|
Ozopore
An ozopore is the opening of a defensive gland present in some arthropods, notably in millipedes of the order PolydesmidaOzopore. External Anatomy of Polydesmida. polydesmida.info and in , the eight-legged arachnids also known as "daddy long-legs". The glands themselves are known as ozadenes, also called "scent glands", "repugnatorial glands", "odoriferous glands" or "stink glands" by various authors. The name is derived from ''ozo'' "smell" and ''porus'' "por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozophore
An ozophore is an elevated cone present in the harvestman ("daddy long-legs") suborder Cyphophthalmi. It carries the openings, called ozopores, of the defensive glandsPinto-da-Rocha ''et al.'' 2007: 22f that are present in many harvestmen. The name is derived from Ancient Greek Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ... ''ozo'' "smell" and ''phorein'' "to bear". Footnotes References * (eds.) (2007): Harvestmen - The Biology of Opiliones. ''Harvard University Press'' Harvestmen Arachnid anatomy {{Opiliones-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
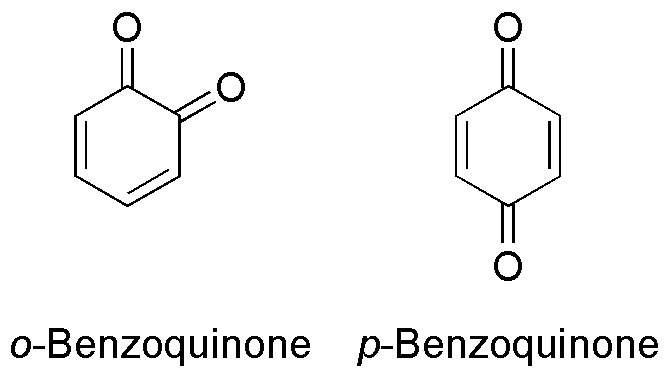
Benzoquinone
Benzoquinone (C6H4O2) is a quinone with a single benzene ring. There are 2 (out of 3 hypothetical) benzoquinones: * 1,4-Benzoquinone, most commonly, right image (also ''para''-benzoquinone, ''p''-benzoquinone, ''para''-quinone, or just quinone) * 1,2-Benzoquinone, less commonly, left image (also ''ortho''-benzoquinone, ''o''-benzoquinone, ''ortho''-quinone) *1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known. An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the rhizomes of '' Iris kemaonensis''. See also * Arene substitution pattern Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon. ''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution * ... References {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Anatomy
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired ventral nerve cords running through all segments and forming paired ganglia in each segment. Their heads are formed by fusion of varying numbers of segments, and their brains are formed by fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julida
Julida is an order of millipedes. Members are mostly small and cylindrical, typically ranging from in length. Eyes may be present or absent, and in mature males of many species, the first pair of legs is modified into hook-like structures. Additionally, both pairs of legs on the 7th body segment of males are modified into gonopods. Distribution Julida contains predominantly temperate species ranging from North America to Panama, Europe, Asia north of the Himalayas, Asir region, Saudi Arabia, and Southeast Asia. Classification The order Julida contains approximately 750 species, divided into the following superfamilies and families: ;Blaniuloidea C. L. Koch, 1847 * Blaniulidae C. L. Koch, 1847 * Galliobatidae Brolemann, 1921 * Okeanobatidae Verhoeff, 1942 * Zosteractinidae Loomis, 1943 ;Juloidea Leach, 1814 *Julidae Julidae is a family of millipedes in the order Julida, containing more than 600 species in around 20 genera. Its members are largely confined to the Western P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerida
Glomerida is an order of pill-millipedes found primarily in the Northern Hemisphere. Also known as northern pill millipedes, they superficially resemble pill-bugs or woodlice, and can enroll into a protective ball. They have twelve body segments, 17 to 19 pairs of legs, and males have enlarged rear legs involved in mating. The order includes about 30 genera and at least 280 species, including ''Glomeris marginata'', the common European pill-millipede. The order contains members in Europe, South-east Asia and the Americas from California to Guatemala. Although historically considered closely related with the similar sphaerotheriidans that also enroll, some DNA evidence suggest they may be more closely related to glomeridesmidans, a poorly known order that does not enroll. Description Glomeridans are small, oval-shaped millipedes reaching up to long. Like the Sphaerotheriida (so-called Giant Pill-millipedes), they are capable of enrolling into a ball ("volvation"), a trait also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthoquinone
Naphthoquinones constitute a class of organic compounds structurally related to naphthalene. Two isomers are common for the parent naphthoquinones: * 1,2-Naphthoquinone * 1,4-Naphthoquinone Natural products * Alkannin * Hexahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione * Juglone * Lapachol * Lawsone * Menatetrenone * 2-Methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, a compound found in '' Impatiens'' species * Nigrosporin B * Phylloquinone * Plumbagin * Spinochrome B * Spinochrome D * Vitamin K and related compounds ** Phylloquinone ** Vitamin K2 ** Menadione Menadione is a natural organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2C2H(CH3). It is an analog of 1,4-naphthoquinone with a methyl group in the 2-position. It is sometimes called vitamin K3. Use is allowed as a nutritional supplement in animal ... (2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) Synthetic naphthoquinones * 5,8-Dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and dihydroxynaphthoquinones * Atovaquone * Buparvaquone, an antiprotozoal drug used in veterinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalangiidae
The Phalangiidae are a family of harvestmen with about 380 known species. The best known is ''Phalangium opilio''. ''Dicranopalpus ramosus'' is a common introduced species in Europe. It is not to be confused with the harvestman family Phalangodidae, which belongs to the suborder Laniatores. Name The name of the type genus is derived from Ancient Greek ''phalangion'' "harvestman". (2007): Phalangiidae Latreille, 1802. In: Pinto-da-Rocha ''et al.'' 2007: 123ff Systematics * Dicranopalpinae :* '' Amilenus'' Martens, 1969 (1 species; central Europe) :* '' Dicranopalpus'' Doleschall, 1852 (12 species; Europe, South America) * Oligolophinae Banks, 1893 :* '' Lacinius'' Thorell, 1876 (17 species; China, Europe, North America) :* '' Mitopiella'' Banks, 1930 (1 species; Borneo) :* '' Mitopus'' Thorell, 1876 (9 species; Eurasia, North America) :* '' Odiellus'' Roewer, 1923 (17 species; Eurasia, North Africa, North America) :* '' Oligolophus'' C. L. Koch, 1871 (4 species; Europe, Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Chain Compound
In chemistry, an open-chain compound (or open chain compound) or acyclic compound (Greek prefix ''α'' 'without' and ''κύκλος'' 'cycle') is a compound with a linear structure, rather than a cyclic one. An open-chain compound having no side groups is called a straight-chain compound (also spelled as straight chain compound). Many of the simple molecules of organic chemistry, such as the alkanes and alkenes, have both linear and ring isomers, that is, both acyclic and cyclic. For those with 4 or more carbons, the linear forms can have straight-chain or branched-chain isomers. The lowercase prefix ''n-'' denotes the straight-chain isomer; for example, ''n''-butane is straight-chain butane, whereas ''i''-butane is isobutane. Cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes, not of alkanes, because the ring's closure involves a C-C bond. Having no rings (aromatic or otherwise), all open-chain compounds are aliphatic. Typically in biochemistry Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |