|
Periodic Systems Of Small Molecules
Periodic systems of molecules are charts of molecules similar to the periodic table of the elements. Construction of such charts was initiated in the early 20th century and is still ongoing. It is commonly believed that the periodic law, represented by the periodic chart, is echoed in the behavior of molecules, at least small molecules. For instance, if one replaces any one of the atoms in a triatomic molecule with a rare gas atom, there will be a drastic change in the molecule’s properties. Several goals could be accomplished by constructing an explicit representation of this periodic law as manifested in molecules: (1) a classification scheme for the vast number of molecules that exist, starting with small ones having just a few atoms, for use as a teaching aid and tool for archiving data, (2) forecasting data for molecular properties based on the classification scheme, and (3) a sort of unity with the periodic chart and the periodic system of fundamental particles. Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
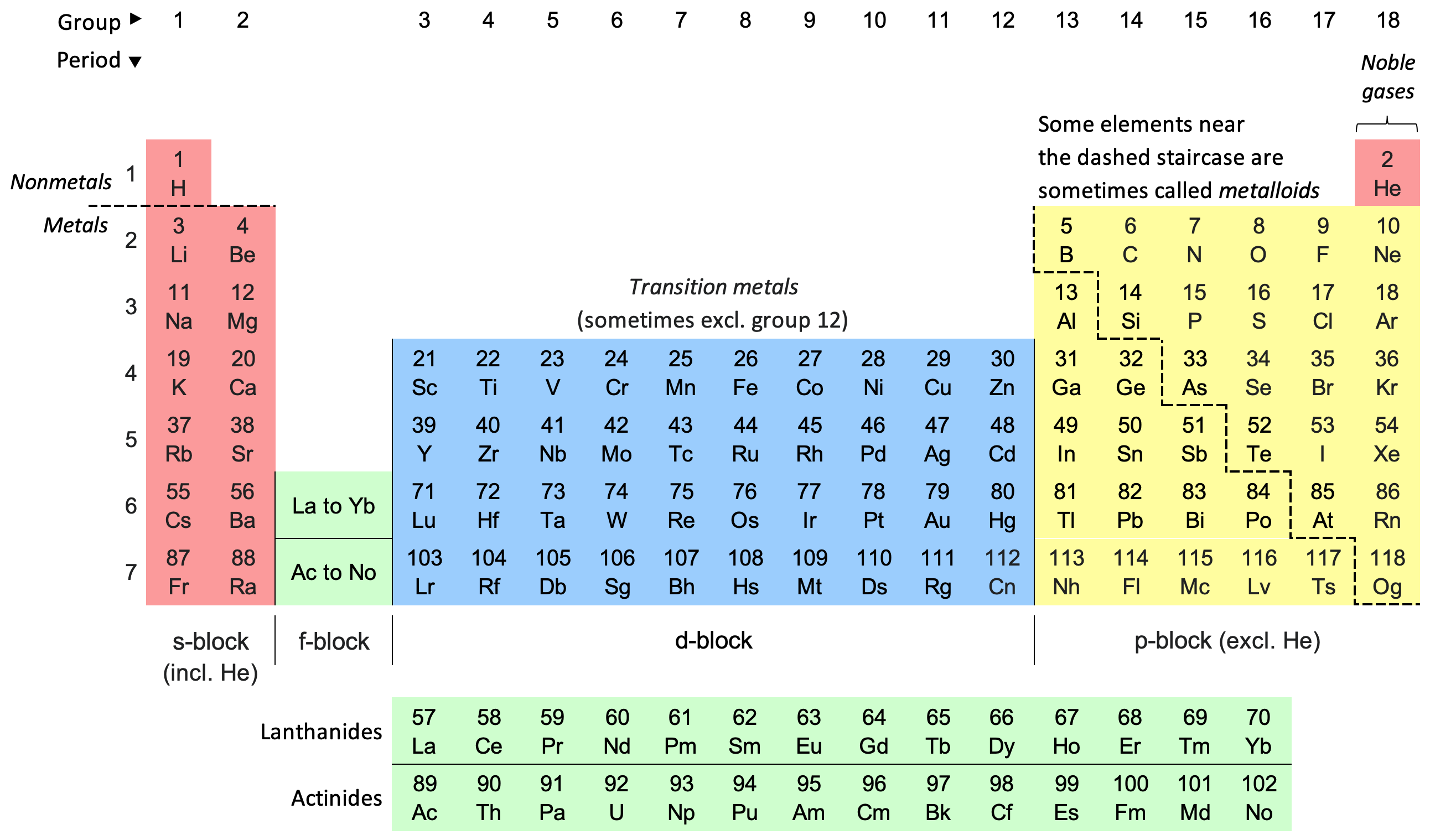
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Charge
Core electrons are the electrons in an atom that are not valence electrons and do not participate as directly in chemical bonding. The nucleus and the core electrons of an atom form the atomic core. Core electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus. Therefore, unlike valence electrons, core electrons play a secondary role in chemical bonding and reactions by screening the positive charge of the atomic nucleus from the valence electrons. The number of valence electrons of an element can be determined by the periodic table group of the element (see valence electron): *For main-group elements, the number of valence electrons ranges from 1 to 8 (''n''s and ''n''p orbitals). *For transition metals, the number of valence electrons ranges from 3 to 12 (''n''s and (''n''−1)d orbitals). *For lanthanides and actinides, the number of valence electrons ranges from 3 to 16 (''n''s, (''n''−2)f and (''n''−1)d orbitals). All other non-valence electrons for an atom of that element are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aufbau Principle
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the Aufbau principle (, from ), also called the Aufbau rule, states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons first fill Electron shell#Subshells, subshells of the lowest available energy, then fill subshells of higher energy. For example, the 1s subshell is filled before the 2s subshell is occupied. In this way, the electrons of an atom or ion form the most stable electron configuration possible. An example is the configuration for the phosphorus atom, meaning that the 1s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2p subshell has 6 electrons, and so on. The configuration is often abbreviated by writing only the valence electrons explicitly, while the core electrons are replaced by the symbol for the last previous noble gas in the periodic table, placed in square brackets. For phosphorus, the last previous noble gas is neon, so the configuration is abbreviated to [Ne] 3s2 3p3, where [Ne] signifies the core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Spin
Spin is an intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Spinors and bispinors behave similarly to vectors: they have definite magnitudes and ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Model
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. The definition of the word "atom" has changed over the years in response to scientific discoveries. Initially, it referred to a hypothetical concept of there being some fundamental particle of matter, too small to be seen by the naked eye, that could not be divided. Then the definition was refined to being the basic particles of the chemical elements, when chemists observed that elements seemed to combine with each other in ratios of small whole numbers. Then physicists discovered that these particles had an internal structure of their own and therefore perhaps did not deserve to be called "atoms", but renaming atoms would have been impractical by that point. Atomic theory is one of the most important scientific developments in history, crucial to all the physical sciences. At the start of ''The Feynman Lectures on Physics'', physicist and Nobel laureate Richard Feynman offers the atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in Atomic physics, atomic and Quantum mechanics, quantum physics, and also educated and mentored many students for the new era of theoretical physics. He served as doctoral advisor and Postdoctoral researcher, postdoc advisor to seven Nobel Prize winners and supervised at least 30 other famous physicists and chemists. Only J. J. Thomson's record of mentorship offers a comparable list of high-achieving students. He introduced the second quantum number, azimuthal quantum number, and the third quantum number, magnetic quantum number. He also introduced the fine-structure constant and pioneered X-ray wave theory. Early life and education Sommerfeld was born in 1868 to a family with deep ancestral roots in Prussia. His mother Cäcilie Matthias (1839–1902) was the daughter of a Potsdam builder. His father Franz Sommerfeld (1820� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (, ; ; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish theoretical physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and old quantum theory, quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of Complementarity (physics), complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a Wave–particle duality, wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Descriptor
Molecular descriptors play a fundamental role in chemistry, pharmaceutical sciences, environmental protection policy, and health researches, as well as in quality control, being the way molecules, thought of as real bodies, are transformed into numbers, allowing some mathematical treatment of the chemical information contained in the molecule. This was defined by Todeschini and Consonni as: "''The molecular descriptor is the final result of a logic and mathematical procedure which transforms chemical information encoded within a symbolic representation of a molecule into a useful number or the result of some standardized experiment.''" By this definition, the molecular descriptors are divided into two main categories: experimental measurements, such as log P, molar refractivity, dipole moment, polarizability, and, in general, additive physico-chemical properties, and theoretical molecular descriptors, which are derived from a symbolic representation of the molecule and can be fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Potential Curve
Reduction, reduced, or reduce may refer to: Science and technology Chemistry * Reduction (chemistry), part of a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. ** Organic redox reaction, a redox reaction that takes place with organic compounds ** Ore reduction: see smelting Computing and algorithms * Reduction (complexity), a transformation of one problem into another problem * Reduction (recursion theory), given sets A and B of natural numbers, is it possible to effectively convert a method for deciding membership in B into a method for deciding membership in A? * Bit Rate Reduction, an audio compression method * Data reduction, simplifying data in order to facilitate analysis * Graph reduction, an efficient version of non-strict evaluation * L-reduction, a transformation of optimization problems which keeps the approximability features * Partial order reduction, a technique for reducing the size of the state-space to be searched b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimm's Hydride Displacement Law
Grimm's Hydride Displacement Law is an early hypothesis, formulated in 1925, to describe bioisosterism, the ability of certain chemical groups to function as or mimic other chemical groups. :“Atoms anywhere up to four places in the periodic system before an inert gas change their properties by uniting with one to four hydrogen atoms, in such a manner that the resulting combinations behave like pseudoatoms, which are similar to elements in the groups one to four places respectively, to their right.” According to Grimm, each vertical column (of Table below) would represent a group of isostere Classical Isosteres are molecules or ions with similar shape and often electronic properties. Many definitions are available. but the term is usually employed in the context of bioactivity and drug development. Such biologically-active compounds c ...s. References # Grimm, H. G. ''Structure and Size of the Non-metallic Hydrides'' ''Z. Electrochem.'' 1925, ''31'', 474–480. # Grimm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |