|
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
A permanent magnet synchronous generator is a generator where the excitation field is provided by a permanent magnet instead of a coil. The term ''synchronous'' refers here to the fact that the rotor and magnetic field rotate with the same speed, because the magnetic field is generated through a shaft-mounted permanent magnet mechanism, and current is induced into the stationary armature. Description Synchronous generators are the majority source of commercial electrical energy. They are commonly used to convert the mechanical power output of steam turbines, gas turbines, reciprocating engines, and hydro turbines into electrical power for the grid. Some designs of wind turbines also use this generator type. In the majority of designs, the rotating assembly in the center of the generator—the ''rotor''—contains the magnet, and the ''stator'' is the stationary armature that is electrically connected to a load. As shown in the diagram, the perpendicular component of the stato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an external circuit. In most generators which are rotating machines, a source of kinetic power rotates the generator's shaft, and the generator produces an electric current at its output terminals which flows through an external circuit, powering electrical loads. Sources of mechanical energy used to drive generators include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. Generators produce nearly all of the electric power for worldwide electric power grids. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternators
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Gordon R. Selmon, ''Magnetoelectric Devices'', John Wiley and Sons, 1966 no ISBN pp. 391-393 Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually, the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids. History Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
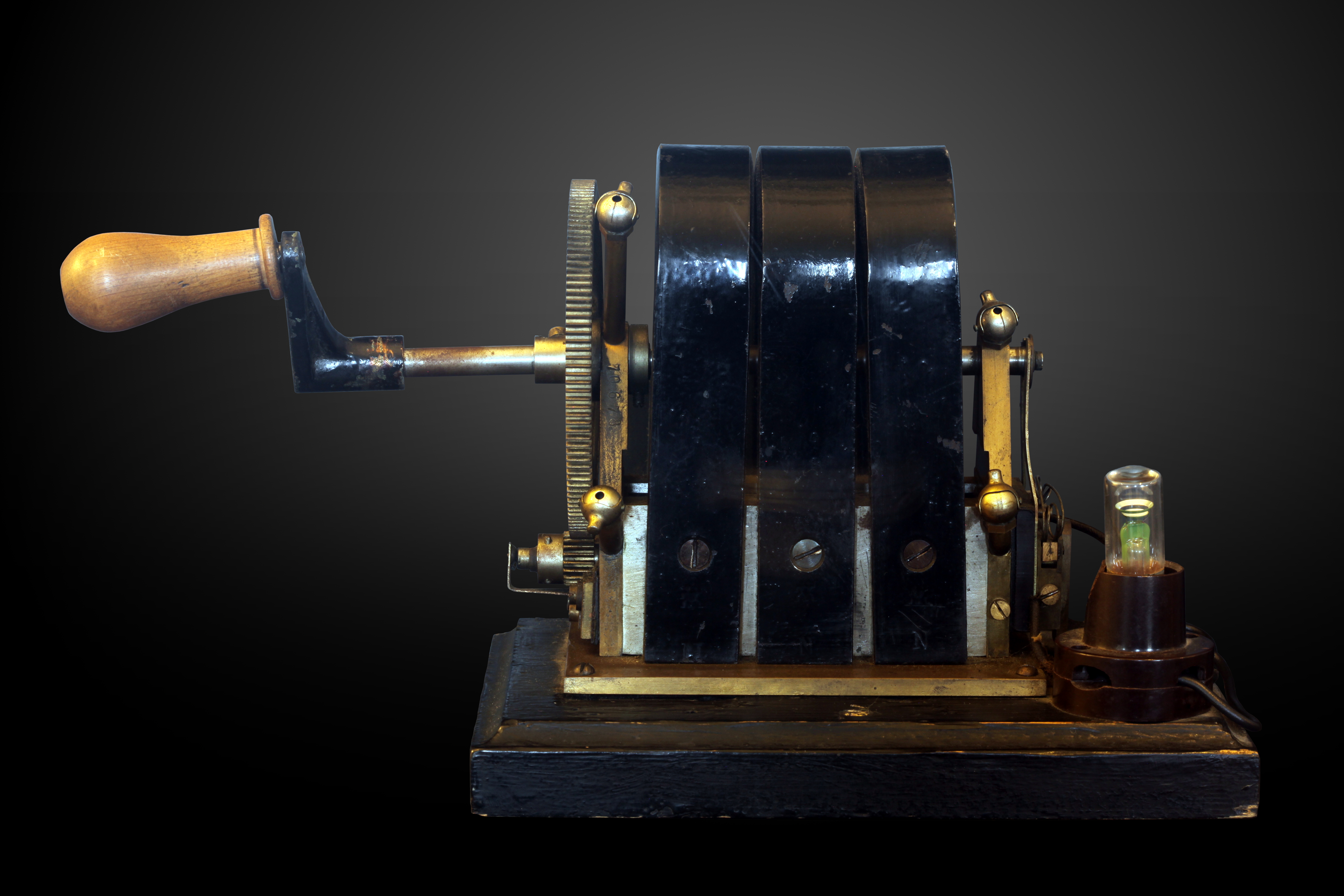
Telephone Magneto
A telephone magneto is a hand-cranked electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce alternating current from a rotating armature. In early telegraphy, magnetos were used to power instruments, while in telephony they were used to generate electrical current to drive electromechanical ringers in telephone sets and activate signals on operator consoles. Telegraphy Telegraphy pre-dated telephony and magnetos were used to drive some of the early printing telegraph instruments. Manual telegraphy with keys and reception by either a needle instrument or a syphon recorder could be powered by batteries. The later automatic and printing instruments, such as the Wheatstone ABC telegraph, required greater currents that could be delivered by a hand-cranked magneto. A hand-crank was used to rotate a belt drive that increases the rotational speed of an armature with a pair of coils between the poles of a stationary horseshoe magnet. Telephony Many early manual telephones h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition Magneto
An ignition magneto (also called a high-tension magneto) is an older type of ignition system used in spark-ignition engines (such as petrol engines). It uses a magneto and a transformer to make pulses of high voltage for the spark plugs. The older term "high-tension" means "high-voltage". Design A simple magneto (an electrical generator using permanent magnets) is able to produce relatively low voltage electricity, however it is unable to produce the high voltages required by a spark plug as used in most modern engines (aside from diesel engines). An ''ignition magneto'' also includes an electrical transformer, which converts the electricity to a higher voltage (with the trade-off being a corresponding reduction in the output electric current, current). As the points begin to open, point spacing is initially such that the voltage across the primary coil would arc across the points. A capacitor is placed across the points which absorbs the energy stored in the leakage inductanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, although it is usually considered distinct from most other alternators, which use field coils rather than permanent magnets. Hand-cranked magneto generators were used to provide ringing current in telephone systems. Magnetos were also adapted to produce pulses of high voltage in the ignition systems of some gasoline-powered internal combustion engines to provide power to the spark plugs. Use of such ignition magnetos for ignition is now limited mainly to engines without a low-voltage electrical system, such as lawnmowers and chainsaws, and to aircraft engines, in which keeping the ignition independent of the rest of the electrical system ensures that the engine continues running in the event of alternator or battery failure. For redund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternator
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Gordon R. Selmon, ''Magnetoelectric Devices'', John Wiley and Sons, 1966 no ISBN pp. 391-393 Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually, the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip Ring
A slip ring is an electromechanical device that allows the transmission of Electric power, power and electrical Signal, signals from a stationary to a rotating structure. A slip ring can be used in any Electromechanics, electromechanical system that requires rotation while transmitting power or signals. It can improve mechanical performance, simplify system operation and eliminate damage-prone wires dangling from movable joints. Also called rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, collectors, swivels, or electrical rotary joints, these rings are commonly found in slip ring motors, electrical generators for alternating current (AC) systems and alternators and in packaging machinery, cable reels, and wind turbines. They can be used on any rotating object to transfer power, control circuits, or Analog signal, analog or Digital signal, digital signals including data such as those found on aerodrome beacons, rotating tanks, power shovels, radio telescopes, telemet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth element, rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.Staff. "Understanding Alternators. What Is an Alternator and How Does It Work." N.p., n.d. Web. 24 November 2014 . Early development An early example of electromagnetic rotation was the first rotary machine built by Ányos Jedlik with electromagnets and a commutator, in 1826-27. Other pioneers in the field of electricity include Hippolyte Pixii who built an alternating current generator in 1832, and William Ritchie's construction of an electromagnetic generator with four rotor coils, a commutator and brushes, also in 1832. Development quickly included more useful applications such as Moritz Hermann Jacobi's motor that could lift 10 to 12 pounds with a speed of one foot per second, about 15 watts of mechanical power in 1834. In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |