|
Paolo Zamboni
Paolo Zamboni (born 25 March 1957, Ferrara, Italy) is an Italians, Italian doctor and scientist. He is full Professor and Director of the School of Vascular Surgery at the University of Ferrara in Italy. He is known for his description and proposed cure of the vascular disease chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency (CCSVI) strongly related with multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases such as Ménière's disease, Ménière and Parkinson's disease, Parkinson's, but the existence of this disease is very controversial, with significantly more detractors than supporters, and there is no good evidence that the surgery helps MS patients. Biography Graduated with honors in Medicine and Surgery in 1982, Zamboni specialized in General Surgery in 1987 and in Vascular Surgery 1992. In 1992 he obtained the fellowship at the Department of Vascular Surgery of the University of California in San Francisco. From 1993 to 2000 he was visiting professor at the Department of Sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrara
Ferrara (; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Emilia-Romagna, Northern Italy, capital of the province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream of the Po (river), Po River, located north. The town has broad streets and numerous palaces dating from the Renaissance, when it hosted the court of the House of Este. For its beauty and cultural importance, it has been designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. History Antiquity and Middle Ages The first documented settlements in the area of the present-day Province of Ferrara date from the 6th century BC. The ruins of the Etruscan civilization, Etruscan town of Spina, established along the lagoons at the ancient mouth of Po river, were lost until modern times, when drainage schemes in the Valli di Comacchio marshes in 1922 first officially revealed a necropolis with over 4,000 tombs, evidence of a population centre that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHIVA Method
CHIVA method is a type of surgery used to treat varicose veins that occur as a result of long term venous insufficiency. The term is a French acronym for Conservatrice Hémodynamique de l'Insuffisance Veineuse en Ambulatoire (ambulatory conservative hemodynamic treatment venous insufficiency). The method is based on the assumption that the symptoms of varicose veins are mainly the expression of an hemodynamic circulatory disorder, induced by various venous system malfunctions. CHIVA attempts to improve symptoms and signs without destroying the veins which remain available for vascular by pass. A very detailed free PDF document on the principles of the CHIVA method is available online Venous insufficiency of the pelvis and lower limbs __TOC__ Procedure CHIVA involves Doppler ultrasonography to assess the hemodynamics Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition characterized by blood pooling in the veins, leading to increased pressure and strain on the vein walls. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux, which often results in the formation of varicose veins, a treatable condition. Since functional venous valves are necessary to facilitate efficient Venous return, blood return from the lower extremities, CVI primarily affects the legs. When impaired vein function leads to significant symptoms such as oedema (swelling) or venous ulcer formation, the condition is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is also known as ''chronic peripheral venous insufficiency'' and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome, a separate condition caused by damage to the deep veins following deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Most cases of CVI can be managed or improved through treatments targeting the superficial venous system or stenting the deep venous system. For instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
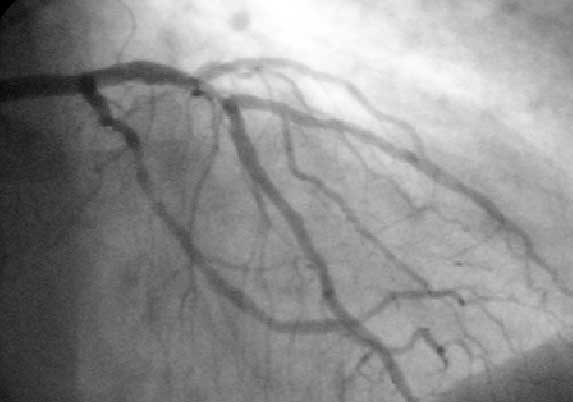
Balloon Angioplasty
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter (a balloon catheter) is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously. Uses and indications Coronary angioplasty A coronary angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure to treat the stenotic (narrowed) coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary heart disease. These stenotic segments of the corona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Control
A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable (i.e. confounding variables). This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method. Controlled experiments Controls eliminate alternate explanations of experimental results, especially experimental errors and experimenter bias. Many controls are specific to the type of experiment being performed, as in the molecular markers used in SDS-PAGE experiments, and may simply have the purpose of ensuring that the equipment is working properly. The selection and use of proper controls to ensure that experimental results are valid (for example, absence of confounding variables) can be very difficult. Control measurements may also be used for other purposes: for example, a measurement of a microphone's background noise in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blind Experiment
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expectations, observer's effect on the participants, observer bias, confirmation bias, and other sources. A blind can be imposed on any participant of an experiment, including subjects, researchers, technicians, data analysts, and evaluators. In some cases, while blinding would be useful, it is impossible or unethical. For example, it is not possible to blind a patient to their treatment in a physical therapy intervention. A good clinical protocol ensures that blinding is as effective as possible within ethical and practical constraints. During the course of an experiment, a participant becomes unblinded if they deduce or otherwise obtain information that has been masked to them. For example, a patient who experiences a side effect may co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thieme Medical Publishers
Thieme Medical Publishers is a German academic publishing, medical and science publisher in the Thieme Publishing Group. It produces professional journals, textbooks, atlases, monographs and reference books in both German and English covering a variety of medical specialties, including neurosurgery, orthopaedics, endocrinology, urology, radiology, anatomy, chemistry, otolaryngology, ophthalmology, audiology and speech-language pathology, complementary medicine, complementary and alternative medicine. Thieme has more than 1,000 employees and maintains offices in seven cities worldwide, including New York City, Beijing, Delhi, Stuttgart, and three other cities in Germany. History Georg Thieme Verlag was founded in 1886 in Leipzig, Germany, by Georg Thieme when he was 26 years old. Thieme remains privately held and family-owned. The company received some early success in 1896 by publishing Wilhelm Röntgen's famous picture of his wife's hand in what is still one of Thieme's and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Medicine
An experimental drug is a medicinal product (a drug or vaccine) that has not yet received approval from governmental regulatory authorities for routine use in human or veterinary medicine. A medicinal product may be approved for use in one disease or condition but still be considered experimental for other diseases or conditions. United States In the United States, the body responsible for approval is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which must grant the substance Investigational New Drug (IND) status before it can be tested in human clinical trials. IND status requires the drug's sponsor to submit an IND application that includes data from laboratory and animal testing for safety and efficacy. A drug that is made from a living organism or its products undergoes the same approval process but is called a biologics license application (BLA). Biological drugs include antibodies, interleukins, and vaccines. In 2018 federal " Right to Try" laws were enacted in the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |