|
Peridexion Tree
The peridexion tree (from Greek δένδρον περιδέξιον, ''déndron peridéxion'') or perindens is a mythological tree discussed in the ''Physiologus'', an early Greek-language Christian didactic text and compendium, and popular in medieval bestiaries. It is described as growing in India, attracting doves and deterring serpents, making for a fable about Christian salvation. Etymology The name comes from the Greek δένδρον περιδέξιον (''déndron peridéxion''), ''peridéxion'' meaning ambidextrous, dextrous, or convenient. Latin-language manuscripts, such as the Aberdeen Bestiary, refer to it as "perindens." Description ''Physiologus'' describes the tree as growing in India and having a sweet fruit that doves enjoy eating. A serpent that seeks to eat the doves is afraid of the tree and its shadow, so it waits for the doves to stray from the protection of the tree in order to attack them. This is a reminder to the text's Christian audience of salvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet in the Western tradition to regard himself as an individual persona with an active role to play in his subject.' Ancient authors credited Hesiod and Homer with establishing Greek religious customs. Modern scholars refer to him as a major source on Greek mythology, farming techniques, early economic thought, archaic Greek astronomy and ancient time-keeping. Life The dating of Hesiod's life is a contested issue in scholarly circles (''see § Dating below''). Epic narrative allowed poets like Homer no opportunity for personal revelations. However, Hesiod's extant work comprises several didactic poems in which he went out of his way to let his audience in on a few details of his life. There are three explicit references in '' Works and Days ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the three canonical poets of Latin literature. The Imperial scholar Quintilian considered him the last of the Latin love elegists.Quint. ''Inst.'' 10.1.93 Although Ovid enjoyed enormous popularity during his lifetime, the emperor Augustus banished him to Tomis, a Dacian province on the Black Sea, where he remained a decade until his death. Overview A contemporary of the older poets Virgil and Horace, Ovid was the first major Roman poet to begin his career during Augustus's reign. Collectively, they are considered the three canonical poets of Latin literature. The Imperial scholar Quintilian described Ovid as the last of the Latin love elegists.Quint. ''Inst.'' 10.1.93 He enjoyed enormous popularity during his lifetime, but the emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
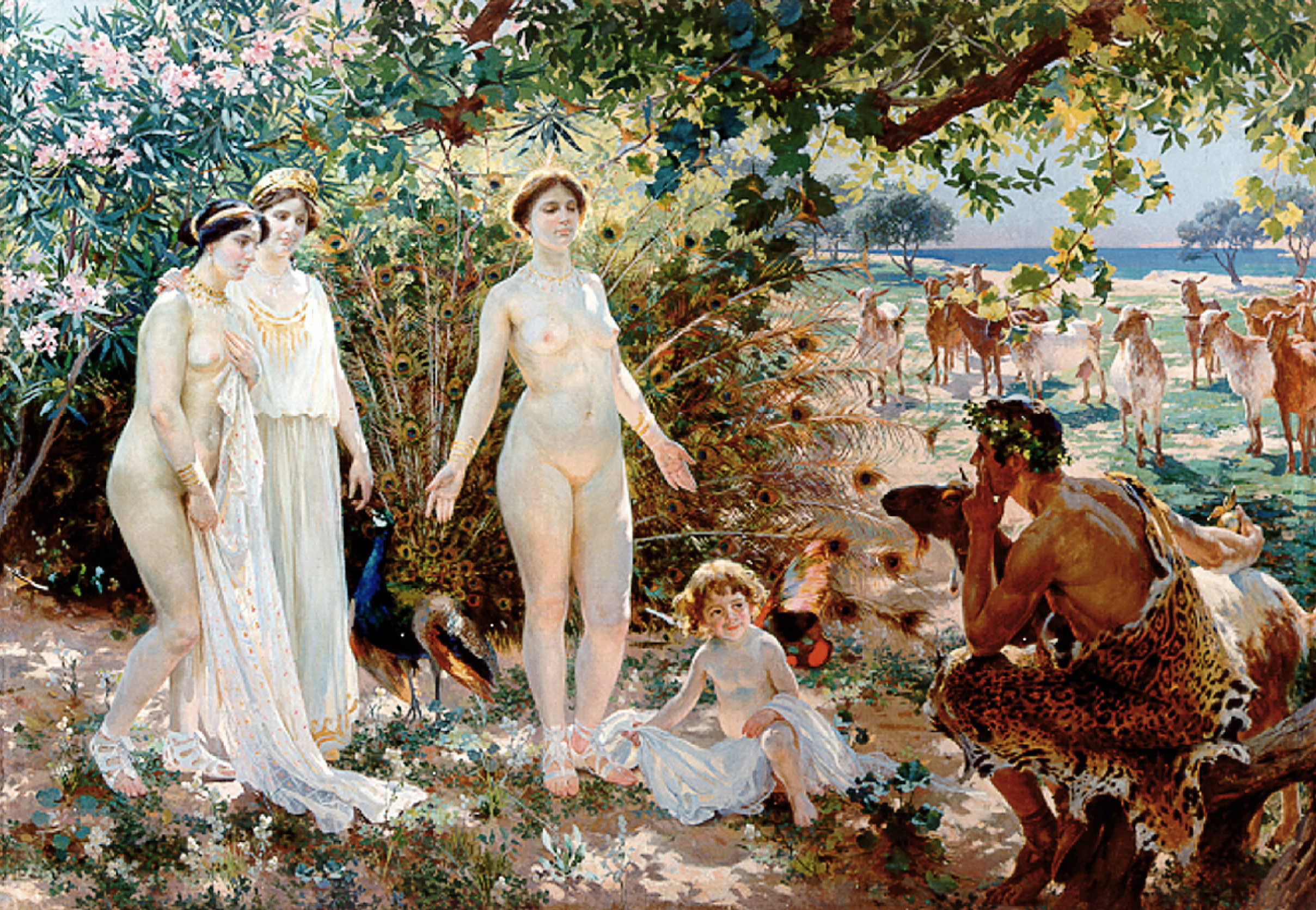
Hesperides
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides (; , ) are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides () from their reputed father, the Titan Atlas.Diodorus Siculus. ''Library4.27.2' Etymology The name means ''originating from Hesperos'' (evening). ''Hesperos'', or ''Vesper'' in Latin, is the origin of the name Hesperus, the evening star (i.e. the planet Venus) as well as having a shared root with the English word "west". Mythology The nymphs of the evening Ordinarily, the Hesperides number three, like the other Greek triads (the Three Graces and the Three Fates). "Since the Hesperides themselves are mere symbols of the gifts the apples embody, they cannot be actors in a human drama. Their abstract, interchangeable names are a symptom of their impersonality", classicist Evelyn Byrd Harrison has observed. They are sometimes portrayed as the evening daughters of Night (Nyx) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Apple
The golden apple is an element that appears in various national and ethnic folk legends or fairy tales. Recurring themes depict a hero (for example Hercules or Făt-Frumos) retrieving the golden apples hidden or stolen by a monstrous antagonist. Gold apples also appear on the Silver Branch of the Otherworld in Irish mythology. Greek mythology Golden apples appear in three Greek myths: Atalanta and Melanion A huntress named Atalanta who raced against a suitor named Melanion, also known as Hippomenes. Melanion used golden apples to distract Atalanta so that he could win the race. Though abandoned by her father as an infant, Atalanta became a skilled hunter and received acclaim for her role in the hunt for the Calydonian boar. Her father claimed her as his daughter and wished to marry her off. However, Atalanta was reluctant to marry due to a prophecy that marriage would be her downfall. Because of her beauty, she gained a number of suitors and finally agreed to marry, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladon (mythology)
Ladon (; Ancient Greek: Λάδων; gen.: Λάδωνος ''Ladonos'') was a monster in Greek mythology, the dragon that guarded the golden apples in the Garden of the Hesperides. Family According to Hesiod's ''Theogony'', Ladon was the last of the progeny of Phorcys and Ceto. A scholion on Apollonius of Rhodes' ''Argonautica'', however, cites Hesiod as calling him the son of Typhon, and the same scholion on Apollonius of Rhodes claims that one "Peisandros" called Ladon born of the earth. The mythographer Apollodorus calls Ladon the offspring of the monstrous Typhon and Echidna, a parentage repeated by Hyginus and Pherecydes; similarly, Ladon is called the son of Typhon in Tzetzes' ''Chiliades''. According to Ptolemy Hephaestion's ''New History'', as recorded by Photius in his '' Bibliotheca'', Ladon was the brother of the Nemean lion. Mythology Ladon was the serpent-like dragon that twined and twisted around the tree in the Garden of the Hesperides and guarded the gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its aftermath became part of the oral tradition of Homer's epic poems, the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey''. Two poems by Homer's near contemporary Hesiod, the '' Theogony'' and the '' Works and Days'', contain accounts of the genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reclam
Reclam Verlag is a German publishing house, established in Leipzig in 1828 by Anton Philipp Reclam (1807–1896).Reclam-Museum öffnet in Leipzig in (23.10.2018). Retrieved 28 October 2018 It is particularly well known for the "little yellow books" of its ''Universal-Bibliothek'' ("universal library"), simple paperback editions of literary classics for schools and universities. History In 1802 Charles Henri Reclam (1776–1844), whose family originated from , had moved to Leip ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Of Life (biblical)
In Judaism and Christianity, the tree of life ( he, עֵץ הַחַיִּים, ‘ēṣ haḥayyīm) is first described in of the Book of Genesis as being "in the midst of the Garden of Eden" with the tree of the knowledge of good and evil (). After the fall of man, "lest he put forth his hand, and take also of the tree of life, and eat, and live for ever", cherubim and a flaming sword are placed at the east end of the Garden to guard the way to the tree of life. The tree of life has become the subject of some debate as to whether or not the tree of the knowledge of good and evil is the same tree. In the Bible outside of Genesis, the term "tree of life" appears in Proverbs () and Revelation (). It also appears in 2 Esdras () and 4 Maccabees (), which are included among the Jewish apocrypha. According to the Greek Apocalypse of Moses, the tree of life is also called the Tree of Mercy. Adam believed the oil of the tree of Life would relieve him of his ailments and sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraxinus
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of subtropical species are evergreen. The genus is widespread across much of Europe, Asia, and North America. The leaves are opposite (rarely in whorls of three), and mostly pinnately compound, though simple in a few species. The seeds, popularly known as "keys" or "helicopter seeds", are a type of fruit known as a samara. Some ''Fraxinus'' species are dioecious, having male and female flowers on separate plants but sex in ash is expressed as a continuum between male and female individuals, dominated by unisexual trees. With age, ash may change their sexual function from predominantly male and hermaphrodite towards femaleness ; if grown as an ornamental and both sexes are present, ashes can cause a considerable litter problem with their seeds. Rowans or mountain ashes have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (Pliny)
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work's title, its subject area is not limited to what is today understood by natural history; Pliny himself defines his scope as "the natural world, or life". It is encyclopedic in scope, but its structure is not like that of a modern encyclopedia. It is the only work by Pliny to have survived, and the last that he published. He published the first 10 books in AD 77, but had not made a final revision of the remainder at the time of Pliny the Elder#Death, his death during the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. The rest was published posthumously by Pliny's nephew, Pliny the Younger. The work is divided into 37 books, organised into 10 volumes. These cover topics including astronomy, mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)