|
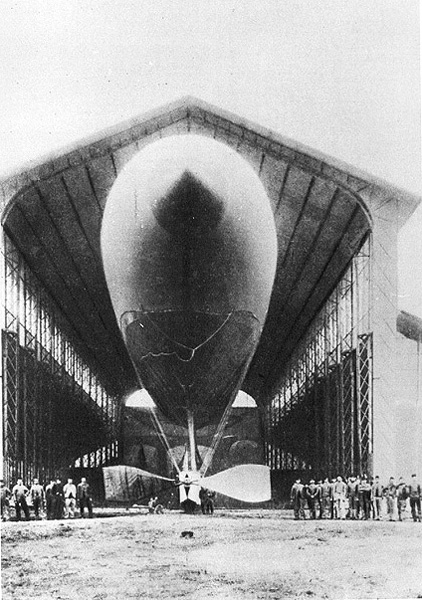
Parseval-Sigsfeld Kite Balloon
The Parseval-Sigsfeld kite balloon (German: ''Parseval-Sigsfeld Drachenballon'') was a type of non-rigid military observation balloon, designed in 1898 by August von Parseval and . Its aerodynamic shape and the rear air capsule ensured a stable position owing to the force of the wind, similar to the way in which kites are stabilized; for this reason it was known as the kite balloon (German: ''Drachenballon''). This aircraft was widely used as the main observation balloon type by the Central Powers during World War I. Design German airship factory owner, August von Parseval, and German military officer, Hans Bartsch von Sigsfeld, had been experimenting with different balloon shapes since 1893, previously using spherical shapes that had proved to be unstable in windy weather. Around 1898 they constructed a balloon with an elongated shape, equipped with stabilizers, which were later replaced by suitably shaped air chambers. Under the pressure of the wind (the permissible s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Équancourt
Équancourt () is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. INSEE Geography Équancourt is situated on the D58 road, some northwest of Saint-Quentin.Population See also *Communes of the Somme department
The following is a list of the 771 communes of the Somme department of France.
The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caquot Kite Balloon
Caquot kite balloon (in French language, French ''Caquot Captif'') was a type of non-rigid military observation balloon, designed in 1915 by Albert Caquot. The type became widely used by Allied forces in World War I , World War I warfare for multiple observation or naval defence uses and later also as a Anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft barrage balloon. Design At the beginning of World War I French Army headquarters quickly realized a need of observation balloon units, which has been dismantled in 1912. German army used their successful Parseval-Sigsfeld kite balloons (or ''Drachen'') in large quantities, so the first French-produced pieces were produced as a copies of a German original. Being mobilized on 1 August 1914 as a commander of the 21st company of balloonists, French officer Albert Caquot made some aerial observations in a spherical "Fleurus" type balloon, a type dating from 1880s. To balance a balloon dangling even in light winds Caquot designed a new balloon type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rzeczpospolita
() is a traditional Polish term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "rzeczpospolita", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage" "thing, matter" and "common" is analogous to the Latin ''rēs pūblica'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in English also rendered as '' commonwealth'' (historic) and ''republic'' (current). In modern Polish, the word is used exclusively in relation to the Republic of Poland, while any other republic is referred to in Polish as a (e.g. Italian Republic – ). Origins The term has been used in Poland since the beginning of the 16th century. It was adapted for Poland, as it at that time had a unique republican system, similar to the former Roman . The famous quote by Jan Zamoyski, the Lord Chancellor of the Crown, on the importance of education is an example of its use: The meaning of is well described by the term '' commonwealth''. As a result, the literal meaning of is "Polish Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
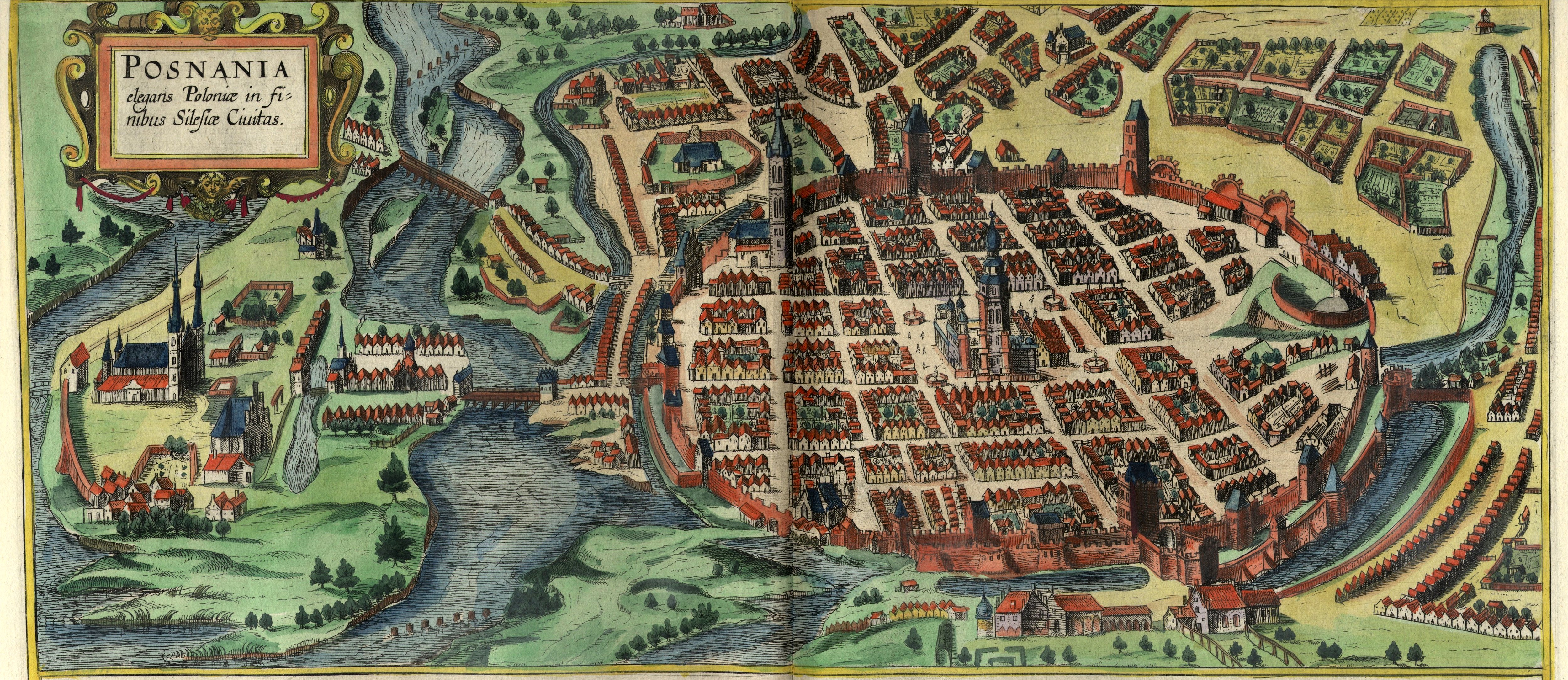
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winogrady
Winogrady is a part of the Stare Miasto district of the city of Poznań in western Poland. It is situated north of the ''Cytadela'' park (the former Poznań citadel). The name refers to the vineyards which formerly existed in the area – historically there were two villages there called Winiary (although "Winiary" today refers to a neighbourhood in Jeżyce district, to which the inhabitants were moved when the citadel fortifications were built in the 1830s). The southern part of Winogrady, between the streets ''ul. Winogrady'' and ''ul. Słowiańska'', consists mainly of houses, although there are also some apartment blocks (including the "Batman" development, named for its black colour) and student halls of residence. North of this is an area which consists of large estates of apartment blocks, mostly built from pre-fabricated concrete panels from 1968 onwards. Most of these blocks and the estate infrastructure belong to the PSM Winogrady ''(Poznańska Spółdzielnia Mieszka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army, also known as the Imperial and Royal Army,; was the principal ground force of Austria-Hungary from 1867 to 1918. It consisted of three organisations: the Common Army (, recruited from all parts of Austria-Hungary), the Imperial-Royal Landwehr (recruited from Cisleithania) and the Royal Hungarian Honvéd (recruited from Transleithania). In the wake of fighting between the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary and the subsequent two decades of uneasy co-existence, Hungarian troops served either in ethnically mixed units or were stationed away from Hungarian regions. With the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the Austro-Hungarian Army was brought into being. It existed until the disestablishment of Austria-Hungary in 1918 following the end of World War I. Common Army units were generally poorly trained and had very limited access to new equipment, because the governments of the Austrian and Hungarian parts of the empire often preferred to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballonet
A ballonet is an inflatable bag inside the outer envelope of an airship which, when inflated, reduces the volume available for the lifting gas, making it more dense. Because air is also denser than the lifting gas, inflating the ballonet reduces the overall lift, while deflating it increases lift. In this way, the ballonet can be used to adjust the lift as required. Ballonets may typically be used in non-rigid or semi-rigid airships, commonly with multiple ballonets located both fore and aft to maintain balance and to control the pitch of the airship. The image illustrates the principle of a balloon within a balloon. The outer balloon represents the airship's outer envelope or gasbag, while the red inner balloon represents the ballonet. In an airship the ballonet would be much smaller relative to the size of the gasbag; for example, in the French airship Lebaudy Patrie the volume of the ballonet was approximately one-fifth that of the envelope. History The ballonet was fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phallic
A phallus (: phalli or phalluses) is a penis (especially when erect), an object that resembles a penis, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. In art history, a figure with an erect penis is described as ''ithyphallic''. Any object that symbolically—or, more precisely, iconically—resembles a penis may also be referred to as a phallus; however, such objects are more often referred to as being phallic (as in "phallic symbol"). Such symbols often represent fertility and cultural implications that are associated with the male sexual organ, as well as the male orgasm. Etymology The term is a loanword from Latin ''phallus'', itself borrowed from Greek (''phallos''), which is ultimately a derivation from the Proto-Indo-European root *''bʰel''- "to inflate, swell". Compare with Old Norse (and modern Icelandic) ''boli'', "bull", Old English ''bulluc'', "bullock", Greek , "whale". Archaeology The Hohle phallus, a 28,000-year-old siltstone phallus discovered in the Hohle Fels c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria; this was also known as the Quadruple Alliance., , , The Central Powers' origin was the Dual Alliance (1879), alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary in 1879. Despite having nominally joined the Triple Alliance (1882), Triple Alliance before, Kingdom of Italy, Italy did not take part in World War I on the side of the Central Powers and later joined on the side of the Allies of World War I, Allies. The Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria did not join until after World War I had begun. The Central Powers faced, and were defeated by, the Allied Powers, which themselves had formed around the Triple Entente. They dissolved in 1918 after they lost the war. Name The name 'Central Powers' is derived from the location of its member countries. All f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Riedinger
August Riedinger (9 October 1845 – 15 January 1919) Augsburg city archive was a German businessman who operated gas companies in Germany and Europe and also participated in balloon and airship manufacturing. Life Riedinger was born in 1845 as the son of the industrialist Ludwig August Riedinger in Augsburg. After six years of studies at the Zurich Polytechnic he entered his father's machinery and bronzeworks business in 1877. Richard Winkler page 574 His father died in 1879 Vogt, Wilhelm when the business had 25 gasworks in Bavaria, and another 42 in the rest of Europe and a number of gas plants for factories and public buildings. L. A. Riedinger Augsburg In 1883 Riedinger took over the business and in 1887 when the company converted to the Joint stock company , he became a member of its supervisory board. By then he had already founded the (AG United Gasworks) in Augsburg which by 1896 had grown to 17 gas work companies, for example in Bolzano, Lugano and Marburg.Frà ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |