|
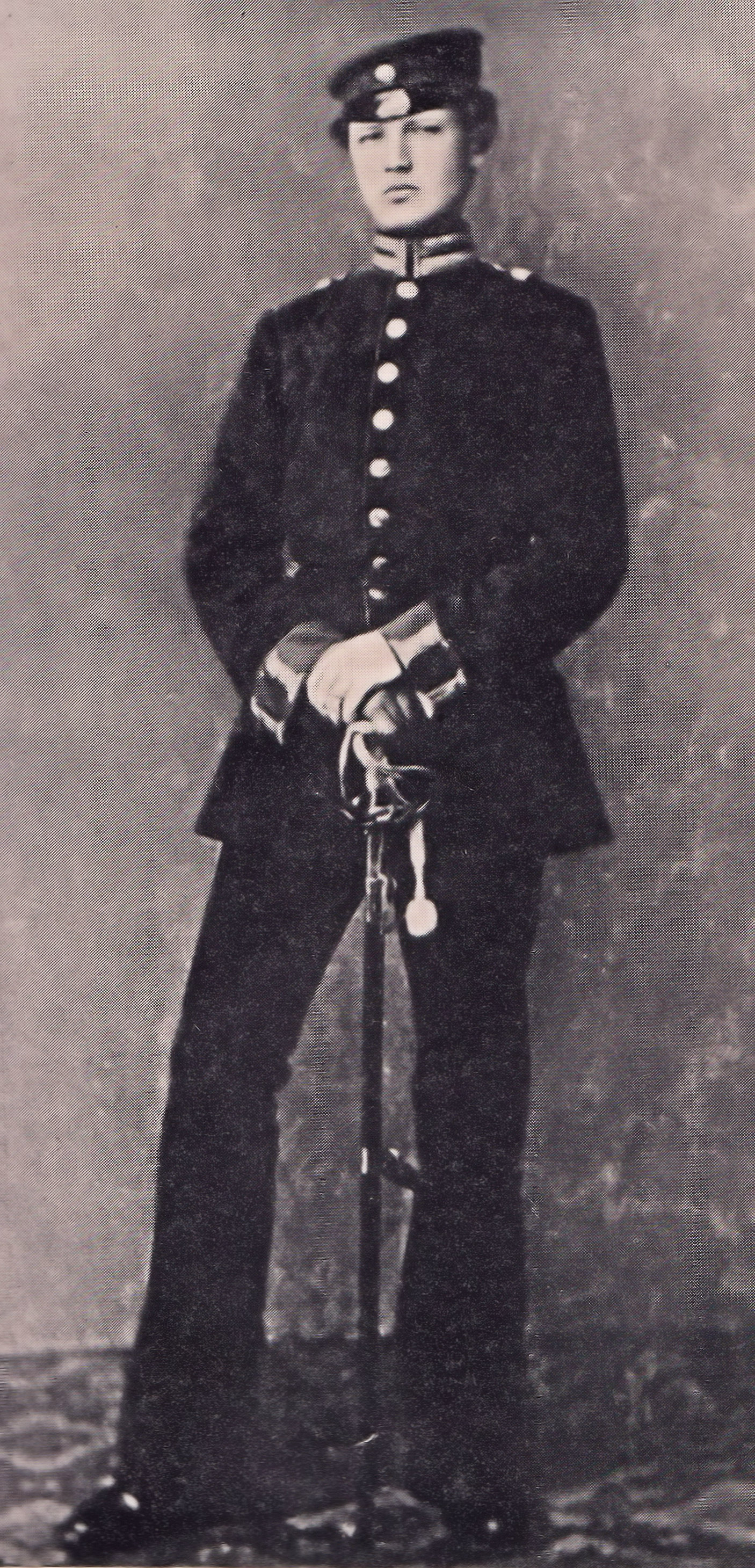
Paul Schulz
Paul Schulz (5 February 1898 – 31 August 1963) was a German military officer and Nazi Party official perhaps best known as a leader of the Black Reichswehr in the 1920s. Early years Schulz entered non-commissioned officers' school in Potsdam in 1912. Wounded several times in World War I, he was promoted to ''Leutnant'' in the spring of 1918 because of bravery and outstanding performance. After the end of the war Schulz joined the ''Freikorps''. He took part in the fighting in the Baltic States in a battalion commanded by Bruno Ernst Buchrucker. He became Buchrucker's adjutant in the ''Reichswehr'' and was promoted to ''Oberleutnant''. Because of their support for the Kapp ''Putsch'' in March 1920, Schulz and Buchrucker both were discharged from the army. Black ''Reichswehr'' Schulz was reinstated by the Ministry of the ''Reichswehr'' under private contract as part of the Black ''Reichswehr''. This was a paramilitary organization in the Weimar Republic that was used to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Schulze (other){{!}}Paul Schulze
Paul Schulze (born June 12, 1962) is an American actor. He is known for appearing in ''The Sopranos'', ''Nurse Jackie'', '' 24'' (2002–2004), and ''The Punisher'' (2017), and his films roles in ''Panic Room'' (2002), and ''Rambo'' (2008). Career He is best known for portraying Ryan Chappelle on the Fox series '' 24'' from 2001 to 2004 and Father Phil Intintola on the HBO series ''The Sopranos'' from 1999 to 2006. Schulze was featured on Fox's legal drama ''Justice'' and has guest-starred on ''Law & Order'', ''Rizzoli & Isles'', '' JAG'', '' CSI: Crime Scene Investigation'', ''The West Wing'', ''NCIS'', '' Oz'', ''Frasier'', ''NYPD Blue'', ''Boston Legal'', ''Cold Case'', ''Numb3rs'', ''Mad Men'', ''Criminal Minds'', ''The Closer'', '' Terminator: The Sarah Connor Chronicles'', '' Suits'', ''Z Nation'', and ''Journeyman''. He played William Rawlins in the Netflix series ''The Punisher'' in 2017. Film appearances include ''New Jersey Drive'' (1995), '' Clockers'' (1995), ''D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
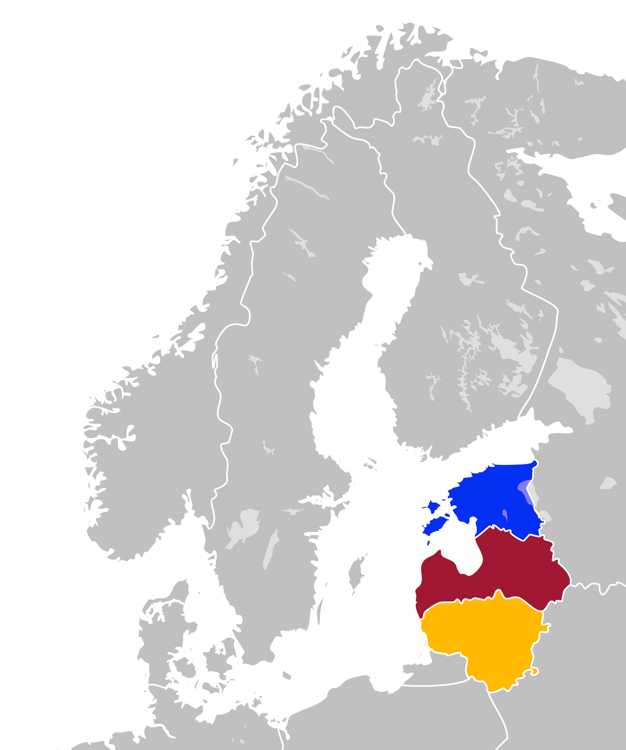
Baltic States
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. The term "Balticum" is sometimes used to describe the region comprising the three states; see e.g All three Baltic countries are classified as World Bank high-income economy, high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. Etymology The term ''Baltic'' stems from the name of the Baltic Sea – a hydronym dating back to at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is not a state of its own. It ranks as the 11th-largest city in the European Union. The metropolitan area has around 3 million inhabitants, and the broader Munich Metropolitan Region is home to about 6.2 million people. It is the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, third largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. Munich is located on the river Isar north of the Alps. It is the seat of the Upper Bavaria, Upper Bavarian administrative region. With 4,500 people per km2, Munich is Germany's most densely populated municipality. It is also the second-largest city in the Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect area after Vienna. The first record of Munich dates to 1158. The city ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag (Weimar Republic)
The Reichstag of the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) was the lower house of Germany's parliament; the upper house was the Reichsrat (Germany), Reichsrat, which represented the states. The Reichstag convened for the first time on 24 June 1920, taking over from the Weimar National Assembly, which had served as an interim parliament following the collapse of the German Empire in November 1918. Under the Weimar Constitution of 1919, the Reichstag was elected every four years by universal, equal, secret and direct suffrage, using a system of party-list proportional representation. All citizens who had reached the age of 20 were allowed to vote, including women for the first time, but excluding soldiers on active duty. The Reichstag voted on the laws of the Reich and was responsible for the budget, questions of war and peace, and confirmation of state treaties. Oversight of the Reich government (the ministers responsible for executing the laws) also resided with the Reichstag. It could f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregor Strasser
Gregor Strasser (also , see ß; 31 May 1892 – 30 June 1934) was a German politician and early leader of the Nazi Party. Along with his younger brother Otto, he was a leading member of the party's left-wing faction, which brought them into conflict with the dominant faction led by Adolf Hitler, resulting in his murder in 1934. The brothers' strand of the Nazi ideology is known as Strasserism. Born in Bavaria, Strasser served in an Imperial German Army artillery regiment during World War I, rising to the rank of first lieutenant and winning the Iron Cross of both classes for bravery. After the war, he and his brother became members of Franz Ritter von Epp's ''Freikorps''. He joined the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in 1920 and quickly became an influential and important figure in the fledgling party. In 1923, Strasser took part in the abortive Beer Hall Putsch in Munich and was imprisoned. After securing an early release following his election to the '' Reichstag'', he joined a revived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German military and political leader who led the Imperial German Army during the First World War and later became President of Germany (1919–1945), President of Germany from 1925 until his death in 1934. He played a key role in the Nazi seizure of power in 1933 when he appointed Adolf Hitler as Chancellor of Germany. Hindenburg was born to a family of minor Prussian nobility in the Grand Duchy of Posen. Upon completing his education as a cadet, he enlisted in the Third Regiment of Foot Guards as a second lieutenant. He saw combat during the Austro-Prussian War, Austro-Prussian and Franco-Prussian War, Franco-Prussian wars. In 1873, he was admitted to the prestigious Preußische Hauptkadettenanstalt, War Academy in Berlin, where he studied before being appointed to the General Staff Corps. In 1885, he was promoted to major and became a member of the German General Staff. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feme Murders
The Feme murders ( ) were extrajudicial killings that took place during the early years of the Weimar Republic. They were carried out primarily by far-right groups against individuals, often their own members, who were thought to have betrayed them. Due to their secretive nature, it is not known how many were killed in the Feme murders, which are most often considered a distinct category from political assassinations. The number may have been in the hundreds, although one source reports just 23 between 1920 and 1923 in Bavaria and the eastern states of East Prussia, Pomerania, Mecklenburg, Brandenburg and Upper Silesia. In spite of a number of investigations into the murders, few of the perpetrators were ever identified or prosecuted. The Feme murders had largely ended by 1924. Origin of the term (from Middle High German , meaning "punishment", and meaning "murder"), refers to an act of vigilante justice by a political group: the killing of "traitors" who knew about the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küstrin Putsch
The Küstrin Putsch of 1 October 1923, also known as the Buchrucker Putsch after its leader, was a coup attempt against the Weimar Republic by units of the paramilitary Black Reichswehr under Bruno Ernst Buchrucker. It was launched in response to nationalist anger over the government's decision to end passive resistance against the French and Belgian occupation of the Ruhr. It failed both in Berlin and in the eastern German town of Küstrin when the colonel in charge of the Küstrin Fortress detained Buchrucker and called in the Reichswehr. Buchrucker was convicted of treason and sentenced to prison but was amnestied after serving four years of the ten-year sentence. Background Groups from the Black Reichswehr called labor commandos () led by Bruno Ernst Buchrucker wanted to bring down the Reich government of Chancellor Gustav Stresemann and replace the parliamentary democratic republic with a national dictatorship. The putsch was prompted when on 26 September 1923 the governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrkreis
The military districts, also known in some English-language publications by their German name as Wehrkreise (singular: ''Wehrkreis''), were administrative territorial units in Nazi Germany before and during World War II. The task of military districts was the organization and the handling of reinforcements and resupplies for local military units. The Replacement Army (''Ersatzheer'') managed the districts. Responsibilities such as training, conscription, supply, and equipment were (at least partially) entrusted to the Ersatzheer. History On 30 September 1919, much of the Imperial German Army was dissolved. The Reichswehr (of the Weimar Republic) took its place, and four commands of the type '' Reichswehrgruppenkommando'' were created, as well as seven ''Wehrkreiskommando'' commands, each assigned to one of the seven initial Wehrkreise of the Weimar Republic (numbered I through VII). The ''Reichswehrgruppenkommandos'' (which combined under them several military units across Wehr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Versailles Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, and agreed certain principles and conditions including the payment of reparations, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. Germany was not allowed to participate in the negotiations before signing the treaty. The treaty required Germany to disarm, make territorial concessions, extradite alleged war criminals, agree to Kaiser Wilhelm being put on trial, recognise the independence of states whose territory had previously been part of the German Empire, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic. The period's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the republic was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" (a term introduced by Adolf Hitler in 1929) not commonly used until the 1930s. The Weimar Republic had a semi-presidential system. Toward the end of the First World War (1914–1918), Germany was exhausted and suing for peace, sued for peace in desperate circumstances. Awareness of imminent defeat sparked a German Revolution of 1918–1919, revolution, Abdication of Wilhelm II, the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, the proclamation of the Weimar Republic on 9 November 1918, and formal cessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |