|
Phari Lapcha
Phari Lapcha is a mountain in Nepal. Description Phari Lapcha, also known as Machhermo Peak, is a summit in the Khumbu region of the Nepalese Himalaya. It is situated west of Mount Everest and northwest of Machhermo in the Gokyo Valley of Sagarmatha National Park. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises over 1,300 metres (4,265 ft) above Tanjung Cho in . Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains into tributaries of the Dudh Koshi. Trekkers pass by this peak en route to Everest Base Camp. This peak is a popular climbing destination and was added to the list of permitted trekking peaks in 2002. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Phari Lapcha is located in a tundra climate zone with cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Weather systems coming off the Bay of Bengal are forced upwards by the Himalaya mountains (orographic lift), causing heavy precipitation in the form of rainfall and snowfall. Mid-June through early-August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokyo Lakes
Gokyo Lakes are oligotrophic lakes in Nepal's Sagarmatha National Park, located at an elevation of . They were named after Gokyo Ri peak. These lakes are the world's highest freshwater lake system comprising six main lakes, of which Thonak Lake is the largest. In September 2007, Gokyo and its associated wetlands of have been designated a Ramsar site. Lake system Gokyo Lakes are located in the Khumjung Village Development Committee of Solukhumbu District in the Sagarmatha Zone in north-eastern Nepal. Gokyo Cho, also called Dudh Pokhari, is the main lake with an area of , and the village of Gokyo lies on its eastern shore. Thonak Cho is the largest lake with an area of . Gyazumpa Cho is in size, followed by Tanjung Cho with an area of , and Ngojumba Cho with an area of . As sources of permanent fresh water they have high hydrological value. They feed on waters from various sources, such as seepage from the Ngozumpa glacier, a stream coming from the Renjo La pass from the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trekking Peak
The term "Trekking Peak" is a commonly misunderstood colloquial term which may refer to a variety of types of peaks in the Himalayas, Himalayan Region. The term is most often associated with Group "B" NMA Climbing Peaks classified by the Nepal Mountaineering Association or easier. Some may use the term "Trekking Peak" to solely describe peaks requiring little to no technical climbing experience. Others may use the term to describe all mountains regulated by the Nepal Mountaineering Association including Group "A" NMA Expedition Peaks which may require considerable difficulties and technical climbing skill. Because of the term's loose classification of peaks it can be misleading, encompassing peaks of significant varying difficulties. There is less general consensus for the use of the term in this context of Group "A" NMA Expedition Peaks. Nepal Fifteen peaks classified as Group "B" NMA Climbing Peaks are generally considered "trekking" peaks. These peaks do not exceed in elevatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Koshi Province
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arakam Tse
Arakam Tse is a mountain in Nepal. Description Arakam Tse is a summit in the Khumbu region of the Nepalese Himalaya. It is situated west of Mount Everest and north of Cholatse. Topographic relief is significant as the east slope rises 1,100 metres (3,609 ft) in . Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains into tributaries of the Dudh Koshi. Trekkers pass by this peak en route to Everest Base Camp. The first ascent of the summit was made on October 26, 2013, by Josep Maria Esquirol, Silvestre Barrientos, Alfonso Gaston, and Ferran Rodríguez. This team of Spaniards climbed the northeast face via a route they named ''Tatopani'', (1,000m, M5+). Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Arakam Tse is located in a tundra climate zone with cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Weather systems coming off the Bay of Bengal are forced upwards by the Himalaya mountains (orographic lift), causing heavy precipitation in the form of rainfall and snowfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
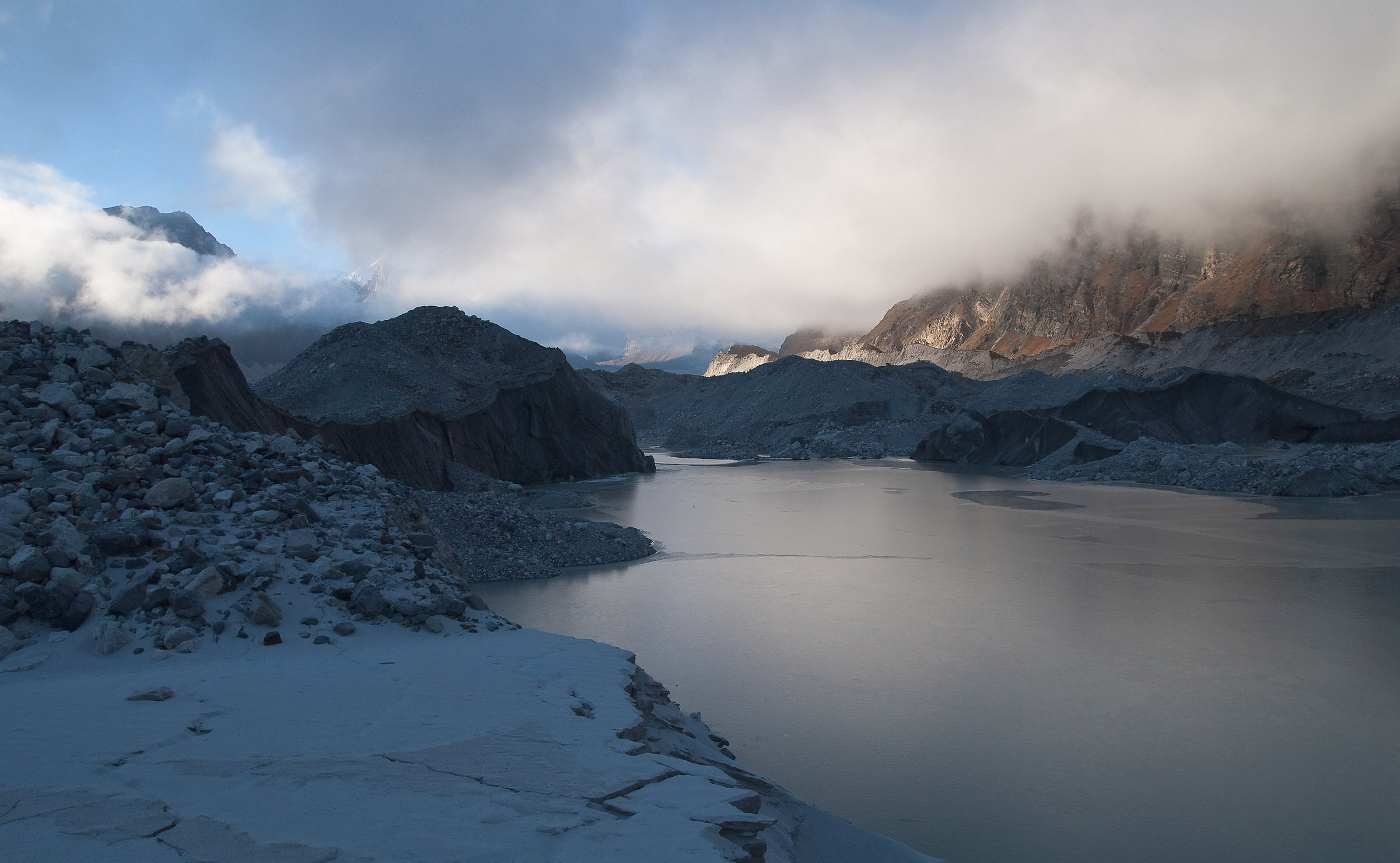
Ngozumpa Glacier
The Ngozumpa glacier, below the sixth highest mountain in the world Cho Oyu in Nepal, at , is the longest glacier in the Himalayas. Ngozumpa Glacier is a large persistent body of ice. It flows slowly due to stresses induced by its weight. Ngozumpa Spillway lake The Nepali Himalayas The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ... have been warming significantly over recent decades. Ngozumpa glacier is showing signs of shrinking and thinning, producing melt water. Some of this water pools on the surface where an enormous lake is growing. This lake, called Spillway, has the potential to be about long, wide and deep. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokyo
Gokyo is a small village in Solukhumbu District in the Himalayas of Nepal, at the foot of Gokyo Ri, located on the eastern shore of the third Gokyo Lake, Dudh Pokhari. To the southeast is the village of Chharchung. Gokyo is best viewed on Google Earth at . Located at an elevation of , the village is one of the highest settlements in Nepal and in the world. Almost all the buildings are guest houses for trekkers. The people who live in the village leave during the winter and move to other (lower) villages, or Kathmandu. In 1995, an avalanche killed 42 people, including 17 foreign nationals (13 Japanese, two Canadians, one Irish woman and a German). A cyclone in the Bay of Bengal The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region. Many South Asian and Southe ... had resulted in of snow being dumped into the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
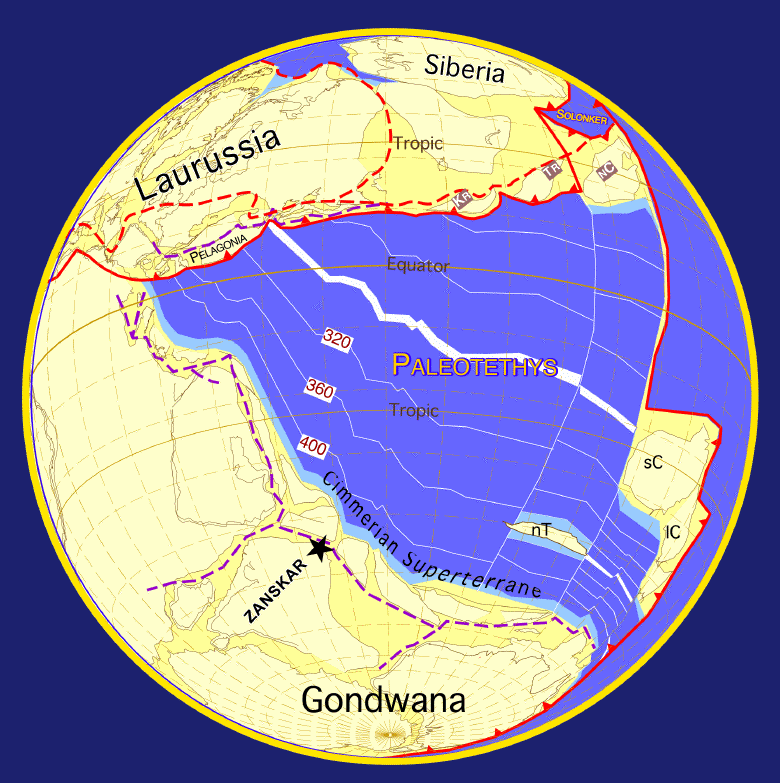
Geology Of The Himalayas
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift (nearly 10 mm/year at Nanga Parbat), the highest relief (8848 m at Mt. Everest Chomolangma), among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cho La (Nepal)
Cho La is a summit pass located above sea level in the Solukhumbu District in northeastern Nepal. It connects the village of Dzongla () to the east and the village of Thagnak () to the west. Tourism The pass is on the Gokyo trail in the Khumbu Everest region. To the west the trail continues to the Gokyo Lakes, crossing the Ngozumpa glacier on the way. To the east the trail joins the Everest Base Camp trek. The pass can be physically demanding and may require crampons A crampon is a traction device attached to footwear to improve mobility on snow and ice during ice climbing. Besides ice climbing, crampons are also used for secure travel on snow and ice, such as crossing glaciers, snowfields and icefields, as ... on top of the slippery glacier. The edge of the glacier is unstable. The Cho la Pass is covered in snow for 9 months of the year, with the temperature being below 0 degrees Celsius for a long time. References Mountain passes of Nepal Mountain passes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokyo Ri
Gokyo Peak () is a -high peak in the Khumbu region of the Nepal Himalayas. It is located on the west side of the Ngozumpa glacier, which is the largest glacier in Nepal and reputed to be the largest in the whole Himalayas. Gokyo (4,750 m, 15,583 ft above sea level), at the base of Gokyo Ri, is a small village with several houses and lodges, and is one of the highest settlements in the world. From the summit of Gokyo Ri it is possible to see four 8,000-metre peaks: Mount Everest, Lhotse, Makalu and Cho Oyu. The Gokyo Lakes are in the area. Other mountains, such as Pumori and Nuptse are also visible from the top, along with five tranquil glacier lakes named together as gokyo lakes. The Gokyo-Ri summit is a 3-hour hike from the nearest village. Gokyo trek is a fairly popular trekking route. The route itself ends aGokyo Ri and trekkers typically turn around at this point and retrace their steps back to the trailhead. There is an alternative mountaineering route that beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orographic Lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation. Orographic lifting can have a number of effects, including precipitation, rain shadowing, leeward winds, and associated clouds. Precipitation Precipitation induced by orographic lift occurs in many places throughout the world. Examples include: * The Mogollon Rim in central Arizona * The western slope of the Sierra Nevada range in California. * The western slope of the Wasatch Range in Utah. Specifically the Little and Big Cottonwood Canyons. * The mountains near Baja California North – specifically La Bocana to Laguna Hanson. * The windward slopes of Khasi and Jayantia Hills (see Mawsynram) in the state of Meghalaya in India. * The Western Highlands of Yemen, which rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region. Many South Asian and Southeast Asian Countries of the Bay of Bengal, countries are dependent on the Bay of Bengal. Geopolitically, the bay is bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the northwesternmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. Cox's Bazar Beach, Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges–Hooghly River, Hooghly, the Padma River, Padma, the Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundra Climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. It is classified as ET according to the Köppen climate classification. It is a climate which at least one month has an average temperature high enough to melt snow (), but no month with an average temperature in excess of . If the climate occurs at high elevations, it is known as alpine climate. Despite the potential diversity of climates in the ''ET'' category involving precipitation, extreme temperatures, and relative wet and dry seasons, this category is rarely subdivided. Rainfall and snowfall are generally slight due to the low vapor pressure of water in the chilly atmosphere, but as a rule potential evapotranspiration is extremely low, allowing soggy terrain of swamps and bogs even in places that get precipitation typical of deserts of lower and middle latitudes. The amount of native tundra biomass depends more on the local temperature than the amount of precipitation. Tundra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |