|
P-process
The term p-process (''p'' for proton) is used in two ways in the scientific literature concerning the astrophysical origin of the elements (nucleosynthesis). Originally it referred to a proton capture process which was proposed to be the source of certain, naturally occurring, neutron-deficient isotopes of the elements from selenium to mercury. These nuclides are called p-nuclei and their origin is still not completely understood. Although it was shown that the originally suggested process cannot produce the p-nuclei, later on the term p-process was sometimes used to generally refer to any nucleosynthesis process supposed to be responsible for the p-nuclei. Often, the two meanings are confused. Recent scientific literature therefore suggests to use the term p-process only for the actual proton capture process, as it is customary with other nucleosynthesis processes in astrophysics. The proton capture p-process Proton-rich nuclides can be produced by sequentially adding one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-nuclei
p-nuclei (''p'' stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury inclusive which cannot be produced in either the s- or the r-process. Definition The classical, ground-breaking works of Burbidge, Burbidge, Fowler and Hoyle (1957) and of A. G. W. Cameron (1957) showed how the majority of naturally occurring nuclides beyond the element iron can be made in two kinds of neutron capture processes, the s- and the r-process. Some proton-rich nuclides found in nature are not reached in these processes and therefore at least one additional process is required to synthesize them. These nuclei are called p-nuclei. Since the definition of the p-nuclei depends on the current knowledge of the s- and r-process (see also nucleosynthesis), the original list of 35 p-nuclei may be modified over the years, as indicated in the Table below. For example, it is recognized today that the abundances of 152Gd and 164Er cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rp-process
The rp-process (rapid proton capture process) consists of consecutive proton captures onto seed nuclei to produce heavier elements. It is a nucleosynthesis process and, along with the ''s''-process and the ''r''-process, may be responsible for the generation of many of the heavy elements present in the universe. However, it is notably different from the other processes mentioned in that it occurs on the proton-rich side of stability as opposed to on the neutron-rich side of stability. The end point of the rp-process (the highest-mass element it can create) is not yet well established, but recent research has indicated that in neutron stars it cannot progress beyond tellurium. The rp-process is inhibited by alpha decay, which puts an upper limit on the end point at 104Te, the lightest observed alpha-decaying nuclide, and the proton drip line in light antimony isotopes. At this point, further proton captures result in prompt proton emission or alpha emission, and thus the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
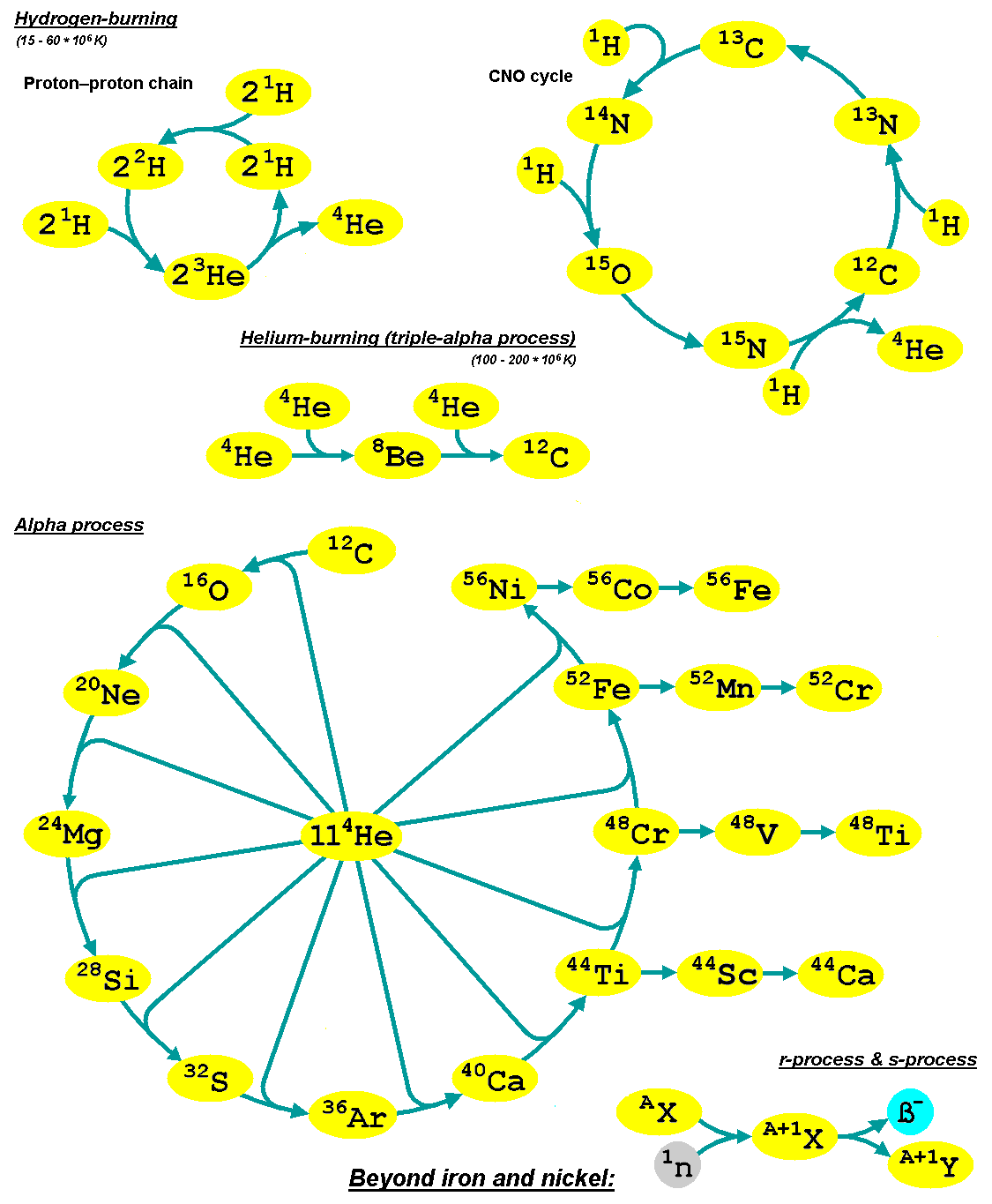
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in a process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. After about 20 minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled to a point at which these high-energy collisions among nucleons ended, so only the fastest and simplest reactions occurred, leaving our universe containing hydrogen and helium. The rest is traces of other elements such as lithium and the hydrogen isotope deuterium. Nucleosynthesis in stars and their explosions later produced the variety of elements and isotopes that we have today, in a process called cosmic chemical evolution. The amounts of total mass in elements heavier than hydrogen and helium (called 'metals' by astrophysicists) remains small (few percent), so that the universe still has approximately the same composition. Stars ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Drip Line
The nuclear drip line is the boundary beyond which atomic nuclei are unbound with respect to the emission of a proton or neutron. An arbitrary combination of protons and neutrons does not necessarily yield a stable nucleus. One can think of moving up or to the right across the table of nuclides by adding a proton or a neutron, respectively, to a given nucleus. However, adding nucleons one at a time to a given nucleus will eventually lead to a newly formed nucleus that immediately decays by emitting a proton (or neutron). Colloquially speaking, the nucleon has ''leaked'' or ''dripped'' out of the nucleus, hence giving rise to the term ''drip line''. Drip lines are defined for protons and neutrons at the extreme of the proton-to-neutron ratio; at p:n ratios at or beyond the drip lines, no bound nuclei can exist. While the location of the proton drip line is well known for many elements, the location of the neutron drip line is only known for elements up to neon. General descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for nucleosynthesis, the creation of approximately half of the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy metals, heavier than iron, the "heavy elements", with the other half produced by the p-process and s-process, ''s''-process. The ''r''-process usually synthesizes the most neutron-rich stable isotopes of each heavy element. The ''r''-process can typically synthesize the heaviest four isotopes of every heavy element; of these, the heavier two are called ''r-only nuclei'' because they are created exclusively via the ''r''-process. Abundance peaks for the ''r''-process occur near mass numbers (elements Se, Br, and Kr), (elements Te, I, and Xe) and (elements Os, Ir, and Pt). The ''r''-process entails a succession of ''rapid'' neutron captures (hence the name) by one or more heavy Seed nucleus, seed nuclei, typically beginning with nuclei in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodisintegration
Photodisintegration (also called phototransmutation, or a photonuclear reaction) is a nuclear process in which an atomic nucleus absorbs a high-energy gamma ray, enters an excited state, and immediately decays by emitting a subatomic particle. The incoming gamma ray effectively knocks one or more neutrons, protons, or an alpha particle out of the nucleus. The reactions are called (γ,n), (γ,p), and (γ,α), respectively. Photodisintegration is endothermic (energy absorbing) for atomic nuclei lighter than iron and sometimes exothermic (energy releasing) for atomic nuclei heavier than iron. Photodisintegration is responsible for the nucleosynthesis of at least some heavy, proton-rich elements via the p-process in supernovae of type Ib, Ic, or II. This causes the iron to further fuse into the heavier elements. Photodisintegration of deuterium A photon carrying 2.22 MeV or more energy can photodisintegrate an atom of deuterium: : James Chadwick and Maurice Goldhaber used this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of nuclear reactions, reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation (nucleosynthesis) of approximately half the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy metal (chemical element), heavier than iron. In the ''s''-process, a seed nucleus undergoes neutron capture to form an isotope with one higher atomic mass. If the new isotope is stable nuclide, stable, a series of increases in mass can occur, but if it is unstable nucleus, unstable, then beta decay will occur, producing an element of the next higher atomic number. The process is ''slow'' (hence the name) in the sense that there is sufficient time for this radioactive decay to occur before another neutron is captured. A series of these reactions produces stable isotopes by moving along the valley of stability, valley of beta-decay stable isobars in the table of nuclides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B2FH Paper
The B2FH paper was a landmark scientific paper on the origin of the chemical elements. The paper's title is ''Synthesis of the Elements in Stars'', but it became known as B2FH from the initials of its authors: Margaret Burbidge, Geoffrey Burbidge, William A. Fowler, and Fred Hoyle. It was written from 1955 to 1956 at the University of Cambridge and Caltech, then published in ''Reviews of Modern Physics'' in 1957. The B2FH paper reviewed stellar nucleosynthesis theory and supported it with astronomical and laboratory data. It identified nucleosynthesis processes that are responsible for producing the elements heavier than iron and explained their relative abundances. The paper became highly influential in both astronomy and nuclear physics. Nucleosynthesis prior to 1957 Prior to the publication of the B2FH paper, George Gamow advocated a theory of the Universe in which almost all chemical elements, or equivalently atomic nuclei, were synthesized during the Big Bang. Gamow's theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionuclides
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
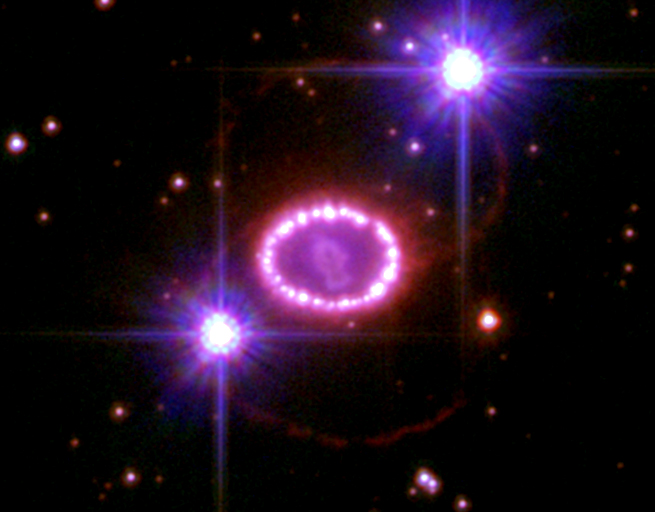
Type II Supernova
A Type II supernova or SNII (plural: ''supernovae'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo this type of explosion. Type II supernovae are distinguished from other types of supernovae by the presence of hydrogen in their spectra. They are usually observed in the spiral arms of galaxies and in H II regions, but not in elliptical galaxies; those are generally composed of older, low-mass stars, with few of the young, very massive stars necessary to cause a supernova. Stars generate energy by the nuclear fusion of elements. Unlike the Sun, massive stars possess the mass needed to fuse elements that have an atomic mass greater than hydrogen and helium, albeit at increasingly higher temperatures and pressures, causing correspondingly shorter stellar life spans. The degeneracy pressure of electrons and the energy generated by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |