|
Pasteurella Multocida
''Pasteurella multocida'' is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Strains of the species are currently classified into five serogroups (A, B, D, E, F) based on capsular composition and 16 somatic serovars (1–16). ''P. multocida'' is the cause of a range of diseases in mammals and birds, including fowl cholera in poultry, atrophic rhinitis in pigs, and bovine hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and buffalo. It can also cause a zoonotic infection in humans, which typically is a result of bites or scratches from domestic pets. Many mammals (including domestic cats and dogs) and birds harbor it as part of their normal respiratory microbiota. History ''Pasteurella multocida'' was first found in 1878 in cholera-infected birds. However, it was not isolated until 1880, by Louis Pasteur, in whose honor ''Pasteurella'' is named. Disease :''See: Pasteurellosis'' ''P. multocida'' causes a range of diseases in wild and domesticat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884. Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram-positive cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that retains the primary stain, crystal violet. Gram-negative cells have a thinner peptidoglycan layer that allows the crystal violet to wash out on addition of ethanol. They are stained pink or red by the counterstain, commonly safranin or fuchsine. Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to strengthen the bonds of the stain with the cell membrane. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the preliminary identification of a bacterial organism. While Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. Typically, the first infected human transmits the infectious agent to at least one other human, who, in turn, infects others. Major modern diseases such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Most strains of influenza that infect humans are human diseases, although many strains of bird flu and swine flu are zoonoses; these viruses occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 1918 Spanish flu or the 2009 swine flu. ''Taenia solium'' infection is one of the neglected tropical diseases with public health and veterinary concern in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula. Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infections (from minor causes such as the common cold and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS), autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting. Causes Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acute infection (''e.g.,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
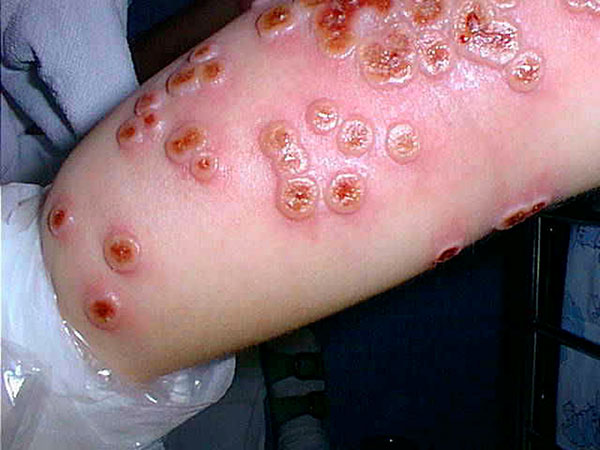
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired. The legs and face are the most common sites involved, although cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The leg is typically affected following a break in the skin. Other risk factors include obesity, leg swelling, and old age. For facial infections, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually the case. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci and ''Staphylococcus aureus''. In contrast to cellulitis, erysipelas is a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Normally, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukocyte
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes ( monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells ( myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saiga Antelope
The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a critically endangered antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in the southwest into Mongolia in the northeast and Dzungaria in the southeast. During the Pleistocene, they also occurred in Beringian North America and the British Isles. Today, the dominant subspecies (''S. t. tatarica'') is only found in one region in Russia (in the Republic of Kalmykia and he official la ... and Astrakhan Oblast) and three areas in Kazakhstan">Astrakhan Oblast">he official la ... and Astrakhan Oblast) and three areas in Kazakhstan (the Ural, Ustiurt, and Betpak-Dala populations). A portion of the Ustiurt population migrates south to Uzbekistan and occasionally Turkmenistan in winter. It is extirpated from China, Ukraine, and southwestern Mongolia. The Mongolian subspecies (''S. t. mongolica'') is found only in western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Respiratory Disease
Bovine respiratory disease (BRD) is the most common and costly disease affecting beef cattle in the world. It is a complex, bacterial or viral infection that causes pneumonia in calves which can be fatal. The infection is usually a sum of three codependent factors: stress, an underlying viral infection, and a new bacterial infection. The diagnosis of the disease is complex since there are multiple possible causes. The disease manifests itself most often in calves within four weeks of weaning, when calves are sorted and often sold to different farms; a common nickname for BRD is "shipping fever." It is not known whether the stress itself, co-mingling, or travel conditions are at most to blame, and while studies have identified general stressing factors like transport and cold weather conditions, there is still no conclusive evidence on more specific factors (e.g. distance, transport mode, temperature, or temperature volatility). Causes BRD is a "multi-factorial syndrome" that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, a poor ability to cough (such as following a stroke), and a weak immune system. Vaccine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or Body of water, water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide. Wetlands occur naturally on every continent. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main wetland typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
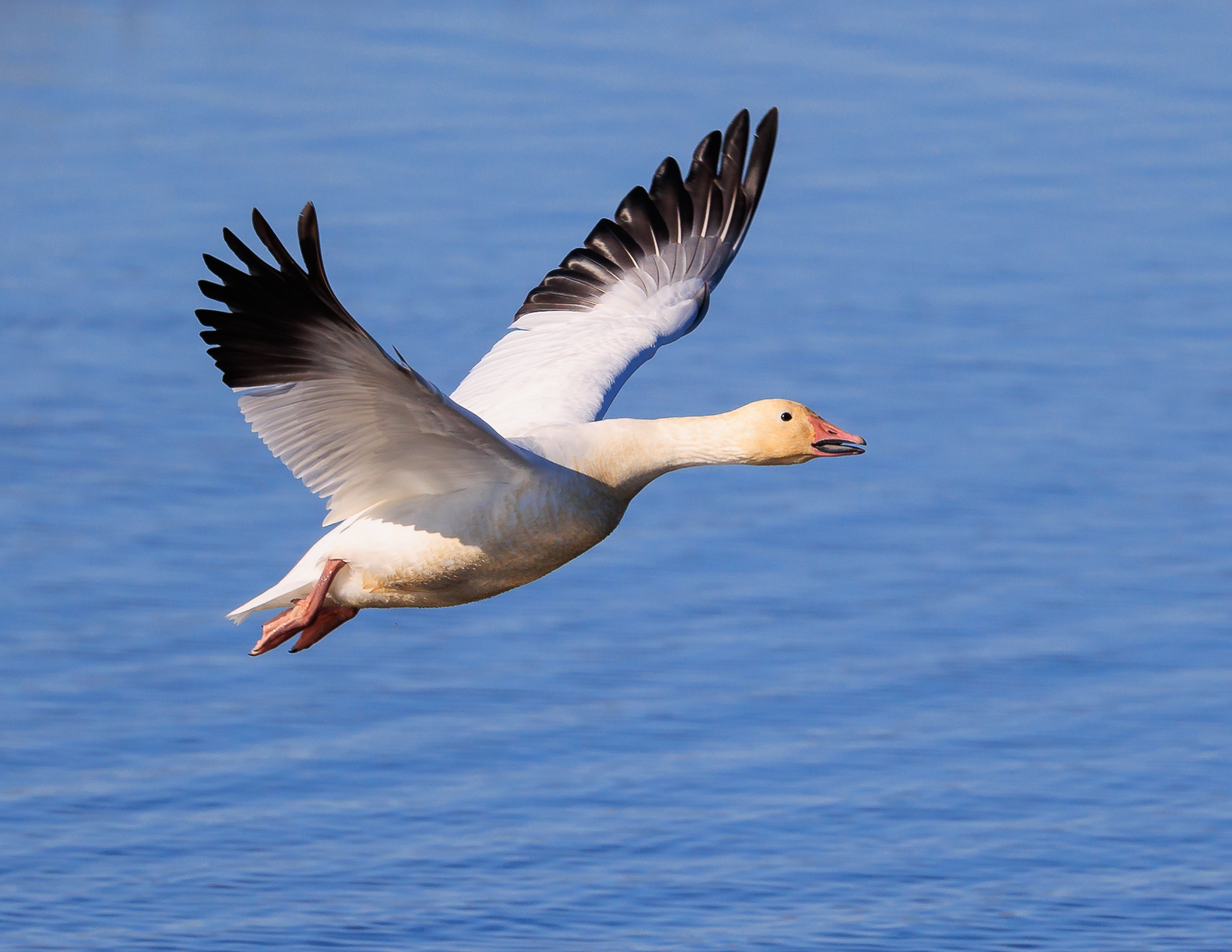
Snow Goose
The snow goose (''Anser caerulescens'') is a species of goose native to North America. Both white and dark morphs exist, the latter often known as blue goose. Its name derives from the typically white plumage. The species was previously placed in the genus ''Chen'', but is now typically included in the "gray goose" genus ''Anser''. Snow geese breed north of the timberline in Greenland, Canada, Alaska, and the northeastern tip of Siberia, and spend winters in warm parts of North America from southwestern British Columbia through parts of the United States to Mexico. Snow goose populations increased dramatically in the 20th century. Taxonomy In 1750 the English naturalist George Edwards included an illustration and a description of the snow goose in the third volume of his ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. He used the English name "The blue-winged goose". Edwards based his hand-coloured etching on a preserved specimen that had been brought to London from the Hudson Bay a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Zoonosis
A feline zoonosis is a viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, nematode or arthropod infection that can be transmitted to humans from the domesticated cat, ''Felis catus''. Some of these diseases are reemerging and newly emerging infections or infestations caused by zoonotic pathogens transmitted by cats. In some instances, the cat can display symptoms of infection (these may differ from the symptoms in humans) and sometimes the cat remains asymptomatic. There can be serious illnesses and clinical manifestations in people who become infected. This is dependent on the immune status and age of the person. Those who live in close association with cats are more prone to these infections. But those that do not keep cats as pets are also able to acquire these infections because of the transmission can be from cat feces and the parasites that leave their bodies. People can acquire cat-associated infections through bites, scratches or other direct contact of the skin or mucous membranes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |