Benzoquinone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benzoquinone (C6H4O2) is a 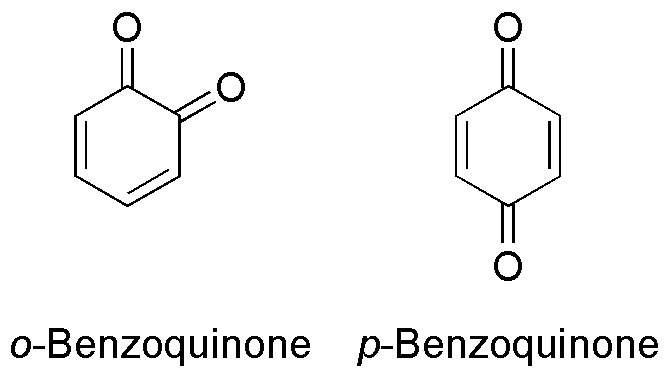 *1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known.
An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the
*1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known.
An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the
quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with ...
with a single benzene ring. There are 2 (out of 3 hypothetical) benzoquinones:
* 1,4-Benzoquinone
1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as ''para''-quinone, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, ...
, most commonly, right image (also ''para''-benzoquinone, ''p''-benzoquinone, ''para''-quinone, or just quinone)
* 1,2-Benzoquinone, less commonly, left image (also ''ortho''-benzoquinone, ''o''-benzoquinone, ''ortho''-quinone)
 *1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known.
An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the
*1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known.
An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome ( ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and Shoot (botany), shoots from its Node (botany), nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from ...
s of '' Iris kemaonensis''.
See also
*Arene substitution pattern
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution
* ...
References
{{Chemistry index