Ignition Magneto on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 An ignition magneto (also called a high-tension magneto) is an older type of
An ignition magneto (also called a high-tension magneto) is an older type of

 An ignition magneto (also called a high-tension magneto) is an older type of
An ignition magneto (also called a high-tension magneto) is an older type of ignition system
Ignition systems are used by heat engines to initiate combustion by igniting the fuel-air mixture. In a spark ignition versions of the internal combustion engine (such as petrol engines), the ignition system creates a spark to ignite the fuel-ai ...
used in spark-ignition engine
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, ty ...
s (such as petrol engines). It uses a magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
and a transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
to make pulses of high voltage for the spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
s. The older term "high-tension" means "high-voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
".
Design
A simplemagneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
(an electrical generator using permanent magnets) is able to produce relatively low voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
electricity, however it is unable to produce the high voltages required by a spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
as used in most modern engines (aside from diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compr ...
s). An ''ignition magneto'' also includes an electrical transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
, which converts the electricity to a higher voltage (with the trade-off being a corresponding reduction in the output current).
As the points begin to open, point spacing is initially such that the voltage across the primary coil would arc across the points. A capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
is placed across the points which absorbs the energy stored in the leakage inductance
Leakage inductance derives from the electrical property of an imperfectly coupled transformer whereby each Electromagnetic coil, winding behaves as a self-inductance in series and parallel circuits, series with the winding's respective Electrical r ...
of the primary coil, and slows the rise time of the primary winding voltage to allow the points to open fully.
A second coil, with many more turns than the primary, is wound on the same iron core to form an electrical transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
. The ratio of turns in the secondary winding to the number of turns in the primary winding, is called the ''turns ratio''. Voltage across the primary coil results in a proportional voltage being induced across the secondary winding of the coil. The turns ratio between the primary and secondary coil is selected so that the voltage across the secondary reaches a very high value, enough to arc across the gap of the spark plug. As the voltage of the primary winding rises to several hundred volts, the voltage on the secondary winding rises to several tens of thousands of volts, since the secondary winding typically has 100 times as many turns as the primary winding.
Impulse coupling, induction vibrator, and booster coil
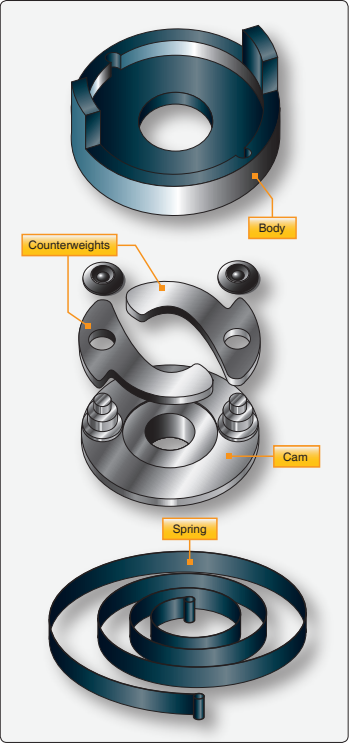
Because the magneto has low voltage output at low speed, starting an engine is more difficult. Therefore, some magnetos have an impulse coupling, a spring-like mechanical linkage between the engine and magneto drive shaft which "winds up" and "lets go" at the proper moment for spinning the magneto shaft. The impulse coupling uses a spring, a hub cam with flyweights, and a shell. The hub of the magneto rotates while the drive shaft is held stationary, and the spring tension builds up. When the magneto is supposed to fire, the flyweights are released by the action of the body contacting the trigger ramp. This allows the spring to unwind giving the rotating magnet a rapid rotation and letting the magneto spin at such a speed to produce a spark.History
In the late 1890s, English engineer Frederick Richard Simms collaborated with the German engineerRobert Bosch
Robert Bosch (23 September 1861 – 12 March 1942) was a German business magnate, engineer and inventor, founder of Bosch (company), Bosch.
Biography
Bosch was born in Langenau, Albeck, in the Swabia, Swabian Highlands near Ulm. He was one of t ...
, and his staff of Arnold Zähringer, Young Rall, and Gottlob Honold, in developing the first practical high-tension magneto. In 1900, the Bosch magneto ignition was used in the Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist. He was a pioneer of internal-combustion engines and automobile development. He invented the high-speed liquid petroleum-fue ...
engines on the Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155� ...
.
The first car to use magneto ignition was the 1901 German Mercedes 35 hp racing car, followed by various cars produced by Benz, Mors, Turcat-Mery, and Nesseldorf. Ignition magnetos were soon used on most cars, for both low voltage systems (which used secondary coils to fire the spark plugs) and high voltage magnetos (which fired the spark plug directly, similar to induction coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" ( archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich Rühmkorff) is a type of transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 To create the ...
ignition). Ignition magnetos were largely replaced by ignition coil
An ignition coil is used in the ignition system of a spark-ignition engine to transform the battery voltage to the much higher voltages required to operate the spark plug(s). The spark plugs then use this burst of high-voltage electricity to ig ...
s once batteries became common in cars, since a battery-operated coil can provide a high-voltage spark even at low speeds, making starting easier.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ignition MagnetoMagneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
Electrical generators