|
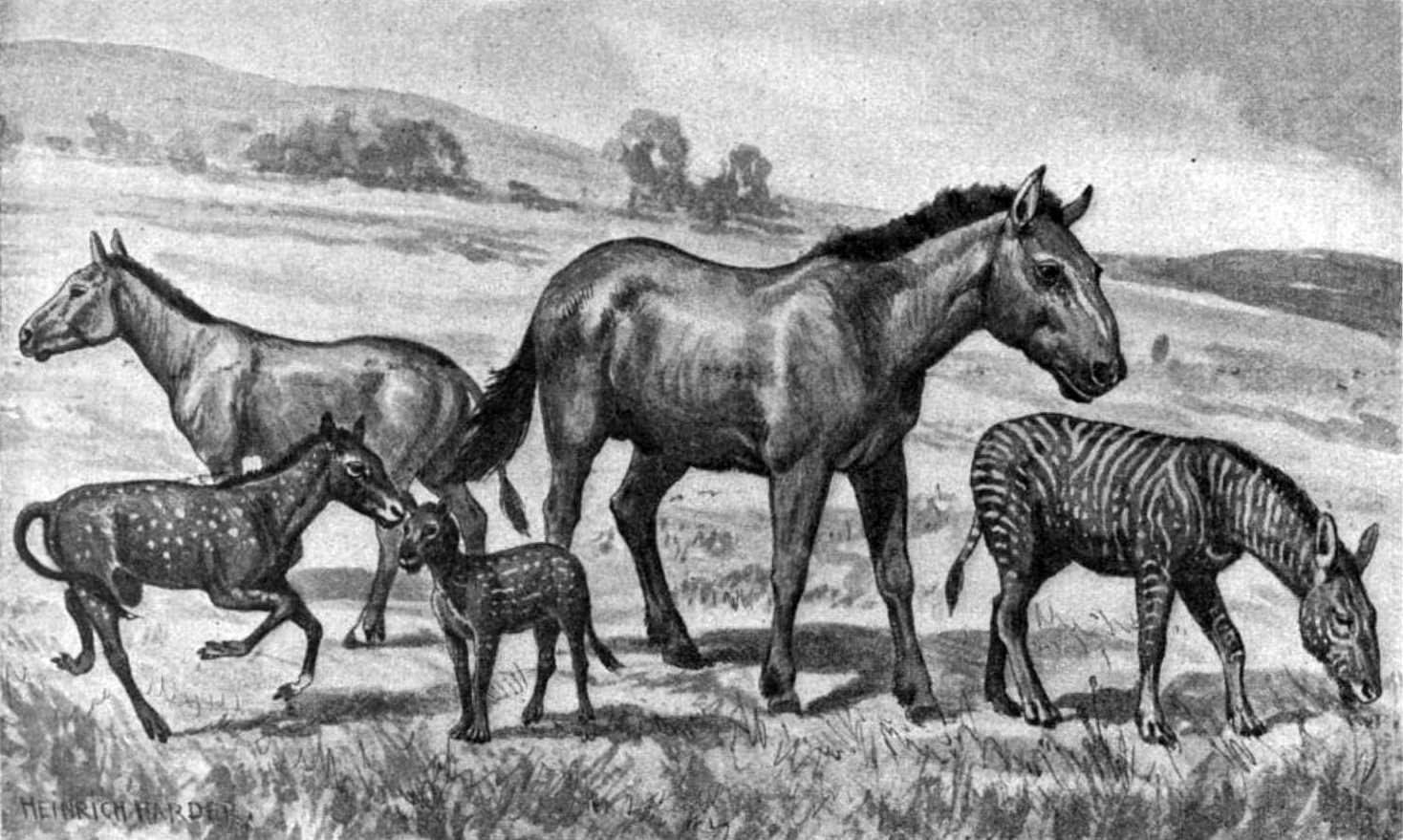
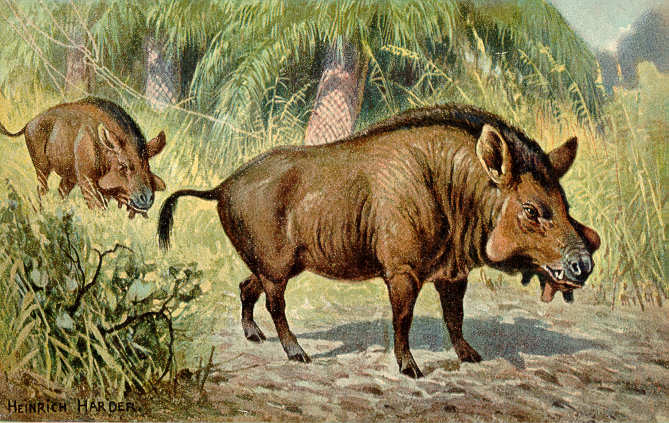
Paleotherium Magnum
''Palaeotherium'' is an extinct genus of equoid that lived in Europe and possibly the Middle East from the Middle Eocene to the Early Oligocene. It is the type genus of the Palaeotheriidae, a group exclusive to the Palaeogene that was closest in relation to the Equidae, which contains horses plus their closest relatives and ancestors. Fossils of ''Palaeotherium'' were first described in 1782 by the French naturalist Robert de Lamanon and then closely studied by another French naturalist, Georges Cuvier, after 1798. Cuvier erected the genus in 1804 and recognized multiple species based on overall fossil sizes and forms. As one of the first fossil genera to be recognized with official taxonomic authority, it is recognized as an important milestone within the field of palaeontology. The research by early naturalists on ''Palaeotherium'' contributed to the developing ideas of evolution, extinction, and succession and demonstrating the morphological diversity of different species withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Aymard
Auguste Aymard (5 December 1808 – 26 June 1889) was a French prehistorian and palaeontologist who lived and died in Puy-en-Velay (Haute-Loire). He described the fossil '' Entelodon magnus'' and the fossil genera ''Anancus ''Anancus'' is an extinct genus of "tetralophodont gomphothere" native to Afro-Eurasia, that lived from the Tortonian stage of the late Miocene until its extinction during the Early Pleistocene, roughly from 8.5–2 million years ago. Taxonomy ...'' and '' Amphechinus''. Auguste Aymard was the archivist for the Departement Haute-Loire and Conservateur of Musée du Puy-en-Velay. He made archaeological discoveries in Puy-en-Velay, Polignac, Haute-Loire and Espaly-Saint-Marcel. Works * Aymard, A., 1848, Essai monographique sur un nouveau genre de Mammifère fossile trouvé dans la Haute-Loire, et nommé Entélodon, ''Annales de la Société d’Agriculture Sciences, Arts et Commerce du Puy'', Vol.12, 1848, pp. 227–268 * Aymard, A. 1854, Acquisit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils. Cuvier's work is considered the foundation of vertebrate paleontology, and he expanded Linnaean taxonomy by grouping classes into phylum, phyla and incorporating both fossils and living species into the classification. Cuvier is also known for establishing extinction as a fact—at the time, extinction was considered by many of Cuvier's contemporaries to be merely controversial speculation. In his ''Essay on the Theory of the Earth'' (1813) Cuvier proposed that now-extinct species had been wiped out by periodic catastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert De Lamanon
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, '' Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE in Central Asia, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, which are horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidae
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of Wild horse, horses and related animals, including Asinus, asses, zebra, zebras, and many extinct species known only from fossils. The family evolved more than 50 million years ago, in the Eocene epoch, from a small, multi-toed ungulate into larger, single-toed animals. All Extant taxon, extant species are in the genus ''Equus (genus), Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. It is more specifically grouped within the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Equoidea, the only other family being the extinct Palaeotheriidae. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equinae, equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeotheriidae
Palaeotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous perissodactyl mammals that inhabited Europe, with less abundant remains also known from Asia, from the mid-Eocene to the early Oligocene. They are classified in Equoidea, along with the living family Equidae (which includes zebras, horses and asses). Morphology Palaeotheres ranged widely in size, from small species like '' Palaeotherium lautricense,'' which is estimated to have only weighed to large species like '' Palaeotherium magnum'', which are comparable in size to living equines, with body masses over . Their teeth are brachydont (low crowned). According to Danilo et al. 2013., paleotheriids are distinguished from other equoids by one unambiguous synapomorphy "the nasal notch opening distally to the canine, above the postcanine diastema" and two unambiguous character state changes "an average metaconule on he fourth premolar and "an oblique metastyle on he first and second molars. Taxonomy Palaeotheriidae is ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Genus
In biological taxonomy, the type genus (''genus typica'') is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name. Zoological nomenclature According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal family-group taxon is a nominal genus called the 'type genus'; the family-group name is based upon that of the type genus." Any family-group name must have a type genus (and any genus-group name must have a type species, but any species-group name may, but need not, have one or more type specimens). The type genus for a family-group name is also the genus that provided the stem to which was added the ending -idae (for families). :Example: The family name Formicidae has as its type genus the genus ''Formica'' Linnaeus, 1758. Botanical nomenclature In botanical nomenclature, the phrase "type genus" is used, unofficially, as a term of convenience. In the '' ICN'' this phrase has no status. The code uses type specimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equoidea
Equoidea is a superfamily of hippomorph perissodactyls containing the Equidae, Palaeotheriidae, and other basal equoids of unclear affinities, of which members of the genus '' Equus'' are the only extant species. The earliest fossil record of the Equoidea proves unclear, but they possibly could have originated during the late Paleocene in Europe or Asia. Definite fossil records of equoids are recorded by the earliest Eocene, in which the earliest equids in North America and basal equoids of unclear affinities in Europe both appeared. Palaeotheres are thought to have originated later in the early Eocene of Europe, although some researchers disagree on whether the subfamily Pachynolophinae belongs to the Palaeotheriidae. Equoids may in part be defined by dental synapomorphies from its molars The molars or molar teeth are large, flat tooth, teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammal, mammals. They are used primarily to comminution, grind food during mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Toussaint Marcel De Serres De Mesplès
Pierre Toussaint Marcel de Serres de Mesplès (3 November 1780 – 22 July 1862 in Montpellier), also known as Marcel de Serres, was a French caver, geologist and naturalist. Biography Professor of mineralogy and geology in the faculty of science at Montpellier University from 1809. He occupied this university chair for 53 years. His professional interests included the human and animal fossils of the caves of the south of France. At his end, he contributed to the French state a large number of fossils of the region Languedoc. He was contemporary with Cuvier (either ''Frédéric'' or '' Georges'' ).MEMOIR ON THE QUESTION – WHETHER ANY LAND MAMMALS HAVE CEASED TO EXIST SINCE MAN'S FORMATION; AND WHETHER MAN HAS BEEN CONTEMPORAOUS WITH SPECIES NOW LOST OR APPEARING NO LONGER TO HAVE REPRESENTATIVES ON THE EARTH ? (pp. 160–175 and 285–289 of Robert Jameson, Royal Society of Edinburgh, Wernerian Natural History Society – The Edinburgh New Philosophical Journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Ruetimeyer
(Karl) Ludwig Rütimeyer (26 February 1825 in Biglen, Canton of Bern – 25 November 1895 in Basel) was a Swiss zoologist, anatomist and paleontologist, who is considered one of the fathers of zooarchaeology. Career Rütimeyer studied at the University of Bern. He began his studies in theology before switching to medicine.Hopwood, Nick. (2015). ''Haeckel's Embryos: Images, Evolution, and Fraud''. University of Chicago Press. p. 92. Additional studies in Paris, London, and Leyden were in natural science. Ultimately, he got a habilitation from Bern, becoming the professor of zoology and comparative anatomy at the University of Basel. An area of specialization was the extinct fauna of Switzerland. Another area was the history of various mammalian species. His work in zooarchaeology included a report in 1861 about the remains of fish and domesticated animals from Swiss palafitte settlements. Rütimeyer was an advocate of evolution but rejected natural selection and held anti-materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |