|
Pheniramine
Pheniramine (trade name Avil among others) is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria. It has relatively strong sedative effects, and may sometimes be used off-label as an over-the-counter sleeping pill in a similar manner to other sedating antihistamines such as diphenhydramine. Pheniramine is also commonly found in eyedrops used for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. It was patented in 1948. Pheniramine is generally sold in combination with other medications, rather than as a stand-alone drug, although some formulations are available containing pheniramine by itself. Side effects Pheniramine may cause drowsiness or Tachycardia, and over-dosage may lead to sleep disorders. Overdose may lead to seizures, especially in combination with alcohol. People combining with cortisol in the long term should avoid pheniramine as it may decrease levels of adrenaline (epinephrine) which may lead to loss of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorpheniramine
Chlorphenamine (CP, CPM), also known as chlorpheniramine, is an antihistamine used to treat the symptoms of allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever). It is taken orally (by mouth). The medication takes effect within two hours and lasts for about 4–6 hours. It is a first-generation antihistamine and works by blocking the histamine H1 receptor. Common side effects include sleepiness, restlessness, and weakness. Other side effects may include dry mouth and wheeziness. Chlorpheniramine was patented in 1948 and came into medical use in 1949. It is available as a generic medication and over the counter. In 2022, it was the 291st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 400,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Combination products Chlorphenamine is often combined with phenylpropanolamine to form an allergy medication with both antihistamine and decongestant properties, although phenylpropanolamine was removed from the U.S. m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorphenamine
Chlorphenamine (CP, CPM), also known as chlorpheniramine, is an antihistamine used to treat the symptoms of allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever). It is taken orally (by mouth). The medication takes effect within two hours and lasts for about 4–6 hours. It is a first-generation antihistamine and works by blocking the histamine H1 receptor. Common side effects include sleepiness, restlessness, and weakness. Other side effects may include dry mouth and wheeziness. Chlorpheniramine was patented in 1948 and came into medical use in 1949. It is available as a generic medication and over the counter. In 2022, it was the 291st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 400,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Combination products Chlorphenamine is often combined with phenylpropanolamine to form an allergy medication with both antihistamine and decongestant properties, although phenylpropanolamine was removed from the U.S. market per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brompheniramine
Brompheniramine, sold under the brand name Dimetapp among others, is a first-generation antihistamine drug of the propylamine (alkylamine) class. It is indicated for the treatment of the symptoms of the common cold and allergic rhinitis, such as runny nose, itchy eyes, watery eyes, and sneezing. Like the other first-generation drugs of its class, it is considered a sedating antihistamine. It was patented in 1948 and came into medical use in 1955. In 2022, the combination with dextromethorphan and pseudoephedrine was the 265th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Side effects Brompheniramine's effects on the cholinergic system may include side-effects such as drowsiness, sedation, dry mouth, dry throat, blurred vision, and increased heart rate. It is listed as one of the drugs of highest anticholinergic activity in a study of anticholinergenic burden, including long-term cognitive impairment. Pharmacology Bromphen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
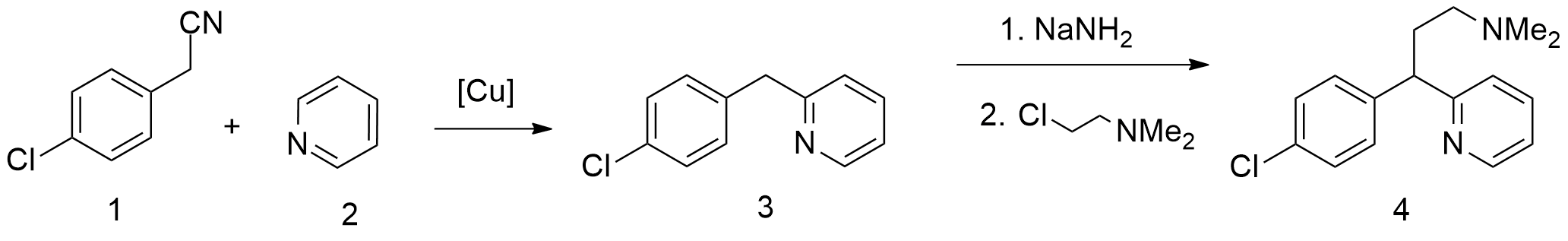
Dexchlorpheniramine
Dexchlorpheniramine (trade name Polaramine) is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria. It is the pharmacologically active dextrorotatory isomer of chlorpheniramine. It came into medical use in 1959 and was patented in 1962. Pharmacology Dexchlorpheniramine is an antihistamine, or an antagonist of the histamine H1 receptor. A study found that dexchlorpheniramine had a Ki value of 20 to 30 μM for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other Cell (biology), cells. They play several role ...s using rat brain tissue. References External links Polaramine consumer information Dimethylamino compounds 4-Chlorophenyl compounds Enantiopure drugs H1 receptor antagonists Muscarinic antagonists 2-Pyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexbrompheniramine
Dexbrompheniramine is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria. It is the pharmacologically active dextrorotatory isomer of brompheniramine. It was formerly marketed in combination with pseudoephedrine under the name Drixoral in the US and Canada. It is an alkylamine antihistamine. Dexbrompheniramine is a first generation antihistamine that reduces the effects of the neurotransmitter histamine Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ... in the body; sneezing, itching, watery eyes, and runny nose. Interactions MAO inhibitors within 14 days. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, and tranylcypromine. Drinking alcohol can increase side effects of dexbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use. Although the general public typically uses the word "antihistamine" to describe drugs for treating allergies, physicians and scientists use the term to describe a class of drug that opposes the activity of histamine receptors in the body. In this sense of the word, antihistamines are subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine, sold under the brand name Benadryl among others, is an antihistamine and sedative. Although generally considered sedating, diphenhydramine can cause paradoxical central nervous system stimulation in some individuals, particularly at higher doses. This may manifest as agitation, anxiety, or restlessness rather than sedation. It is a H1 antagonist#First-generation (non-selective, classical), first-generation H1-antihistamine and it works by blocking certain effects of histamine, which produces its antihistamine and sedative effects. Diphenhydramine is also a potent anticholinergic. It is mainly used to treat allergy, allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremors in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken oral administration, by mouth, injection into a vein, injected into a vein, injection into a muscle, injected into a muscle, or topical medication, applied to the skin. Maximal effect is typically around two hours af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimelidine
Zimelidine (International Nonproprietary Name, INN, British Approved Name, BAN; brand names Zimeldine, Normud, Zelmid) was one of the first selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants to be marketed. It is a pyridylallylamine, and is structurally different from other antidepressants. Zimelidine was developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s by Arvid Carlsson, who was then working for the Sweden, Swedish company AstraZeneca, Astra AB. It was invented following a search for drugs with structures similar to brompheniramine (it is a derivative (chemistry), derivative of brompheniramine), an antihistamine with antidepressant activity. Zimelidine was first sold in 1982. While zimelidine had a very favorable safety profile, within a year and a half of its introduction, rare case reports of Guillain–Barré syndrome emerged that appeared to be caused by the drug, prompting its manufacturer to withdraw it from the market. After its withdrawal, it was succeeded by fluv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or Psychomotor agitation, excitement. They are central nervous system (CNS) Depressant, depressants and interact with brain activity, causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Most sedatives produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or Anxiolytic, relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness), they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative–hypnotic'' drugs. Terminology There is some overlap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system. These agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system by selectively blocking the binding of ACh to its receptor in nerve cells. The nerve fibers of the parasympathetic system are responsible for the involuntary movement of Smooth muscle tissue, smooth muscles present in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, lungs, sweat glands, and many other parts of the body. In broad terms, anticholinergics are divided into two categories in accordance with their specific targets in the central and peripheral nervous system and at the neuromuscular junction: antimuscarinic agents and antinicotinic agents (ganglionic blockers, neuromuscular blockers). The term "anticholinergic" is typically used to refer to antimuscarinics that competitively inhibit the binding of ACh to muscarinic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
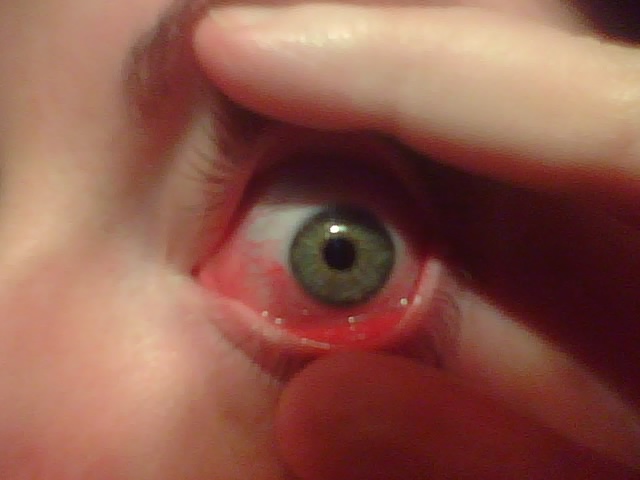
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is Allergic Inflammation, inflammation of the conjunctiva (the membrane covering the white part of the eye) due to allergy. Although allergens differ among patients, the most common cause is hay fever. Symptoms consist of redness (mainly due to vasodilation of the peripheral small blood vessels), edema (swelling) of the conjunctiva, itching, and increased lacrimation (production of tears). If this is combined with rhinitis, the condition is termed allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (ARC). The symptoms are due to release of histamine and other active substances by mast cells, which stimulate dilation of blood vessels, irritate nerve endings, and increase secretion of tears. Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis is by avoiding the allergen (''e.g.'', avoiding grass in bloom during "hay fever season") and treatment with antihistamines, either topical (in the form of eye drops), or systemic (in the form of tablets). Antihistamines, medications that stabilize mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogenation
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (). Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride. Organic chemistry Several pathways exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, including free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate determines the pathway. The facility of halogenation is influenced by the halogen. Fluorine and chlorine are more electrophilic and are more aggressive haloge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |