|
Persis Solo Players
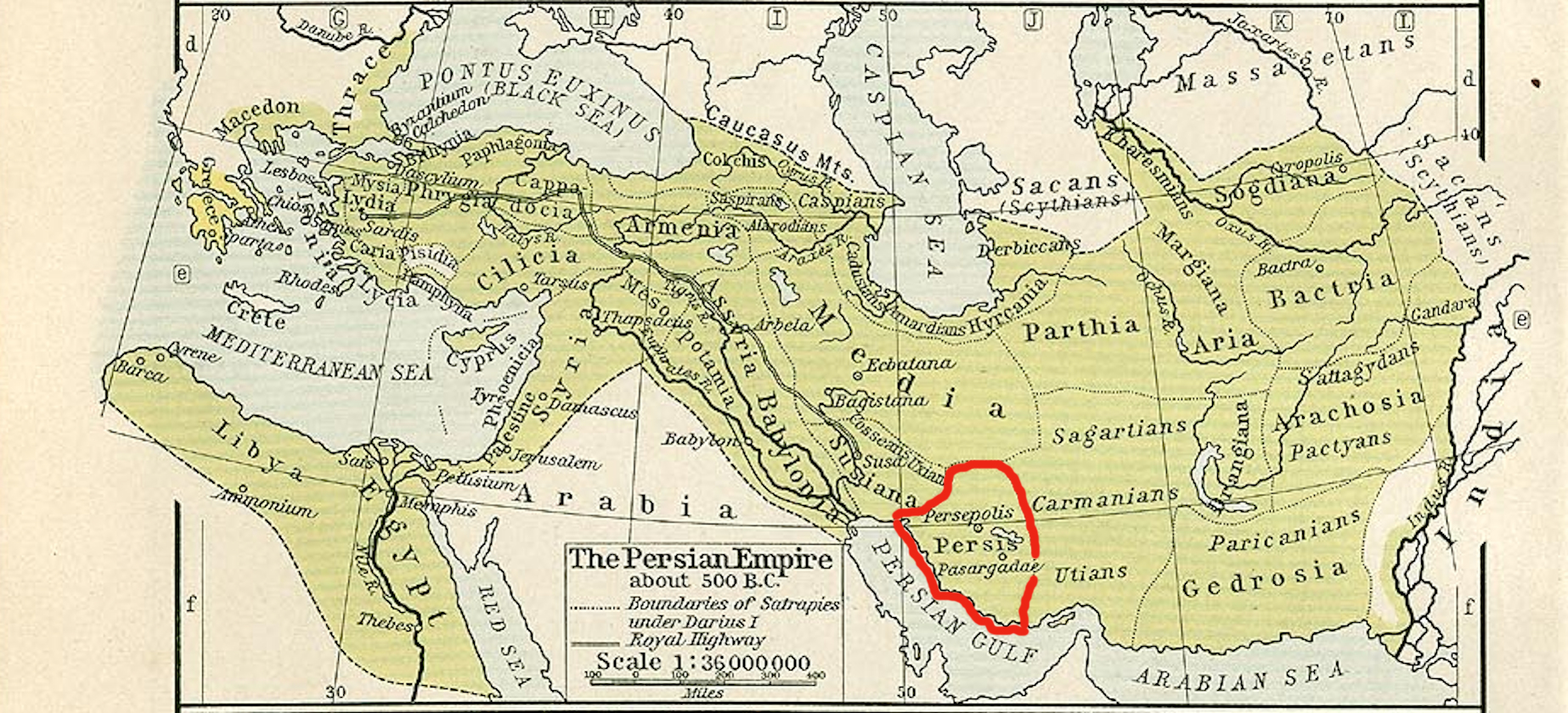
Persis (, ''Persís;'' Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''), also called Persia proper, is a historic region in southwestern Iran, roughly corresponding with Fars province. The Persian ethnic group are thought to have initially migrated either from Central Asia or, more probably, from the north through the Caucasus. They would then have migrated to the current region of Persis in the early 1st millennium BC. Achaemenid Empire The ancient Persians were present in the region of Persis from about the 10th century BC. They became the rulers of the largest empire the world had yet seen under the Achaemenid dynasty which was established in the late 6th century BC, at its peak stretching from Thrace-Macedonia, Bulgaria- Paeonia and Eastern Europe proper in the west, to the Indus Valley in its far east. The ruins of Persepolis and Pasargadae, two of the four capitals of the Achaemenid Empire, are located in Fars. Macedonian Empire The Achaemenid Empire was defeated by Alexand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The earliest remains of Persepolis date back to 515 BC. The city, acting as a major center for the empire, housed a palace complex and citadel designed to serve as the focal point for governance and ceremonial activities. It exemplifies the Achaemenid style of architecture. The complex was taken by the army of Alexander the Great in 330 BC, and soon after, its wooden parts were completely destroyed by fire, likely deliberately. The function of Persepolis remains unclear. It was not one of the largest cities in ancient Iran, let alone the rest of the empire, but appears to have been a grand ceremonial complex that was only occupied seasonally; the complex was raised high on a walled platform, with five "palac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frataraka
Frataraka (Aramaic: ''Prtkr’𐡐𐡓𐡕𐡊𐡓’'', "governor", or more specifically "sub-satrapal governor") is an ancient Persian title, interpreted variously as “leader, governor, forerunner”. It is an epithet or title of a series of rulers in Persis from 3rd to mid 2nd century BC, or alternatively between 295 and 220 BC, at the time of the Seleucid Empire, prior to the Parthian conquest of West Asia and Iran. Studies of ''frataraka coins'' are important to historians of this period. Rulers and period Several rulers have been identified as belonging to Fratarakā dynasty (from the title ''prtrk' zy alhaya'', or "governor of the gods" on their coins): ''bgdt'' ( Baydād), ''rtḥštry'' (Ardaxšīr I), ''whwbrz'' ( Vahbarz, who is called Oborzos in Polyenus 7.40), and ''wtprdt'' ( Vādfradād I). Traditionally, they used to be considered as independent, anti-Seleucid rulers of Persis in the 3rd century BC. It seems however that they were rather representatives of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus I
Antiochus I Soter (, ''Antíochos Sōtér''; "Antiochus the Savior"; 2 June 261 BC) was a Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus succeeded his father Seleucus I Nicator in 281 BC and reigned during a period of instability which he mostly overcame until his death on 2 June 261 BC. He is the last known ruler to be attributed the ancient Mesopotamian title King of the Universe. Biography Antiochus's father was Seleucus I Nicator and his mother was Apama, daughter of Spitamenes, being one of the princesses whom Alexander the Great had given as wives to his generals in 324 BC. The Seleucids fictitiously claimed that Apama was the daughter of Darius III, in order to legitimise themselves as the inheritors of both the Achaemenids and Alexander, and therefore the rightful lords of western and central Asia. In 294 BC, prior to the death of his father Seleucus I, Antiochus married his stepmother, Stratonice, daughter of Demetrius Poliorcetes. The ancient sources report that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC. After receiving the Mesopotamian regions of Babylonia and Assyria in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, and Lebanon, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what are now modern Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KINGS Of PERSIS
The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Iranian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire (6th century BCE – 4th century BCE) and the Sasanian Empire (3rd century CE – 7th century CE). History Persis (also known as Pars), a region in the southwestern Iranian plateau, was the homeland of a southwestern branch of the Iranian peoples, the Persians. It was also the birthplace of the first Iranian Empire, the Achaemenids. The region served as the center of the empire until its conquest by the Macedonian king Alexander the Great (). Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis was ruled by local dynasts subject to the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire. These dynasts held the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary player in the power struggles following Alexander's death, Seleucus rose to become the total ruler of Asia Minor, Syria (region), Syria, Mesopotamia, and the Iranian plateau, assuming the title of ''basileus'' (king). The Seleucid Empire was one of the major powers of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic world, until it was overcome by the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire in the late second and early first centuries BC. While serving under Alexander, Seleucus was commander of the ''Hypaspists, Hypaspistai,'' an elite Macedonian infantry unit. After the death of Alexander in June 323 BC, Seleucus initially supported Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control large parts of Empire of Alexander the Great, Alexander's former empire. He assumed the title of ''basileus'' (king) in 306 BC and reigned until his death. He was the founder of the Antigonid dynasty, which ruled over Macedonia until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 168 BC. Antigonus likely served under Philip II of Macedon. He took part in Alexander's Wars of Alexander the Great, invasion of Achaemenid Persia and was named satrap of Phrygia. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, he also received Pamphylia and Lycia in accordance with the Partition of Babylon. However, he later incurred the enmity of Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's empire, and was driven from Phrygia. He fled to Greece and formed an alliance with Antipater, later joine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gabiene
Battle of Gabiene was the second great battle between Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Antigonus Monophthalmus and Eumenes, two of Alexander the Great's successors (the so-called Diadochi). The battle was fought near Gabiene in Persia in the winter of 316-315 BC and ended the Second War of the Diadochi. It established Antigonus as the most powerful of the successors. Since the sole reference of this battle is ultimately from Eumenes' personal aide Hieronymus of Cardia (later transmitted through the historian Diodorus Siculus, Diodorus), who later switched his allegiance to Antigonus, he provides a unique perspective from both sides' point of view. Background After the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, his generals immediately began squabbling over his empire. Soon it degenerated into open warfare, with each general attempting to claim a portion of Alexander's vast kingdom. One of the most talented generals among the Diadochi was Antigonus Monophthalmus (Antigonus the One-eyed), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persophile
Persophilia (, pârsi dusti) is the feeling or expression of interest in, respect for, and appreciation of Persians on the part of a non-Persian. More specifically, a Persophile is someone who has a strongly positive predisposition or sympathy towards Persia and the Persian people, with an admiration for their Persian language, language and Persian literature, literature, Persian culture, culture (Persian art, art, Music of Persia, music, Persian cuisine, cuisine, etc.), History of Iran, history, or Government of Iran, government. The earliest use of the word may have been by the Royal Numismatic Society of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom in 1838, referring to the pro-Persian policy of a Cypriot king of Marion, Cyprus, Marion. The opposite sentiment is known as Anti-Iranian sentiment, Persophobia.Ram, H. (2009): ''Iranophobia: The Logic of an Israeli Obsession'', Stanford University Press, Origins Ancient Iran Foreign admiration of Persian soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peucestas
Peucestas (, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in Macedonia, and a distinguished officer in the service of Alexander the Great. His name is first mentioned as one of those appointed to command a trireme on the Hydaspes. Prior to this he must have distinguished himself for his personal valour and prowess, as he was the person selected by Alexander to carry before him in battle the sacred shield, which he had taken down from the temple of Athena at Troy. In this capacity he was in close attendance upon the king's person in the assault on the capital city of the Malavas (325 BC); and all authors agreed in attributing the chief share in saving the life of Alexander upon that occasion to Peucestas, while they differed as to almost all the other circumstances and persons concerned. For his services on this occasion he was rewarded by the king with almost every distinction which it was in his power to confer. On the arrival of Alexander at Persepol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orxines
Orxines was a Persian noble, descended from Cyrus the Great. He was present at the Battle of Gaugamela. He belonged to the Pasargadae. In 323 BCE, when Alexander the Great returned to Pasargadae, Orxines presented expensive gifts to Alexander and his entourage, but deliberately ignored Alexander's lover, the Persian eunuch Bagoas. When he was told of Alexander's affection for the eunuch, Orxines replied "that he paid his respects to the king’s friends, not his whores, and that it was not the Persian custom to regard as men those who allowed themselves to be sexually used as women." As a result, Bagoas turned Alexander against Orxines, accusing him of stealing from the tomb of Cyrus the Great The tomb of Cyrus the Great is located in Pasargadae, which was the first capital city of his Achaemenid Empire and is now an archaeological site in the Fars Province of Iran. Prior to being identified with Cyrus the Great by the British diplom ..., and Orxines was executed. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |