Peucestas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Peucestas (, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in
Peucestas (, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in
Livius
by Jona Lendering ---- {{Hellenistic satraps Somatophylakes Ancient Macedonian generals Generals of Alexander the Great 4th-century BC Macedonians People from Imathia Ancient Miezans Trierarchs of Nearchus' fleet Satraps of the Alexandrian Empire
 Peucestas (, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in
Peucestas (, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
ia, and a distinguished officer in the service of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. His name is first mentioned as one of those appointed to command a trireme
A trireme ( ; ; cf. ) was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and ancient R ...
on the Hydaspes
The Jhelum River is a major river in South Asia, flowing through India and Pakistan, and is the westernmost of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian-administered territory of Jammu an ...
. Prior to this he must have distinguished himself for his personal valour and prowess, as he was the person selected by Alexander to carry before him in battle the sacred shield, which he had taken down from the temple of Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
at Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destina ...
. In this capacity he was in close attendance upon the king's person in the assault on the capital city of the Malavas
The Malavas (Brahmi script: 𑀫𑁆𑀫𑀸𑀭𑀯 ''Mmālava'') or Malwas were an ancient Indian tribe. They are believed to be the Mallian people (Malloi) who lived in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander's invasion in the 4th century ...
(325 BC); and all authors agreed in attributing the chief share in saving the life of Alexander upon that occasion to Peucestas, while they differed as to almost all the other circumstances and persons concerned.
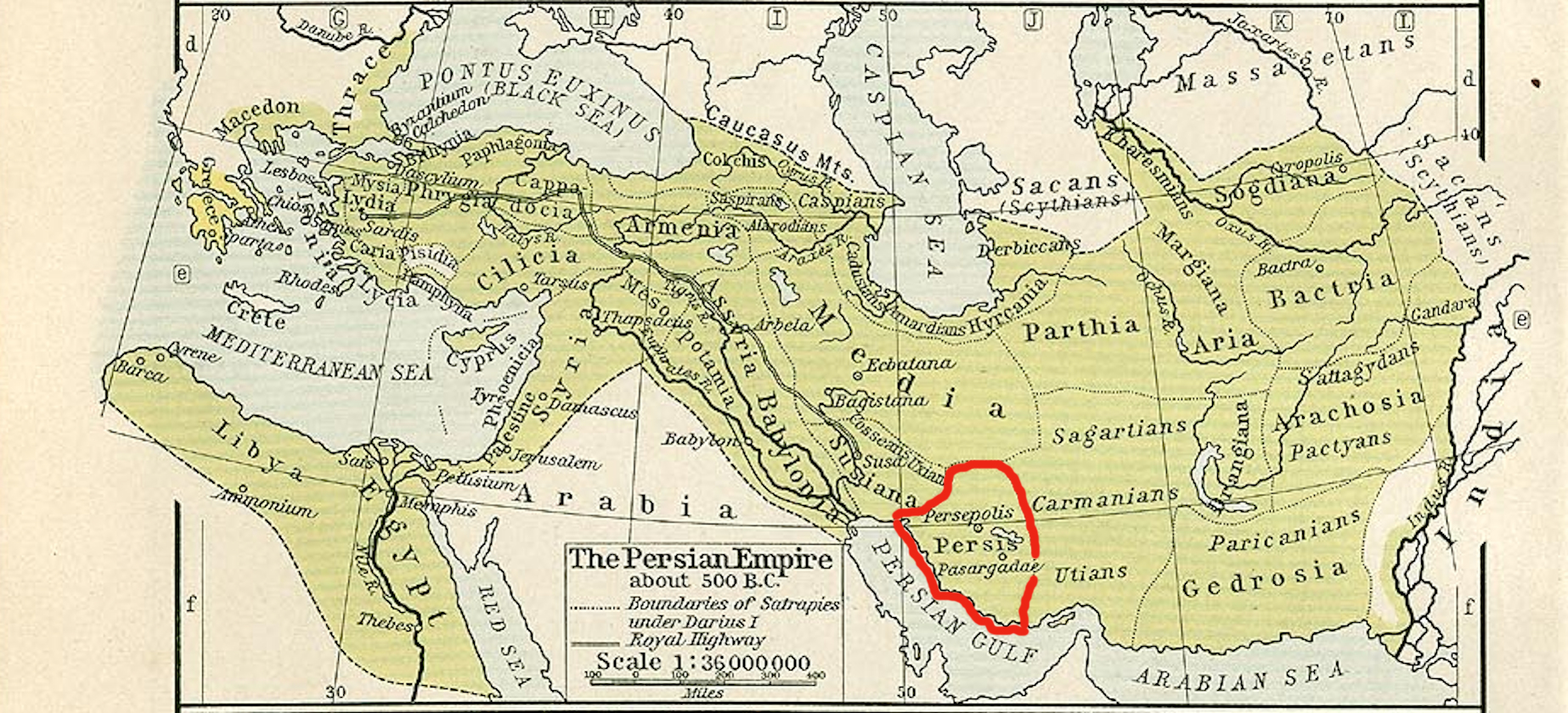
For his services on this occasion he was rewarded by the king with almost every distinction which it was in his power to confer. On the arrival of Alexander at Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and ...
, he bestowed upon Peucestas the important satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
y of Persis
Persis (, ''Persís;'' Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''), also called Persia proper, is a historic region in southwestern Iran, roughly corresponding with Fars province. The Persian ethnic group are thought to have initially migrated ...
, but, previous to this, he had already raised him to the rank of somatophylax (the king's bodyguard), an honour rendered the more conspicuous in this instance by the number of those select officers being augmented on purpose to make room for his admission. At Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
, also, Peucestas was the first of those rewarded with crowns of gold for their past exploits. After this he proceeded to take possession of his government, where he conciliated the favour of the Persians subject to his rule, as well as that of Alexander himself, by adopting the Persian dress and customs, in exchange for those of Macedonia; whence he is considered a Persophile
Persophilia (, pârsi dusti) is the feeling or expression of interest in, respect for, and appreciation of Persians on the part of a non-Persian. More specifically, a Persophile is someone who has a strongly positive predisposition or sympathy towa ...
.
In the spring of 323 BC, Peucestas joined the king at Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
, with an army of 20,000 Persian troops; and is mentioned as one of those in attendance upon him during his last illness. It does not appear that he took any leading part in the discussions that ensued upon the death of Alexander, but in the division of the provinces that followed, he obtained the renewal of his government of Persis, which he also retained in the second partition at Triparadisus, 321 BC. All his attention seems to have been directed to strengthening himself in this position and extending his power and influence as far as possible. In this he so far succeeded, that when he was at length compelled to take an active part in the war between Antigonus and Eumenes
Eumenes (; ; ) was a Ancient Greece, Greek general, satrap, and Diadoch, Successor of Alexander the Great. He participated in the Wars of Alexander the Great, serving as Alexander's personal secretary and later on as a battlefield commander. Eume ...
(317 BC), he obtained by common consent the chief command of all the forces furnished by the satrapies east of the Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
river; and was with difficulty induced to waive his pretensions to the supreme direction of the war. Eumenes, however, by his dexterous management, soothed the irritation of Peucestas, and retained him firmly in his alliance throughout the two campaigns that followed. The satrap was contented to gratify his pride by feasting the whole of the armies assembled in Persis on a scale of royal magnificence, while Eumenes virtually directed all the operations of the war.
But the disaster in the final action at the Battle of Gabiene
Battle of Gabiene was the second great battle between Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Antigonus Monophthalmus and Eumenes, two of Alexander the Great's successors (the so-called Diadochi). The battle was fought near Gabiene in Persia in the winter o ...
near Gadamarta (316 BC) which led to the capture of the baggage, and the surrender of Eumenes by the Argyraspids, appears to have been due to the misconduct and insubordination of Peucestas, who, according to one account, was himself one of the chief advisers of the treaty. His conduct throughout these campaigns shows that he lacked both the ability to command for himself, and the moderation to follow the superior judgment of others. His vain and ambitious character seems to have been appreciated at its just value by Antigonus, who, while he deprived him of his satrapy, and led him away a virtual prisoner, elated him with false hopes and specious promises, which were never fulfilled. Peucestas seems to have become an Antigonid officer, treating with cities like Theangela on their behalf. He maintained his prominence during Demetrius's reign as the king of Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
.
See also
* AlexippusReferences
* Smith, William (editor); ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology
The ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'' is a biographical dictionary of classical antiquity, edited by William Smith (lexicographer), William Smith and originally published in London by John Taylor (English publisher), Tayl ...
'', , Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, (1867)
Notes
External links
Livius
by Jona Lendering ---- {{Hellenistic satraps Somatophylakes Ancient Macedonian generals Generals of Alexander the Great 4th-century BC Macedonians People from Imathia Ancient Miezans Trierarchs of Nearchus' fleet Satraps of the Alexandrian Empire