|
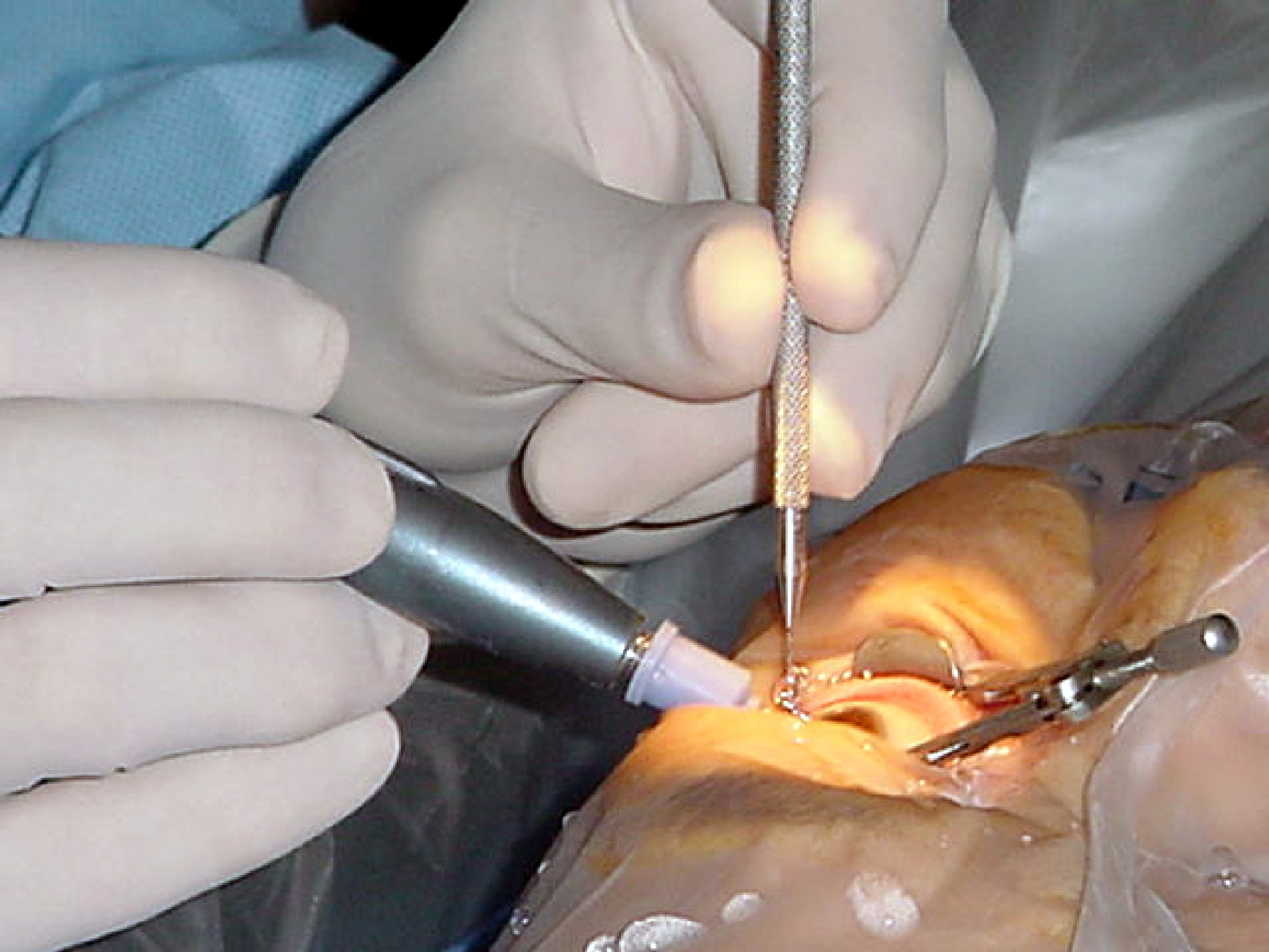
Peritomy
A peritomy is a procedure carried out during eye surgery, where an incision is made around the limbus, usually to expose the sclera and/or extraocular muscles The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ... for a variety of surgical procedures. References Eye surgery {{eye-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic surgery or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa. Eye surgery is part of ophthalmology and is performed by an ophthalmologist or eye surgeon. The eye is a fragile organ, and requires due care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. It continues to be a widely practiced class of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often used for quick procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Limbus
The corneal limbus (''Latin'': corneal border) is a highly vascularized and pigmented zone between the cornea, conjunctiva, and the sclera (the white of the eye) that protects and heals the cornea. The cornea is composed of three primary cell types: epithelial cells, corneal fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. The corneal surface is one of the body's most specialized structures that undergoes continuous cellular renewal and regeneration. It contains limbal epithelial stem cells (LESCs) in the palisades of Vogt. Limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) can lead to disorders where limbal stem cells are damaged or absent. Additional disorders involving the corneal limbus are caused by deficiencies in interactions between ocular structures, developmental anomalies, and cancer. This article explores the structure, functions, disorders, and clinical significance of the corneal limbus. Etymology The word "limbus" comes from the Latin meaning "border." Structure The corneal limbus is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest. In children, it is thinner and shows some of the underlying pigment, appearing slightly blue. In the elderly, fatty deposits on the sclera can make it appear slightly yellow. People with dark skin can have naturally darkened sclerae, the result of melanin pigmentation. In humans, and some other vertebrates, the whole sclera is white or pale, contrasting with the coloured iris (anatomy), iris. The cooperative eye hypothesis suggests that the pale sclera evolved as a method of nonverbal communication that makes it easier for one individual to identify where another individual is looking. Other mammals with white or pale sclera include chimpanzees, many orangutans, some gorillas, and bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraocular Muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior oblique muscles, control Eye movement, movement of the eye. The other muscle, the Levator palpebrae superioris muscle, levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation and depression, elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction. The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles. Structure Since only a small part of the eye called the Fovea centralis, fovea provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target. Eye movements must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |