|
PAPSS1
Bifunctional 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthetase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAPSS1'' gene. Three-prime-phosphoadenosine 5-prime-phosphosulfate ( PAPS) is the sulfate donor cosubstrate for all sulfotransferase (SULT) enzymes (Xu et al., 2000). SULTs catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many endogenous and exogenous compounds, including drugs and other xenobiotics A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compo .... In humans, PAPS is synthesized from adenosine 5-prime triphosphate (ATP) and inorganic sulfate by 2 isoforms, PAPSS1 and PAPSS2 (MIM 603005). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"> References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
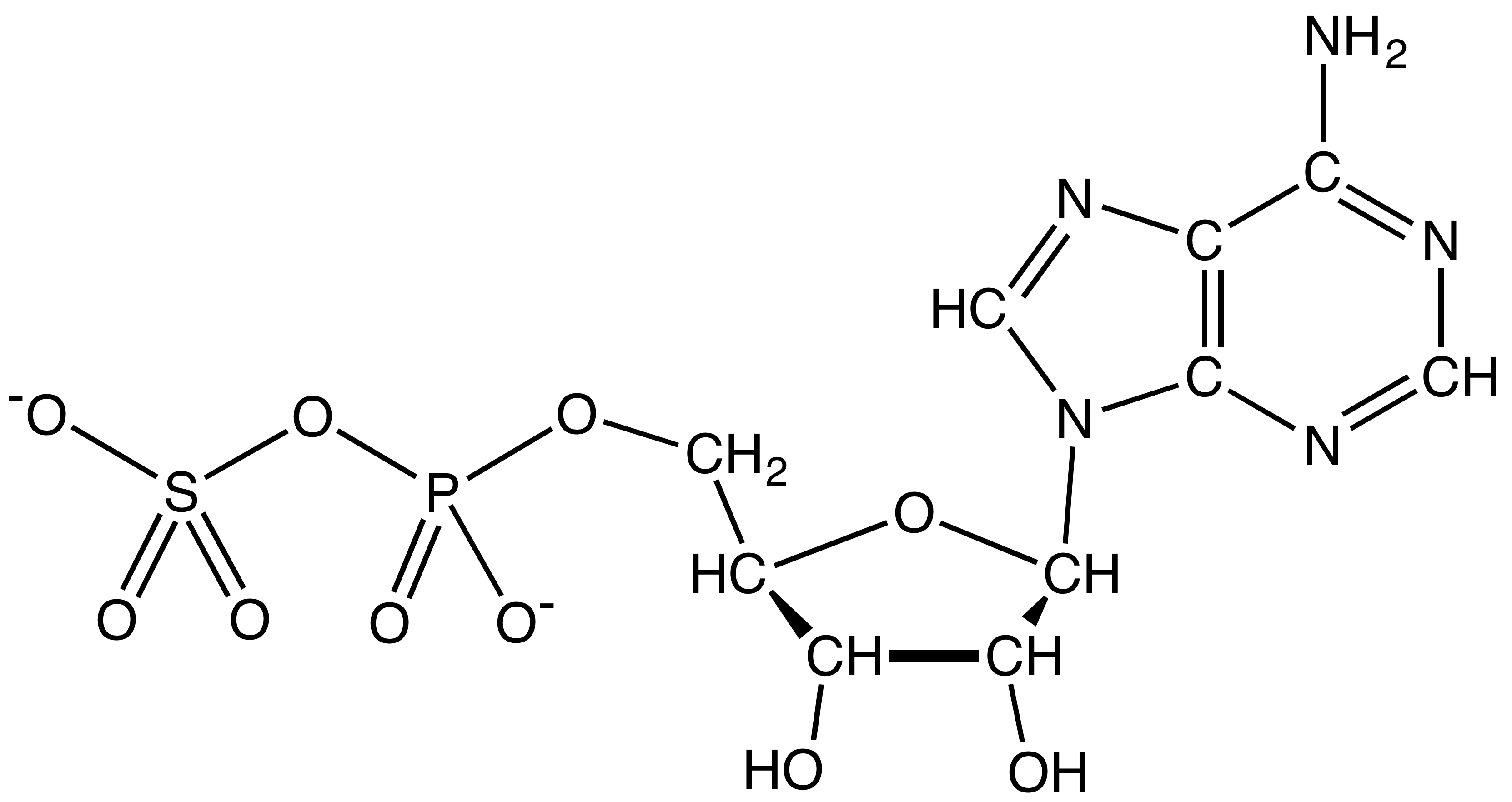
PAPS
3′-Phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) that is phosphorylated at the 3′ position and has a sulfate group attached to the 5′ phosphate. It is the most common coenzyme in sulfotransferase reactions and hence part of sulfation pathways. It is endogenously synthesized by organisms via the phosphorylation of adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (APS), an intermediary metabolite. In humans such reaction is performed by bifunctional 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthases (PAPSS1 and PAPSS2) using ATP as the phosphate donor. Formation and reduction APS and PAPS are intermediates in the reduction of sulfate to sulfite, an exothermic conversion that is carried out by sulfate-reducing bacteria. In these organisms, sulfate serves as an electron acceptor, akin to the use of O2 as an electron acceptor by aerobic organisms. Sulfate is not reduced directly but must be activated by the formation of APS or PAPS. These carriers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry of the isolated anion is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfotransferase
In biochemistry, sulfotransferases (SULTs) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group () from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol () or amine (). The most common sulfo group donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS). In the case of alcohol as acceptor, the product is a sulfate (): :\ce \ + \ \ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce \ + \ \ce whereas an amine leads to a sulfamate (): :\ce \ + \ \ce \quad \xrightarrowtext\quad \ce \ + \ \ce Both reactive groups for a sulfonation via sulfotransferases may be part of a protein, lipid, carbohydrate or steroid. Examples The following are examples of sulfotransferases: * carbohydrate sulfotransferase: CHST1, CHST2, CHST3, CHST4, CHST5, CHST6, CHST7, CHST8, CHST9, CHST10, CHST11, CHST12, CHST13, CHST14 * galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase: GAL3ST1, GAL3ST2, GAL3ST3, GAL3ST4 * heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase: HS2ST1 * heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase: HS3ST1, HS3S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenobiotics
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compounds can also become xenobiotics if they are taken up by another organism, such as the uptake of natural human hormones by fish found downstream of sewage treatment plant outfalls, or the chemical defenses produced by some organisms as protection against predators. The term "xenobiotic" is also used to refer to organs transplanted from one species to another. The term "xenobiotics", however, is very often used in the context of pollutants such as dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls and their effect on the biota, because xenobiotics are understood as substances foreign to an entire biological system, i.e. artificial substances, which did not exist in nature before their synthesis by humans. The term xenobiotic is derived from the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |