|
Oxybelis Rutherfordi
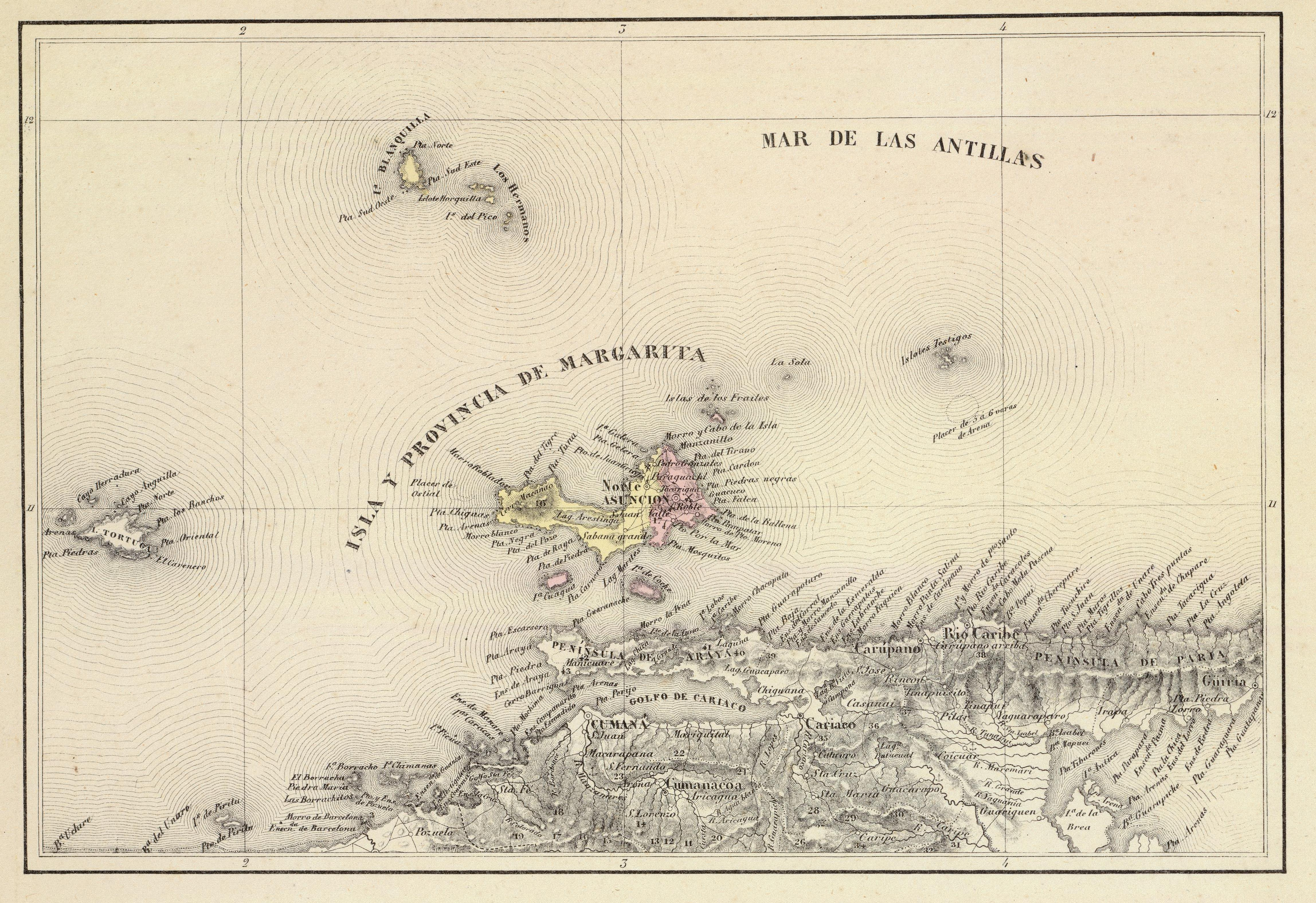
''Oxybelis rutherfordi'' is a species of snake. The species was originally described in 2020 by Robert C. Jadin, Christopher Blair, Sarah A. Orlofske, Michael J. Jowers, Gilson A. Rivas, Laurie J. Vitt, Julie M. Ray, Eric N. Smith & John C. Murphy. Description ''Oxybelis rutherfordi'' is one of the Neotropical vine snakes . In 2020 it was described as being distinct from a similar species of vine snake; ''Oxybelis aeneus''. Phylogenetic analyses has shown distinctive genetic differences. Range & habitat The species has been observed in Trinidad & Tobago, Venezuela including Margarita Island, and French Guiana. The Holotype was collected in the grounds of the William Beebe Tropical Research Station (also known as Simla), in the Arima Valley in the Northern Range of Trinidad Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxybelis
''Oxybelis'' is a genus of colubrid snakes, endemic to the Americas, which are commonly known as vine snakes. Though similar in appearance to the Asian species of vine snakes of the genus ''Ahaetulla'', they are not closely related, and are an example of convergent evolution. Geographic range Species of ''Oxybelis'' are found from the southwestern United States, through Central America, to the northern countries of South America. Description Body slender and laterally compressed, tail long. Head elongated and distinct from neck. Pupil of eye round. Dorsal scales smooth or weakly keeled, with apical pits, and arranged in 15 or 17 rows at midbody. Ventrals rounded at sides, subcaudals paired (divided). Maxillary teeth 20–25, subequal, except for the 3-5 most posterior, which are slightly enlarged and grooved on the outer surface. Anterior mandibular teeth strongly enlarged. Species There are 11 widely recognized species in the genus ''Oxybelis''. *''Oxybelis aeneus'' - Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxybelis Aeneus
''Oxybelis aeneus'', commonly known as the Mexican vine snake or brown vine snake, is a species of colubrid snake, which is endemic to the Americas. Geographic range and habitat ''O. aeneus'' is found from within the Atascosa, Patagonia, and Pajarito mountains of southern Arizona in the United States, through Mexico, to northern South America and Trinidad and Tobago. Within Arizona, ''O. aeneus'' is exclusively affiliated with Madrean Evergreen Woodland communities and the upper reaches of adjacent semidesert grassland habitat. It is usually encountered in trees or shrubs on open, steep, and grassy slopes, but is also associated with wooded canyons, especially those with abundant vegetation. Description ''O. aeneus'' is an extremely slender snake that reaches up to in total length (including a long tail). Its color may vary from gray to brown with a yellow underside. The body is laterally compressed. The snout is prominent, its length more than two times the diameter of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analyses
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad & Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margarita Island
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and morality. He captured a fleet of Spanish ships off p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west. With a land area of , French Guiana is the second-largest Regions of France, region of France (more than one-seventh the size of Metropolitan France) and the largest Special member state territories and the European Union, outermost region within the European Union. It has a very low population density, with only . (Its population is less than that of Metropolitan France.) Half of its 294,436 inhabitants in 2022 lived in the metropolitan area of Cayenne, its Prefectures in France, capital. 98.9% of the land territory of French Guiana is covered by forests, a large part of which is Old-growth forest, primeval Tropical r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Range
The Northern Range is the range of tall hills across north Trinidad, the major island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. The hills range from the Chaguaramas peninsula on the west coast to Toco in the east. The Northern Range covers approximately twenty-five percent of the land area of Trinidad. Geography The Northern Range runs from the Chaguaramas Peninsula in the west to Toco in the east. The eastern Northern Range (areas east of Arima) remain most heavily forested. Portions west of Arima, especially the southern slopes and valleys, have been extensively deforested, since they lie immediately north of the most heavily populated parts of the island. At the western end of the Northern Range, the capital city, Port of Spain, climbs into the hills and the valleys are settled and largely deforested. The Arima Valley remains as the westernmost valley that is still primarily forested, in a large part due to the presence of the Asa Wright Nature Centre in this valley. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of , it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies. Name The original name for the island in the Arawaks' language was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. History Caribs and Arawaks lived in Trinidad long before Christopher Columbus encountered the islands on his third voyage on 31 July 1498. The island remained Spanish until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists from the French Caribbean, especially Martinique.Besson, Gerard (2000-08-27). "Land of Beginnings – A historical digest", ''Newsday Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |