and is typically its speakers' native language, native variety. Regardless of any such stigma, all nonstandard dialects are full-fledged varieties of language with their own consistent grammatical structure, phonology, sound system, body of vocabulary, etc. Overview Like any native language variety, a vernacular has an internally coherent system of grammar. It may be associated with a particular set of vocabulary, and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
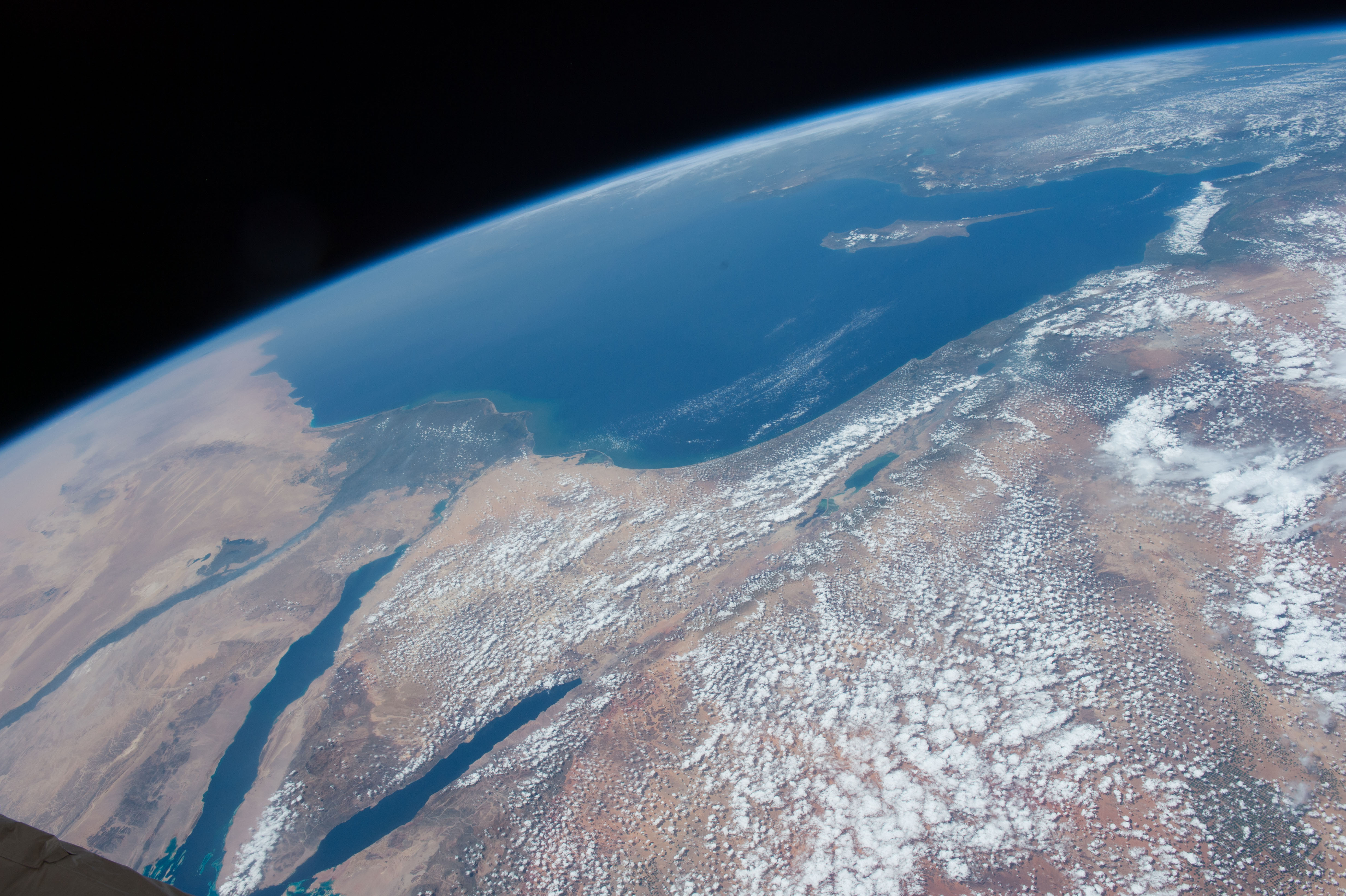
Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey's main region, Anatolia; its smaller Hatay Province; the island of Cyprus; the Greek Dodecanese islands; and the countries of Egypt, Israel, Jordan, State of Palestine, Palestine, Syria and Lebanon. Its broadest uses can encompass the Libyan Sea (thus Libya), the Aegean Sea (thus East Thrace, European Turkey and the mainland and islands of Greece), and the Ionian Sea (thus southern Albania in Southeast Europe) and can extend west to Italy's farthest south-eastern coasts. Jordan is climatically and economically part of the region. Regions The eastern Mediterranean region is commonly interpreted in two ways: *The Levant, including its historically tied neighboring countries, Balkans and islands of Greece. *The Syria (region), region of Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |