Lymphadenopathy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a
 In cervical lymphadenopathy (of the
In cervical lymphadenopathy (of the
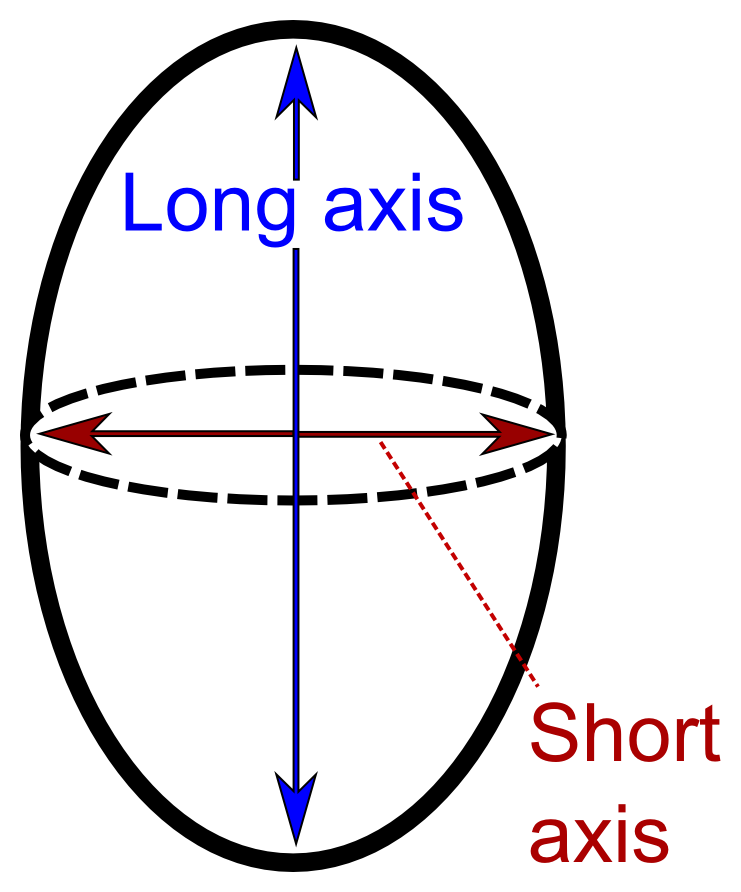
 * By size, where lymphadenopathy in adults is often defined as a short axis of one or more lymph nodes is greater than 10mm. However, there is regional variation as detailed in this table:
Lymphadenopathy of the axillary lymph nodes can be defined as solid nodes measuring more than 15 mm without fatty hilum.Page 559
* By size, where lymphadenopathy in adults is often defined as a short axis of one or more lymph nodes is greater than 10mm. However, there is regional variation as detailed in this table:
Lymphadenopathy of the axillary lymph nodes can be defined as solid nodes measuring more than 15 mm without fatty hilum.Page 559
in: Axillary lymph nodes may be normal up to 30 mm if consisting largely of fat. In children, a short axis of 8 mm can be used. However, inguinal lymph nodes of up to 15 mm and cervical lymph nodes of up to 20 mm are generally normal in children up to age 8–12. Last checked: 24 March 2014 Lymphadenopathy of more than 1.5–2 cm increases the risk of
HPC:13820
on humpath.com (Digital slides) {{Bacterial cutaneous infections Cytopathology Inflammations Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
ous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
s is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula.
Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s (from minor causes such as the common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
), autoimmune diseases, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting.
Causes
Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acuteinfection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
(e.g., bacterial, or viral), or chronic infections ( tuberculous lymphadenitis, cat-scratch disease).
** The most distinctive sign of bubonic plague is extreme swelling of one or more lymph nodes that bulge out of the skin as "buboes". The buboes often become necrotic and may even rupture.
** Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adu ...
is an acute viral infection usually caused by Epstein-Barr virus and may be characterized by a marked enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes.
** It is also a sign of cutaneous anthrax and human African trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma bru ...
** Toxoplasmosis, a parasitic disease, gives a generalized lymphadenopathy (''Piringer-Kuchinka lymphadenopathy'').
** Plasma cell variant of Castleman's disease - associated with HHV-8 infection and HIV infection
** Mesenteric lymphadenitis after viral systemic infection (particularly in the GALT in the appendix) can commonly present like appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the Appendix (anatomy), appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and anorexia (symptom), decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these t ...
.
Infectious causes of lymphadenopathy may include bacterial infections such as cat scratch disease, tularemia, brucellosis
Brucellosis is a zoonosis spread primarily via ingestion of raw milk, unpasteurized milk from infected animals. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.
The bacteria causing this disease, ''Brucella'', are small ...
, or prevotella, as well as fungal infections such as paracoccidioidomycosis.
* Tumoral:
** Primary: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma give lymphadenopathy in all or a few lymph nodes.Status and anamnesis, Anders Albinsson. Page 12
** Secondary: metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
, Virchow's node, neuroblastoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. In CLL, the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to colle ...
.
* Autoimmune: systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
may have a generalized lymphadenopathy.
* Immunocompromised: AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
. Generalized lymphadenopathy is an early sign of infection with human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of th ...
(HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). "Lymphadenopathy syndrome" has been used to describe the first symptomatic stage of HIV progression, preceding a diagnosis of AIDS.
* Bites from certain venomous snakes such as the pit viper
The Crotalinae, commonly known as pit vipers,Mehrtens JM (1987). ''Living Snakes of the World in Color''. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. . or pit adders, are a subfamily (biology), subfamily of Viperidae, vipers found in Asia and the ...
* Unknown: Kikuchi disease, progressive transformation of germinal centers, sarcoidosis, hyaline-vascular variant of Castleman's disease, Rosai-Dorfman disease, Kawasaki disease, Kimura disease
Benign (reactive) lymphadenopathy
lymphadenopathy is a common biopsy finding, and may often be confused with malignant lymphoma. It may be separated into major morphologic patterns, each with its owndifferential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to di ...
with certain types of lymphoma. Most cases of reactive follicular hyperplasia are easy to diagnose, but some cases may be confused with follicular lymphoma. There are seven distinct patterns of benign lymphadenopathy:
* Follicular hyperplasia: This is the most common type of reactive lymphadenopathy.
* Paracortical hyperplasia/ Interfollicular hyperplasia: It is seen in viral infections, skin diseases, and nonspecific reactions.
* Sinus histiocytosis: It is seen in lymph nodes draining limbs, inflammatory lesions, and malignancies.
* Nodal extensive necrosis
* Nodal granulomatous inflammation
* Nodal extensive fibrosis (Connective tissue framework)
* Nodal deposition of interstitial substance
These morphological patterns are never pure. Thus, reactive follicular hyperplasia can have a component of paracortical hyperplasia. However, this distinction is important for the differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to di ...
of the cause.
Diagnosis
 In cervical lymphadenopathy (of the
In cervical lymphadenopathy (of the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
), it is routine to perform a throat examination including the use of a mirror
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera ...
and an endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern ...
.
On ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
, B-mode imaging depicts lymph node morphology, whilst power Doppler can assess the vascular pattern. B-mode imaging features that can distinguish metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
and lymphoma include size, shape, calcification, loss of hilar architecture, as well as intranodal necrosis. Soft tissue edema and nodal matting on B-mode imaging suggests tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis or previous radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
. Serial monitoring of nodal size and vascularity are useful in assessing treatment response.
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has sensitivity and specificity percentages of 81% and 100%, respectively, in the histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopatholog ...
of malignant cervical lymphadenopathy. PET-CT has proven to be helpful in identifying occult primary carcinomas of the head and neck, especially when applied as a guiding tool prior to panendoscopy, and may induce treatment related clinical decisions in up to 60% of cases.
Classification
Lymphadenopathy may be classified by: * Size, where lymphadenopathy in adults is often defined as a short axis of one or more lymph nodes is greater than 10mm. * By extent: ** ''Localized lymphadenopathy'': due to localized spot of infection; e.g., an infected spot on the scalp will cause lymph nodes in the neck on that same side to swell up ** Generalized lymphadenopathy: due to a systemic infection of the body; e.g., influenza or secondarysyphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
*** Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy
Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PGL) is enlarged, painless, non-tender lymph nodes occurring in a couple of different areas for more than three to six months for which no other reason can be found. To expand, the common site where PGL occur ...
(PGL): persisting for a long time, possibly without an apparent cause
* By localization:
** Hilar lymphadenopathy.
** Mediastinal lymphadenopathy
** Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
* Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy: lymphadenopathy associated with skin disease.
* By malignancy: Benign lymphadenopathy is distinguished from malignant types which mainly refer to lymphomas or lymph node metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
.
Size

 * By size, where lymphadenopathy in adults is often defined as a short axis of one or more lymph nodes is greater than 10mm. However, there is regional variation as detailed in this table:
Lymphadenopathy of the axillary lymph nodes can be defined as solid nodes measuring more than 15 mm without fatty hilum.Page 559
* By size, where lymphadenopathy in adults is often defined as a short axis of one or more lymph nodes is greater than 10mm. However, there is regional variation as detailed in this table:
Lymphadenopathy of the axillary lymph nodes can be defined as solid nodes measuring more than 15 mm without fatty hilum.Page 559in: Axillary lymph nodes may be normal up to 30 mm if consisting largely of fat. In children, a short axis of 8 mm can be used. However, inguinal lymph nodes of up to 15 mm and cervical lymph nodes of up to 20 mm are generally normal in children up to age 8–12. Last checked: 24 March 2014 Lymphadenopathy of more than 1.5–2 cm increases the risk of
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
or granulomatous disease as the cause rather than only inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
or infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
. Still, an increasing size and persistence over time are more indicative of cancer.
See also
* Adenitis * Lymphovascular invasionReferences
External links
HPC:13820
on humpath.com (Digital slides) {{Bacterial cutaneous infections Cytopathology Inflammations Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes