|
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT), also known as NORAD Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number, is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM), and previously the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD), in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. For example, catalog number 1 is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 58,010 objects, including 16,645 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 8,936 were still active. 25,717 of the objects were well tracked while 2,055 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 16,600 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably tracked and in constant flux, so their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Space Command
United States Space Command (USSPACECOM or SPACECOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Department of Defense, responsible for military operations in outer space, specifically all operations 100 kilometers (62 miles) and greater above mean sea level. U.S. Space Command is responsible for the operational employment of space forces that are provided by the uniformed services of the Department of Defense (United States), Department of Defense. Space Command was originally created in September 1985 to provide joint command and control for all military forces in outer space and coordinate with the other combatant commands. SPACECOM was disestablished in 2002, and its responsibilities and forces were merged into United States Strategic Command. It was reestablished on 29 August 2019, with a reemphasized focus on space as a warfighting domain. The U.S. Space Force is the military service responsible for organizing, training, and equipping the majority of forces for U.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
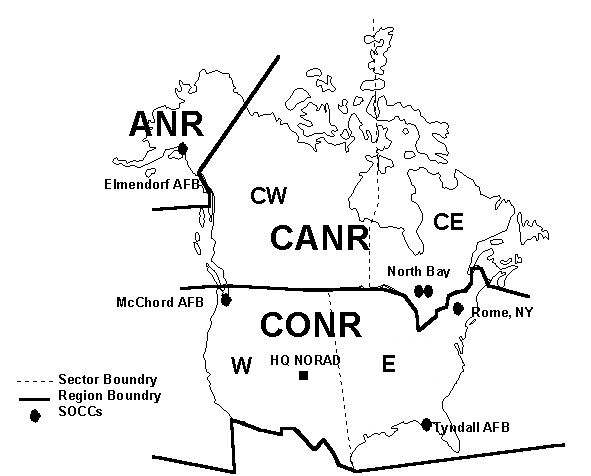
North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ; , CDAAN), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a Combined operations, combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, Colorado, El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The Commander of the North American Aerospace Defense Command, NORAD commander and deputy commander are, respectively, a General (United States), United States four-star general or equivalent and a Lieutenant-general (Canada), Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Command NORAD is headed by its Commander of NORAD, commander, who is a Four-star rank, four-star General (United States), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik (rocket)
The Sputnik rocket was an uncrewed orbital carrier rocket designed by Sergei Korolev in the Soviet Union, derived from the R-7 Semyorka ICBM. On 4 October 1957, it was used to perform the world's first satellite launch, placing ''Sputnik 1'' into a low Earth orbit. Two versions of the Sputnik were built, the Sputnik-PS ( GRAU index 8K71PS), which was used to launch ''Sputnik 1'' and later ''Sputnik 2'', and the Sputnik (8A91), which failed to launch a satellite in April 1958, and subsequently launched '' Sputnik 3'' on 15 May 1958. A later member of the R-7 family, the Polyot, used the same configuration as the Sputnik rocket, but was constructed from Voskhod components. Because of the similarity, the Polyot was sometimes known as the Sputnik 11A59. Specifications *First Stage: Block B, V, G, D (four strap-on boosters) **Gross mass: 43.0 tons **Empty mass: 3.400 tons **Thrust (vac): 4 × 99,000 kgf = 396 Mgf (3.89 MN) ** Isp: 306 s (3,000 N·s/kg) **Burn time: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (, , ''Satellite 1''), sometimes referred to as simply Sputnik, was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for three weeks before its three silver-zinc batteries became depleted. Aerodynamic drag caused it to fall back into the atmosphere on 4 January 1958. It was a polished metal sphere in diameter with four external radio antennas to broadcast radio pulses. Its radio signal was easily detectable by amateur radio operators, and the 65° orbital inclination made its flight path cover virtually the entire inhabited Earth. The satellite's success was unanticipated by the United States. This precipitated the American Sputnik crisis and triggered the Space Race. The launch was the beginning of a new era of political, military, technological, and scientific developments. The word ''sputnik'' is Russian for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Space Control Squadron
The 18th Space Defense Squadron (18 SDS) is a United States Space Force Space Domain Awareness unit located at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The 18th SDS is tasked with executing command and control of the space surveillance network (SSN), maintaining the resident space object (RSO) database and managing United States Space Command's space situational awareness (SSA) sharing program to United States, foreign government, commercial, and academic entities. The squadron also conducts advanced analysis, sensor optimization, conjunction assessment, human spaceflight support, reentry/break-up assessment, and launch analysis. Mission The mission of the 18th SDS is to provide and advance a continuous, comprehensive, and combat-relevant understanding of the space situation. The squadron processes SSN data to monitor all activity to, in, and from space, and maintains custody of all resident space objects. Primary mission functions include launch detection and tracking, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Space Command
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opacity (optics), opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration (physiology), respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Space Defense Squadron
The 18th Space Defense Squadron (18 SDS) is a United States Space Force Space domain awareness, Space Domain Awareness unit located at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The 18th SDS is tasked with executing command and control of the United States Space Surveillance Network, space surveillance network (SSN), maintaining the Resident Space Object, resident space object (RSO) database and managing United States Space Command's space situational awareness (SSA) sharing program to United States, foreign government, commercial, and academic entities. The squadron also conducts advanced analysis, sensor optimization, conjunction assessment, human spaceflight support, reentry/break-up assessment, and launch analysis. Mission The mission of the 18th SDS is to provide and advance a continuous, comprehensive, and combat-relevant understanding of the space situation. The Squadron (aviation), squadron processes United States Space Surveillance Network, SSN data to monitor all activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ; , CDAAN), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/ United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The NORAD commander and deputy commander are, respectively, a United States four-star general or equivalent and a Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Command NORAD is headed by its commander, who is a four-star general or admiral in the United States Armed Forces. The deputy commander is a Royal Canadian Air Force lieutenant general. Prior to the 1968 unification of the Canadian Forces, the deputy commander was an RCAF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Strategic Command
The United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands in the United States Department of Defense. Headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, USSTRATCOM is responsible for Strategic_nuclear_weapon, strategic nuclear deterrence theory, deterrence, Air_Force_Global_Strike_Command, global strike, and operating the Defense Department's Global Information Grid. It also provides a host of capabilities to support the other combatant commands, including integrated missile defense; and global command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR). This command exists to give "national leadership a unified resource for greater understanding of specific threats around the world and the means to respond to those threats rapidly". Mission statement USSTRATCOM employs nuclear, cyber, global strike, joint electronic warfare, missile defense, and intelligence capabilities to deter aggression, decisive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-line Element Set
A two-line element set (TLE, or more rarely 2LE) or three-line element set (3LE) is a file format, data format encoding a list of orbital elements of an Earth-orbiting object for a given point in time, the ''epoch''. Using a suitable prediction formula, the Orbital state vectors, state (position and velocity) at any point in the past or future can be estimated to some accuracy. The TLE data representation is specific to the simplified perturbations models (SGP, SGP4, SDP4, SGP8 and SDP8), so any algorithm using a TLE as a data source must implement one of the SGP models to correctly compute the state at a time of interest. TLEs can describe the trajectories only of Earth-orbiting objects. TLEs are widely used as input for projecting the future orbital tracks of space debris for purposes of characterizing "future debris events to support risk analysis, close approach analysis, Collision avoidance (spacecraft), collision avoidance maneuvering" and forensic analysis. The format was or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |