|
Palaeopanthera
''Palaeopanthera'' () is an extinct genus of pantherine felid which lived during the Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Asia (China and Turkey). It contains two species, ''P. blytheae'' and ''P. pamiri'', which were initially suggested as members of the genera ''Panthera'' and ''Felis'' respectively, but subsequent studies have placed both species to be separate from their original generic assignment. Discovery and naming Known from a partial skull and isolated teeth, the fossils of ''P. blytheae'' were first excavated in August 2010 in the Zanda Basin located in the Ngari Prefecture on the Tibetan Plateau, and were subsequently described and named in 2014. The type specimen, IVPP V18788.1, is dated to the Early Pliocene, approximately . While some material from the latest Miocene has been initially referred to this species, other researchers argued that the putative Late Miocene material is undiagnostic at genus level and that it could belong to other felids, probably the macha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miopanthera
''Miopanthera'' is an extinct genus of '' Pseudaelurus''-grade felids. Taxonomy The genus ''Miopanthera'' was first proposed in 1938 by Kretzoi for the species ''Pseudaelurus lorteti''. ''P. lorteti'' had previously been described as such in 1899, upon the discovery of fossils in Europe. However, Kretzoi's proposal was largely ignored by later authors. A 2010 review of the Felidae proposed splitting the genus ''Pseudaelurus'' in three, and suggested assigning ''P. lorteti'' to the genus ''Styriofelis'' alongside ''P. turnauensis''. Another species, ''Felis pamiri'', was described in 1965 based on a snout fragment found in Turkey. The locality at which it was found was estimated to be from the late Miocene, about 9.9 Ma. After its original description, no further material was assigned to the species. In 2017, a review of the species ''Felis pamiri'' concluded that it was likely closely related to ''S. lorteti'', and reassigned both species to the genus ''Miopanthera''. The paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantherinae
The Pantherinae is a subfamily of the Felidae; it was named and first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1917 as only including the ''Panthera'' species, but later also came to include the clouded leopards (genus ''Neofelis''). The Pantherinae genetically diverged from a common ancestor between and . Characteristics Pantherinae species are characterised by an imperfectly ossified hyoid bone with elastic tendons that enable their larynx to be mobile. They have a flat rhinarium that only barely reaches the dorsal side of the nose. The area between the nostrils is narrow, and not extended sidewards as in the Felinae. The ''Panthera'' species have a single, rounded, vocal fold with a thick mucosal lining, a large vocalis muscle, and a large cricothyroid muscle with long and narrow membranes. A vocal fold that is longer than enables all but the snow leopard among them to roar, as it has shorter vocal folds of that provide a lower resistance to airflow; this distinction w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
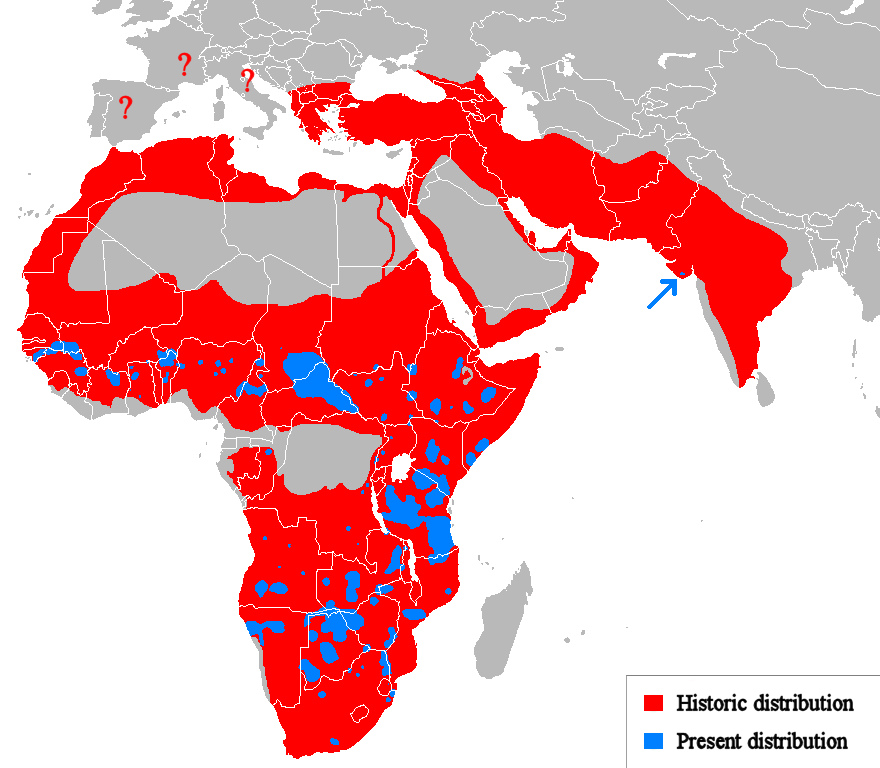
Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family (biology), family Felidae, and one of two extant genera in the subfamily Pantherinae. It contains the largest living members of the cat family. There are five living species: the jaguar, leopard, lion, snow leopard and tiger. Numerous extinct species are also named, including the Panthera spelaea, cave lion and American lion. Etymology The word derives from Classical Latin , itself from the Ancient Greek (). Characteristics In ''Panthera'' species, the dorsal profile of the skull is flattish or evenly convex. The frontal interOrbit (anatomy), orbital area is not noticeably elevated, and the area behind the elevation is less steeply sloped. The basic Cranial cavity, cranial axis is nearly horizontal. The inner chamber of the Auditory bulla, bullae is large, the outer small. The partition between them is close to the external auditory meatus. The convexly rounded chin is sloping. All ''Panthera'' species have an incompletely ossified h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felid
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ). The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the greatest diversity in fur patterns of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest and savanna habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to Diurnality, diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: the Pantherinae, the Felinae and the Acin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia'') is a species of large cat in the genus ''Panthera'' of the family Felidae. The species is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is estimated to number fewer than 10,000 mature individuals and is expected to decline about 10% by 2040. It is mainly threatened by poaching and habitat destruction following infrastructural developments. It inhabits alpine and subalpine zones at elevations of , ranging from eastern Afghanistan, the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau to southern Siberia, Mongolia and western China. In the northern part of its range, it also lives at lower elevations. Taxonomically, the snow leopard was long classified in the monotypic genus ''Uncia''. Since phylogenetic studies revealed the relationships among ''Panthera'' species, it has since been considered a member of that genus. Two subspecies were described based on morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' ("''Palaeo3''") is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing multidisciplinary studies and comprehensive reviews in the field of palaeoenvironmental geology. The journal is edited by Howard Falcon-Lang, Shuzhong Shen, Alex Dickson, Mary Elliot, Meixun Zhao, Lucia Angiolini. It was established in 1965 and is currently published by Elsevier. Indexing and abstracting ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' is indexed and abstracted in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Advance in Space Research'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.318. References External links * Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vallesian
The Vallesian age is a period of geologic time (11.6–9.0 Ma) within the Miocene used more specifically with European Land Mammal Ages. It precedes the Turolian age and follows the Astaracian age. The so-called Vallesian Crisis resulted in the extinction of several mammalian taxa characteristic of the Middle Miocene. The term "Vallesian" was introduced by Catalan palaeontologist Miquel Crusafont in 1950 to mark the arrival of the equid '' Hipparion'' in Europe. The remaining European palaeofaunas, however, had been around since the Middle Miocene, including the moschid '' Micromeryx'' (a musk deer), the cervid '' Euprox'', the suid '' Listriodon'', and the felids '' Sansanosmilus'' and '' Pseudaelurus'', and the Aragonian-Vallesian"Aragonian" is a Spanish term for a continental stage, roughly equivalent to the Middle Miocene or Astaracian (16–11 Ma). boundary does not represent a major shift in the European mammalian record. In contrast, the transition between Lower and U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metailurus
''Metailurus'' is a genus of saber-toothed cat in the family Felidae, and belonging to the tribe Metailurini, which occurred in North America, Eurasia and Africa from the Miocene to the Middle Pleistocene The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen .... History and taxonomy The genus ''Metailurus'' was described by Zdansky in 1924 for the two species ''Metailurus major'' and ''Metailurus minor''. ''Metailurus mongoliensis'' was described in 1939. ''Metailurus boodon'' was described in 1948. ''Metailurus hengduanshanensis'' was described in 1996. ''Metailurus ultimus'' was described in 2014. ''Metailurus minor'' was reassigned to the felid genus '' Yoshi'' in 2015. Description The canines of ''Metailurus'' are longer than those of even the clouded leopard, but significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-orbital Constriction
In physical anthropology, post-orbital constriction is the narrowing of the cranium (skull) just behind the eye sockets (the orbits, hence the name) found in most non-human primates and early hominins. This constriction is very noticeable in non-human primates, slightly less so in Australopithecines, even less in Homo erectus and completely disappears in modern Homo sapiens. Post-orbital constriction index in non-human primates and hominin range in category from increased constriction, intermediate, reduced constriction and disappearance. The post-orbital constriction index is defined by either a ratio of minimum frontal breadth (MFB), behind the supraorbital torus, divided by the maximum upper facial breadth (BFM), bifrontomalare temporale, or as the maximum width behind the orbit of the skull. Cranial evolution Measurement of cranial capacity in hominis has been long used to examine the evolutionary development of increased brain size, allowing for comparing and contrasting amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture (anatomy)
In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an organism, with or without significant overlap of the elements. Sutures are found in the skeletons or exoskeletons of a wide range of animals, in both invertebrates and vertebrates. Sutures are found in animals with hard parts from the Cambrian period to the present day. Sutures were and are formed by several different methods, and they exist between hard parts that are made from several different materials. Vertebrate skeletons The skeletons of vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) are made of bone, in which the main rigid ingredient is calcium phosphate. Cranial sutures The skulls of most vertebrates consist of sets of bony plates held together by cranial sutures. These sutures are held together mainly by Sharpey's fibers which grow from each bone into the adjoining one. Sutures in the ankles of land vertebrates In the type of crurotarsal ankle, which is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |