|
Pegasus 3
Pegasus 3 or III, also known as Pegasus C before launch, was an American satellite which was launched in 1965 to study micrometeoroid impacts in Low Earth orbit. It was the last of three Pegasus satellites to be launched, the previous two having been launched earlier the same year. It was manufactured by Fairchild Hiller, and operated by NASA. Spacecraft Pegasus 3 was a Pegasus spacecraft, consisting of of instruments, attached to the S-IV upper stage of the carrier rocket which had placed it into orbit. It had a total mass of , and was equipped with two sets of micrometeoroid detection panels, and a radio for tracking and returning data. The panels were long, and equipped with 116 individual detectors. Launch Pegasus 3 was launched atop a Saturn I rocket, serial number SA-10, flying from Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Kennedy Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 13:00:00 UTC on 30 July 1965. Following launch, Pegasus 3 was given the COSPAR designation 1965-060A, whilst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegasus (spyware)
Pegasus is spyware developed by the Israeli cyber-arms company NSO Group that is designed to be covertly and remotely installed on mobile phones running iOS and Android. While NSO Group markets Pegasus as a product for fighting crime and terrorism, governments around the world have routinely used the spyware to surveil journalists, lawyers, political dissidents, and human rights activists. The sale of Pegasus licenses to foreign governments must be approved by the Israeli Ministry of Defense. As of September 2023, Pegasus operators were able to remotely install the spyware on iOS versions through 16.6 using a zero-click exploit. While the capabilities of Pegasus may vary over time due to software updates, Pegasus is generally capable of reading text messages, call snooping, collecting passwords, location tracking, accessing the target device's microphone and camera, and harvesting information from apps. The spyware is named after Pegasus, the winged horse of Greek mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT), also known as NORAD Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number, is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM), and previously the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD), in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. For example, catalog number 1 is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 58,010 objects, including 16,645 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 8,936 were still active. 25,717 of the objects were well tracked while 2,055 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 16,600 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably tracked and in constant flux, so their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1965 In Spaceflight
Orbital and Suborbital launches Deep Space Rendezvous EVAs Orbital launch statistics By country By rocket By orbit References U.S. ''Aeronautics and Space Report 1965'' Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1965 1965 in spaceflight, Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
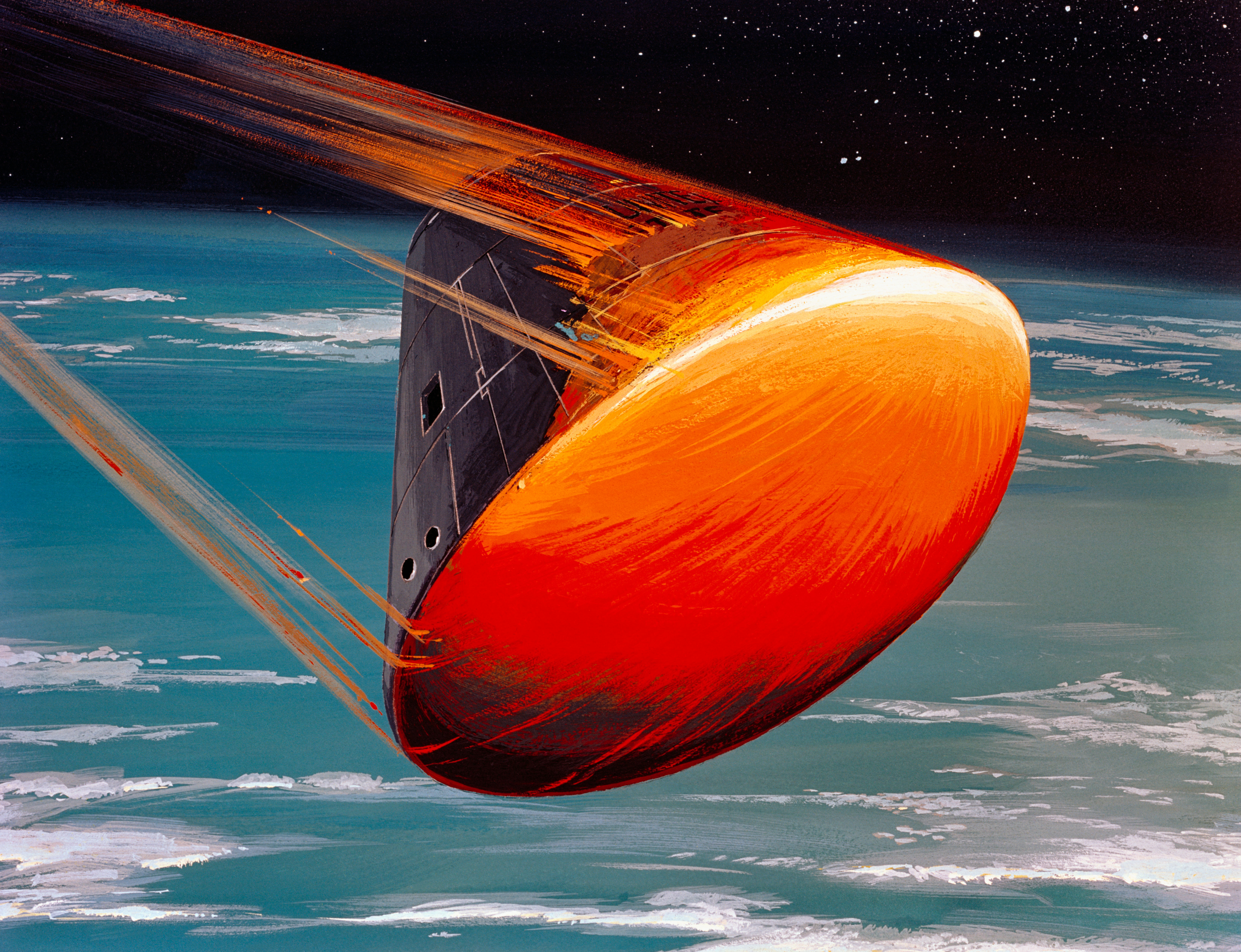
Atmospheric Reentry
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience Drag (physics), atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass (ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Decay
Orbital decay is a gradual decrease of the distance between two orbiting bodies at their closest approach (the periapsis) over many orbital periods. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite, a star and any object orbiting it, or components of any binary system. If left unchecked, the decay eventually results in termination of the orbit when the smaller object strikes the surface of the primary; or for objects where the primary has an atmosphere, the smaller object burns, explodes, or otherwise breaks up in the larger object's atmosphere; or for objects where the primary is a star, ends with incineration by the star's radiation (such as for comets). Collisions of stellar-mass objects are usually accompanied by effects such as gamma-ray bursts and detectable gravitational waves. Orbital decay is caused by one or more mechanisms which absorb energy from the orbital motion, such as fluid friction, gravitational anomalies, or electromagnetic effects. For bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit. For celestial objects in general, the orbital period is determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, ''e.g.'' Earth around the Sun. Periods in astronomy are expressed in units of time, usually hours, days, or years. Its reciprocal is the orbital frequency, a kind of revolution frequency, in units of hertz. Small body orbiting a central body According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period ''T'' of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: :T = 2\pi\sqrt where: * ''a'' is the orbit's semi-major axis * ''G'' is the gravitationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
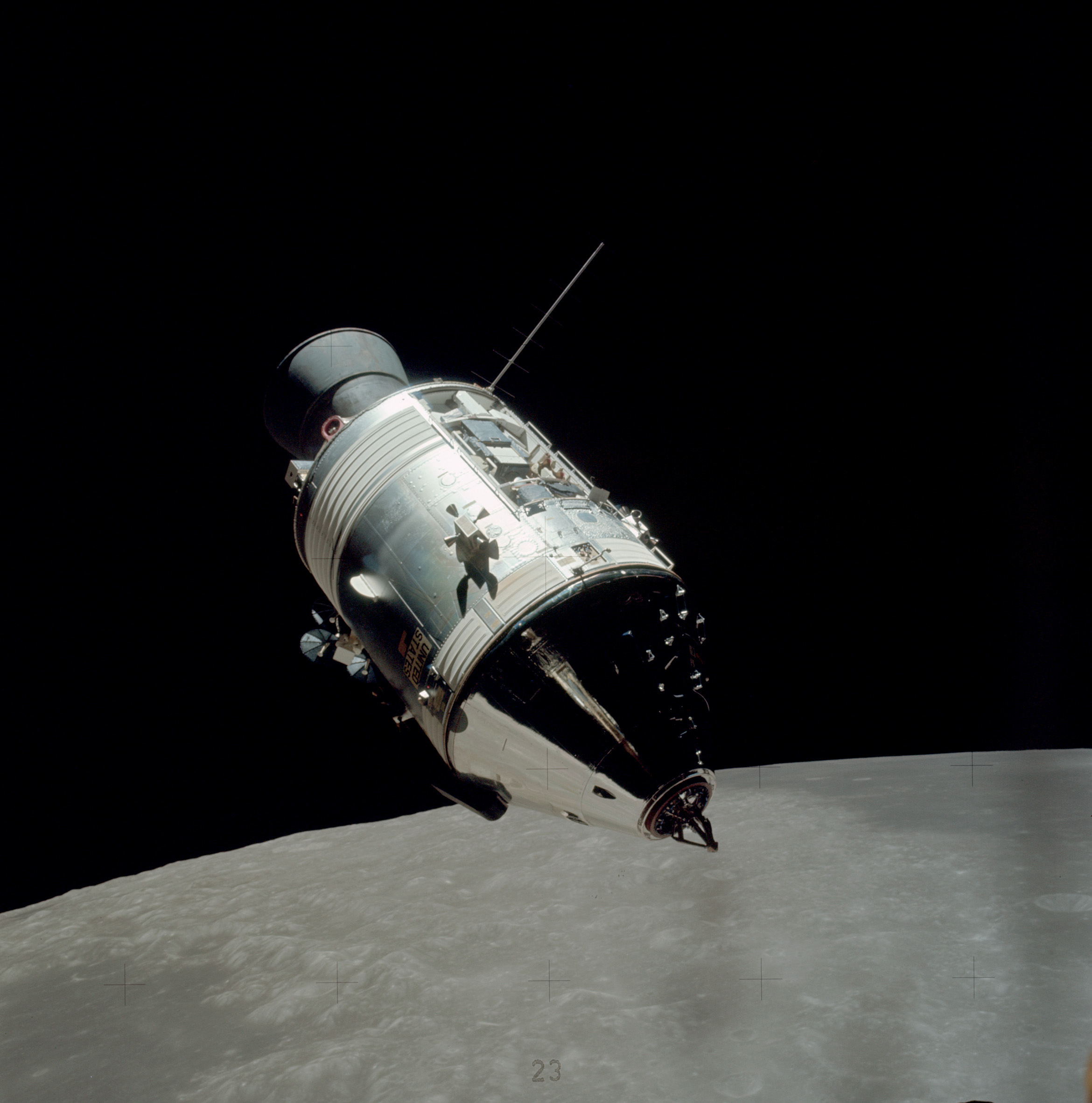
Apollo Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payload Fairing
A payload fairing or nose fairing is a nose cone used to protect a launch vehicle, spacecraft payload (air and space craft), payload against the impact of dynamic pressure and aerodynamic heating during launch through an atmosphere. An additional function on some flights is to maintain the cleanroom environment for precision instruments. Once outside the atmosphere the fairing is jettisoned, exposing the payload to outer space. The standard payload fairing is typically a cone-cylinder combination, due to aerodynamic considerations, although other specialized fairings are in use. The type of fairing which separates into two halves upon jettisoning is called a clamshell fairing by way of analogy to the Bivalve shell, bifurcating shell of a clam. In some cases the fairing may enclose both the payload and the upper stage of the rocket, such as on Atlas V and Proton M. If the payload is attached both to the Booster rocket, booster's core structures and to the fairing, the payload ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-105 (SA-10)
AS-105 was the fifth and final orbital flight of a boilerplate Apollo spacecraft, and the third and final launch of a Pegasus micrometeoroid detection satellite. It was launched by SA-10, the tenth and final Saturn I rocket, in 1965. Overview AS-105 was an Apollo boilerplate spacecraft; boilerplate BP-9A was used for the flight. The spacecraft reentered on November 22, 1975. The Saturn launch vehicle (SA-10) was similar to those of missions AS-103 and AS-104. As on the previous mission, the boilerplate service module was equipped with a test installation of a reaction control engine package. The primary flight objective was to continue demonstration of the launch vehicle's iterative guidance mode and evaluation of system accuracy. Launch AS-105 was launched from Cape Kennedy Launch Complex 37B at 08:00 EST (13:00 GMT) on July 30, 1965, on the last Saturn I rocket, SA-10. A planned thirty-minute hold ensured that launch time coincided with the opening of the Pegasus la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a Apollo command and service module, combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. While the LM separated and landed, the CSM remained in orbit. After the lunar excursion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |