|
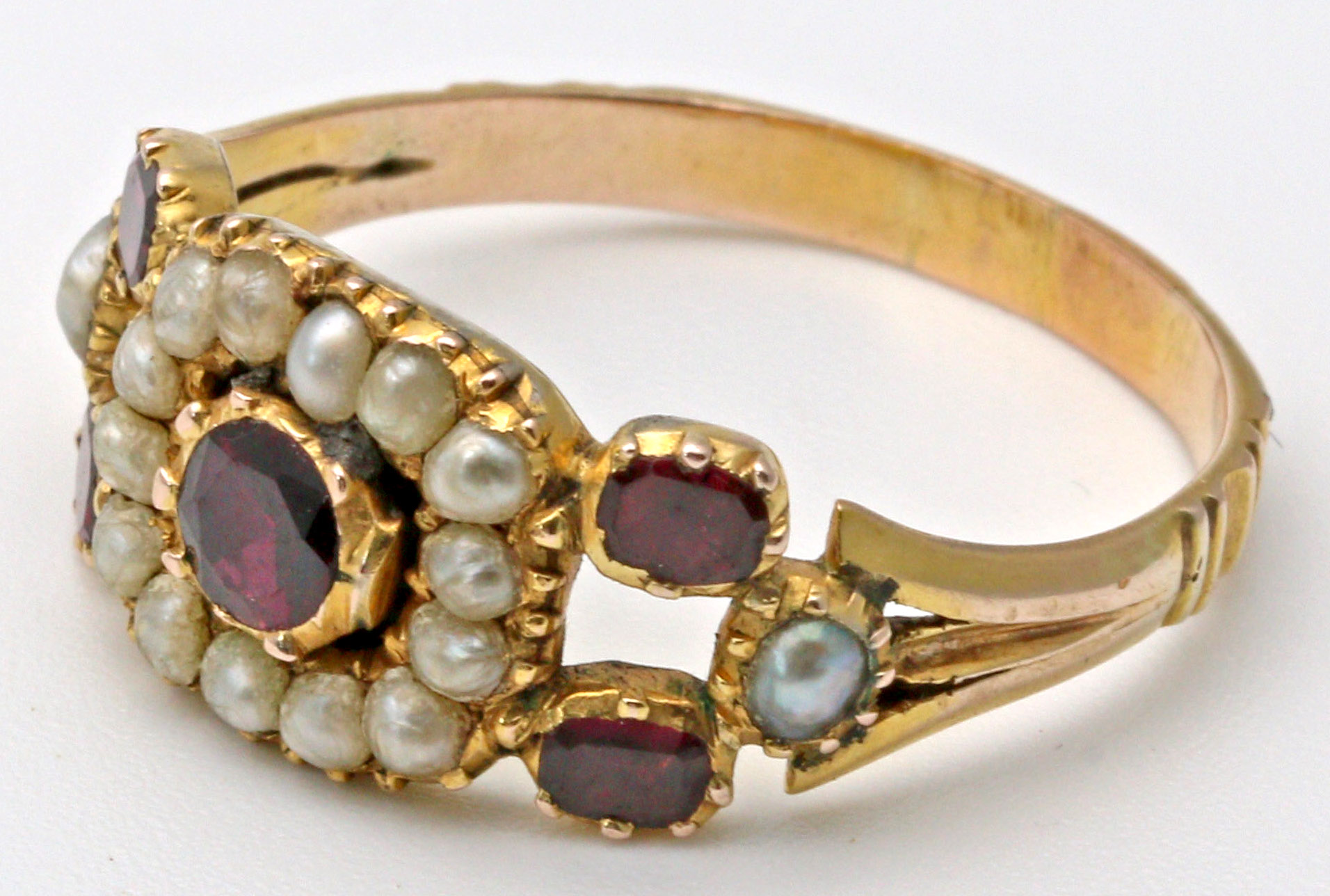
Pearls
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate (mainly aragonite or a mixture of aragonite and calcite) in minute crystalline form, which has deposited in concentric layers. The ideal pearl is perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes, known as baroque pearls, can occur. The finest quality of natural pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries. Because of this, ''pearl'' has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, admirable and valuable. The most valuable pearls occur spontaneously in the wild, but are extremely rare. These wild pearls are referred to as ''natural'' pearls. ''Cultured'' or ''farmed'' pearls from pearl oysters and freshwater mussels make up the majority of those currently sold. Imitation pearls are also widely s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Pearls
Baroque pearls are pearls with an irregular, non-spherical shape. Shapes can range from minor aberrations to distinctly ovoid, curved, pinched, or lumpy shapes. Most cultured freshwater pearls are baroque because freshwater pearls are mantle-tissue nucleated instead of bead nucleated. Cultured saltwater pearls can also be baroque, but tend to be more teardrop-shaped due to the use of a spherical, nucleation bead. The most valuable baroque pearls are the South Sea and the Tahitian pearls, which are produced by ''Pinctada margaritifera'' (black-lipped oyster Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not a ...s) and ''Pinctada maxima'' (gold-lipped and white-lipped oysters). Although these are a variety of cultured saltwater pearls, the amount of time that the pearls are cultured d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
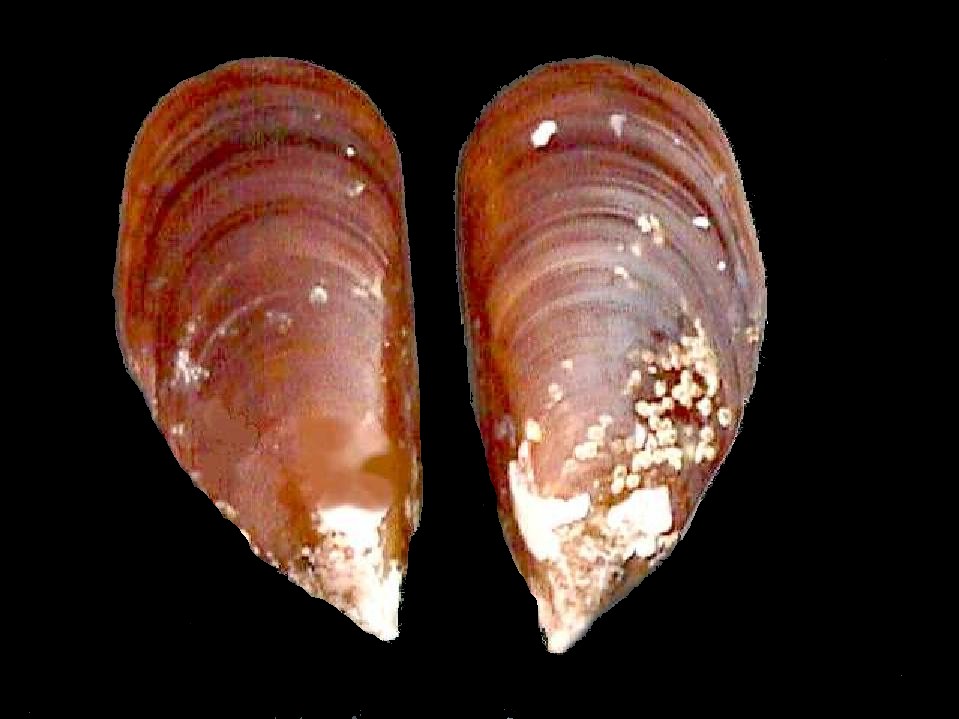
Pinctada
''Pinctada'' is a genus of saltwater oysters, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Pteriidae. These pearl oysters have a strong inner shell layer composed of nacre, also known as "mother of pearl". Pearl oysters are not closely related to either the edible oysters of family Ostreidae or the freshwater pearl mussels of the families Unionidae and Margaritiferidae. ''Pinctada margaritifera'' and '' P. maxima'' are used for culturing South Sea and Tahitian pearls. They are cultured widely primarily in the central and eastern Indo-Pacific. A pearl oyster can be seen on the reverse side of the 1,000-peso note of the Philippines. Species of commercial value All species within the genus produce pearls. Attempts have been made to harvest pearls commercially from many ''Pinctada'' species. However, the only species that are currently of significant commercial interest are: * Gulf pearl oyster, ''Pinctada radiata''; Persian Gulf, Red Sea, Mediterranean Sea and throughout the Indo-Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imitation Pearl
Imitation pearls are man-made ''faux'' pearls. They are not to be confused with cultured pearls, which are real pearls created through artificial intervention. Materials used to create imitation pearls include glass, plastic, and mollusc shells. As an alternative, some plastic beads are coated with a pearlescent substance to imitate the natural iridescence of nacre or mother of pearl. Types *Bathed pearl (also called Angel, Sheba, Mikomo, Kobe, Nikko, Sumo, Fijii, Aloha, or "improved cultured pearl") is a mother-of-pearl core coated with a mixture of plastic enamel, lead carbonate, mica, and titanium dioxide, then with a film of iridescent nylon. *Bohemian pearl is a cut and buffed mother-of-pearl protuberance. *Cotton pearl (also called "Utter Ethical pearl") is made merely from cotton and mica. *Glass pearl is a glass bead dipped or sprayed with pearlescent material, or hollow glass bead filled with pearlescent material. One variation is the Majorica pearl. Wax-filled pearl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conulariid
Conulariida is a poorly understood fossil group that has possible affinity with the Cnidaria. Their exact position as a taxon of extinct medusozoan cnidarians is highly speculative. Members of the Conulariida are commonly referred to as conulariids and appear in the fossil record from the latest parts of the Ediacaran period up until the Triassic. Structure The conulariids are fossils preserved as shell-like structures made up of rows of calcium phosphate rods, resembling an ice-cream cone with fourfold symmetry, usually four prominently-grooved corners. New rods were added as the organism grew in length; the rod-based growth falsely gives the fossils a segmented appearance. Exceptional soft-part preservation has revealed that soft tentacles protruded from the wider end of the cone, and a holdfast from the pointed end attached the organisms to hard substrate. The prevailing reconstruction of the organism has it look superficially like a sea anemone sitting inside an angular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nacre
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother of pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer; it is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent. Nacre is found in some of the most ancient lineages of bivalves, gastropods, and cephalopods. However, the inner layer in the great majority of mollusc shells is porcellaneous, not nacreous, and this usually results in a non-iridescent shine, or more rarely in non-nacreous iridescence such as ''flame structure'' as is found in conch pearls. The outer layer of cultured pearls and the inside layer of pearl oyster and freshwater pearl mussel shells are made of nacre. Other mollusc families that have a nacreous inner shell layer include marine gastropods such as the Haliotidae, the Trochidae and the Turbinidae. Physical characteristics Structure and appearance Nacre is composed of hexagonal platelets of aragonite (a form of calcium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal ** Calcite CaCO3 ** Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 ** Otavite CdCO3 ** Rhodochrosite MnCO3 ** Siderite FeCO3 ** Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic ** Aragonite CaCO3 ** Cerussite PbCO3 ** Strontianite SrCO3 ** Witherite BaCO3 ** Rutherfordine UO2CO3 ** Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal ** Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 ** Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 ** Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 ** Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 ** Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 ** Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 ** Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 ** Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 ** Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 ** Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates * Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (Iranian).''cf.'' , p. 2. Old Persian appears primarily in the inscriptions, clay tablets and seals of the Achaemenid era (c. 600 BCE to 300 BCE). Examples of Old Persian have been found in what is now Iran, Romania ( Gherla), Armenia, Bahrain, Iraq, Turkey and Egypt, with the most important attestation by far being the contents of the Behistun Inscription (dated to 525 BCE). Recent research (2007) into the vast Persepolis Fortification Archive at the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago unearthed Old Persian tablets, which suggest Old Persian was a written language in use for practical recording and not only for royal display. Origin and overview As a written language, Old Persian is attested in royal Achaemenid insc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaritiferidae
Margaritiferidae is a family of medium-sized freshwater mussels, aquatic bivalve molluscs in the order Unionida. Text may have been copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)licence. It is the most threatened of all unionid families. The family is sometimes referred to as the freshwater pearl mussel family, but " freshwater pearl mussel" more often applies to the species ''Margaritifera margaritifera''. The name refers to the thick layer of nacre (mother of pearl) lining the interior of the shell of the species, which enables them to produce pearls. Taxonomy A 2018 study suggested a new phylogeny and systematics of the Margaritiferidae, comprising two subfamilies, Gibbosulinae and Margaritiferinae, and four genera, ''Gibbosula'', ''Cumberlandia'', ''Margaritifera'', and ''Pseudunio''. This family has ancient origins, having diverged from the ancestors of the Unionidae during the Late Triassic with the crown group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perna (bivalve)
''Perna '' is a genus of mussels, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae.Gofas, S. (2010). Perna Philipsson, 1788. In: Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S.; Rosenberg, G. (2010) World Marine Mollusca database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138229 on 16 August 2012 Not to be confused with ''Perna'' Bruguière, 1789 , synonym of ''Isognomon'' Lightfoot, 1786 Species Species within the genus ''Perna '' include: * '' Perna canaliculus'' (Gmelin, 1791) New Zealand green-lipped mussel * ''Perna perna'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * † ''Perna tetleyi'' (Powell & Bartrum, 1929) * '' Perna viridis'': Asian green mussel (Linnaeus, 1758) Species brought into synonymy: * ''Perna africana'' (Chemnitz, 1785): synonym of ''Perna perna'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * ''Perna confusa'' Angas, 1871: synonym of ''Limnoperna securis'' (Lamarck, 1819) * ''Perna fulgida'' H. Adams, 1870: synonym of '' Lioberus ligneus'' (Reeve, 1858) * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |