|
Oxamniquine
Oxamniquine, sold under the brand name Vansil among others, is a medication used to treat schistosomiasis due to ''Schistosoma mansoni''. Praziquantel, however, is often the preferred treatment. It is given Oral administration, by mouth and used as a single dose. Common side effects include sleepiness, headache, nausea, diarrhea, and reddish urine. It is typically not recommended during pregnancy, if possible. Seizures may occur and therefore caution is recommended in people with epilepsy. It works by causing paralysis of the helminth, parasitic worms. It is in the anthelmintic family of medications. Oxamniquine was first used medically in 1972. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States. It is more expensive than praziquantel. Medical uses Oxamniquine is used for treatment of schistosomiasis. According to one systematic review, praziquantel is the standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthelmintic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges (those that stun) or vermicides (those that kill). Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals, particularly small ruminants such as goats and sheep. Anthelmintic medication is also used in mass deworming campaigns of school-aged children in many developing countries. Anthelmintics are also used for mass deworming of livestock. The drugs of choice for soil-transmitted helminths are mebendazole and albendazole; for schistosomiasis and tapeworms it is praziquantel. Types Many early treatments were herbal, such as the oil of herbs of the genus '' Chenopodium'' that were given as anthelmintic treatment for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever is a neglected tropical helminthiasis, disease caused by parasitism, parasitic Schistosoma, flatworms called schistosomes. It affects both humans and animals. It affects the urinary tract or the intestines. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, blood in stool, bloody stool, or hematuria, blood in the urine. Those who have been Infection, infected for a long time may experience liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer. In children, schistosomiasis may cause failure to thrive, poor growth and learning disability, learning difficulties. Schistosomiasis is spread by contact with fresh water contaminated with parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in Developing country, underdeveloped and developing countries because they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Schistosomiasis is also common among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
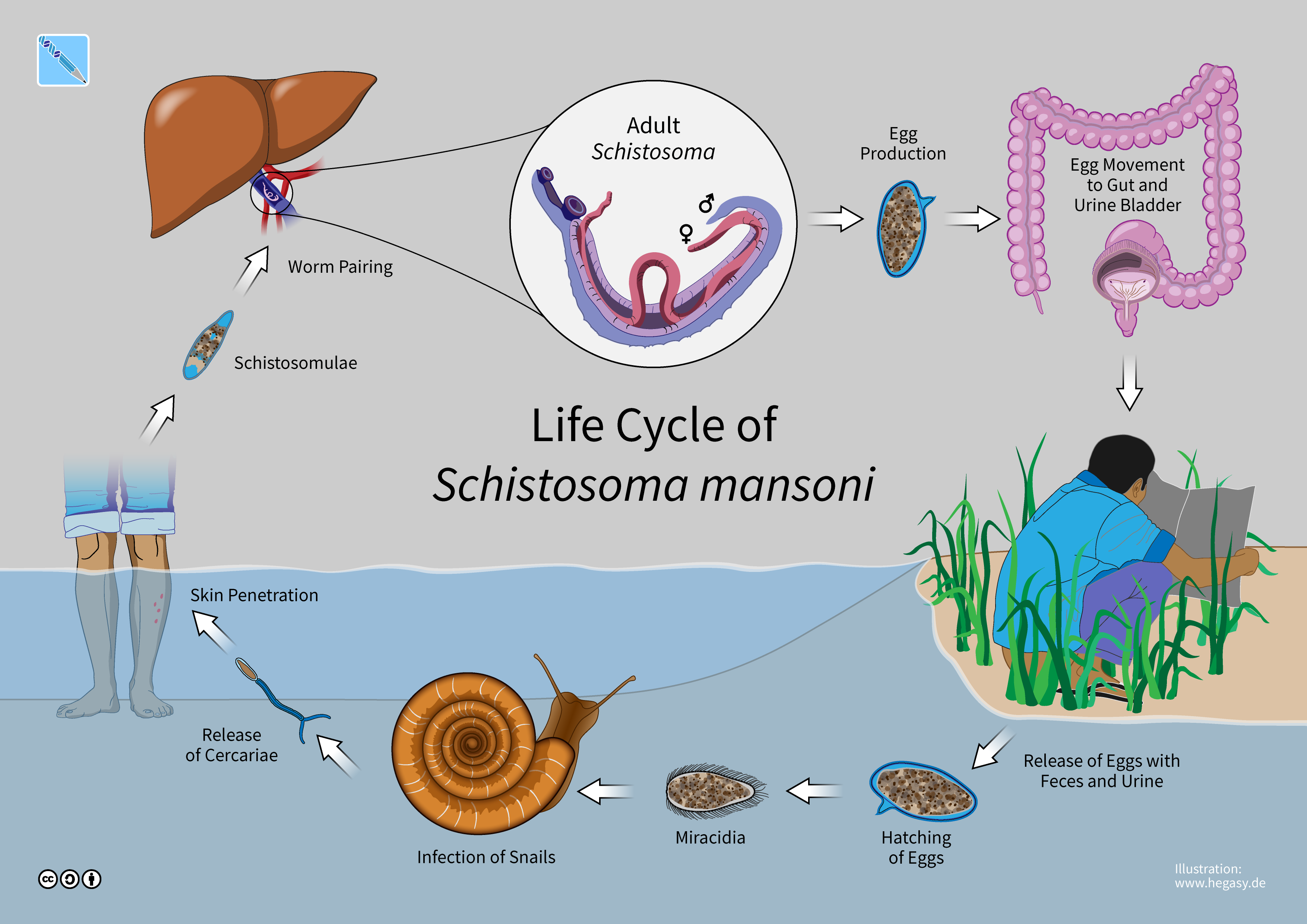
Schistosoma Mansoni
A paired couple of ''Schistosoma mansoni''. ''Schistosoma mansoni'' is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). The adult lives in the blood vessels ( mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to '' S. japonicum'', '' S. mekongi'', ''S. guineensis'', and '' S. intercalatum''). Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to ''S. mansoni''. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname. Unlike other flukes (trematodes) in which sexes are not separate (monoecious), schistosomes are unique in that adults are divided into males and females, thus, gonochoric. However, a permanent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemic Mixture
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate () is a mixture that has equal amounts (50:50) of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. History The first known racemic mixture was racemic acid, which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid. He manually separated the crystals of a mixture, starting from an aqueous solution of the sodium ammonium salt of racemate tartaric acid. Pasteur benefited from the fact that ammonium tartrate salt gives enantiomeric crystals with distinct crystal forms (at 77 °F). Reasoning from the macroscopic scale down to the molecular, he reckoned that the molecules had to have non-superimposable mirror images. A sample with only a single enantiomer is an ''enantiomerically pure'' or ''enantiopure'' compound. Etymology The word ''racemic'' derives from Latin , meaning pertaining to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
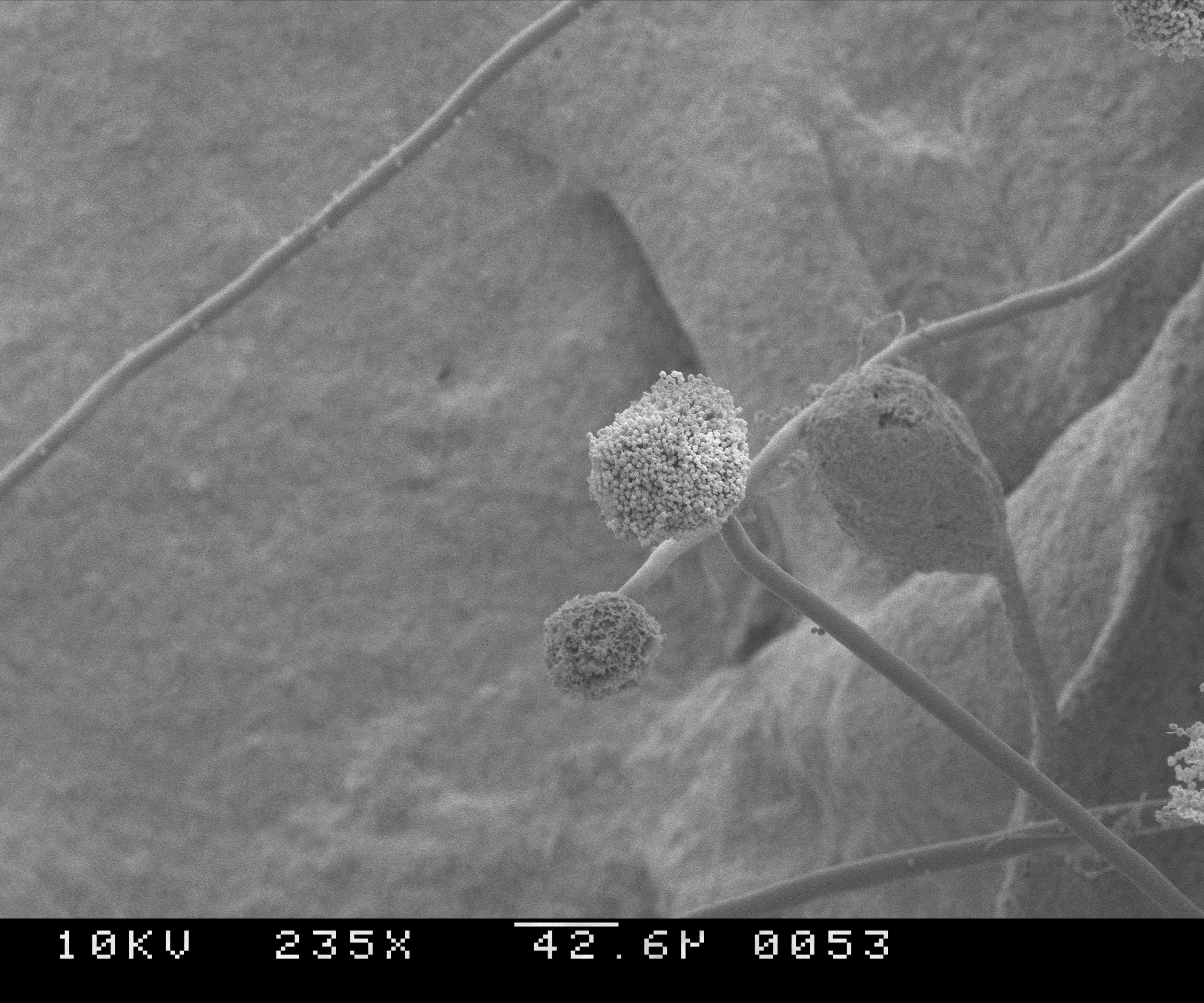
Aspergillus Sclerotiorum
'''' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an ''aspergillum'' (holy water sprinkler), from Latin ''spargere'' (to sprinkle), and named the genus accordingly. Aspergillum is an asexual spore-forming structure common to all ''Aspergillus'' species; around one-third of species are also known to have a sexual stage. While some species of ''Aspergillus'' are known to cause fungal infections, others are of commercial importance. Taxonomy Species In March 2010, ''Aspergillus'' covered 837 species of fungi. Notable species placed in Aspergillus include: * ''Aspergillus flavus'' is a notable plant pathogen impacting crop yields and a common cause of aspergillosis. * ''Aspergillus fumigatus'' is the most common cause of aspergillosis in individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venules
A venule is a very small vein in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the venous system via increasingly larger veins. Post-capillary venules are the smallest of the veins with a diameter of between 10 and 30 micrometres (μm). When the post-capillary venules increase in diameter to 50μm they can incorporate smooth muscle and are known as muscular venules. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Post-capillary venules have a single layer of endothelium surrounded by a basal lamina. Their size is between 10 and 30 micrometers and are too small to contain smooth muscle. They are instead supported by pericytes that wrap around them. When the post-capillary venules increase in diameter to 50μm they can incorporate smooth muscle and are known as muscular venules. They have an inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation refers to the installation of a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound. Hydroxylations generate alcohols and phenols, which are very common functional groups. Hydroxylation confers some degree of water-solubility. Hydroxylation of a hydrocarbon is an oxidation, thus a step in degradation. Biological hydroxylation In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often facilitated by enzymes called hydroxylases. These enzymes insert an O atom into a bond. Typical stoichiometries for the hydroxylation of a generic hydrocarbon are these: : : Since itself is a slow and unselective hydroxylating agent, catalysts are required to accelerate the pace of the process and to introduce selectivity. Hydroxylation is often the first step in the degradation of organic compounds in air. Hydroxylation is important in detoxification since it converts lipophilic compounds into water-soluble (hydrophilic) products that are more readily removed by the kidneys or liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwich, Kent
Sandwich is a town and civil parish in the Dover District of Kent, south-east England. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour and has a population of 4,985. Sandwich was one of the Cinque Ports and still has many original medieval buildings, including several listed building, listed public houses and gates in the old town walls, churches, almshouses and the White Mill, Sandwich, White Mill. While it was once a major port, Sandwich is now from the sea due to the disappearance of the Wantsum Channel. Its historic centre has been preserved. Sandwich Bay, Kent, Sandwich Bay is home to nature reserves and two world-class golf courses, Royal St George's and Prince's Golf Club, Sandwich, Prince's. The town is also a home to many educational and cultural events. Sandwich also gave its name to Sandwich, the food by way of John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, and the word ''sandwich'' is now found in several languages. Etymology The place-name 'Sandwich' is first attested in the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1849 in New York by German entrepreneurs Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891), Pfizer is one of the oldest pharmaceutical companies in North America. Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company's largest products by sales are the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine ($11 billion in 2023 revenues), apixaban ($6 billion in 2023 revenues), a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine ($6 billion in 2023 revenues), palbociclib ($4 billion in 2023 revenues), and tafamidis ($3 billion in 2023 revenues). In 2023, 46% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from Japan, and 48% came from other countries. Pfizer has been a publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
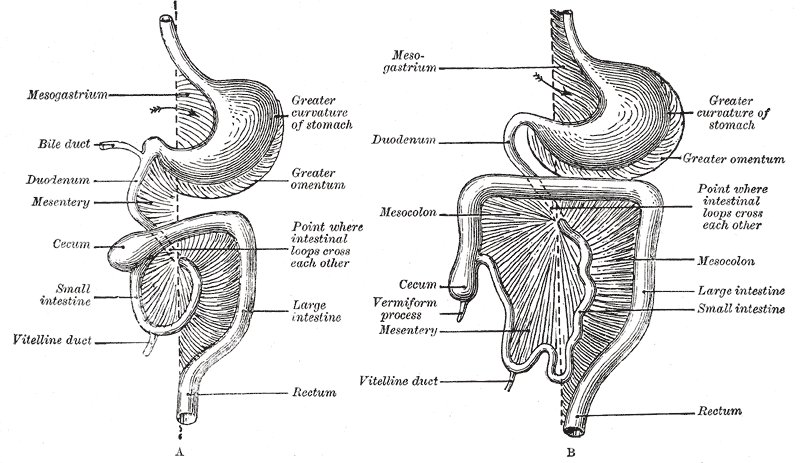
Mesentery
In human anatomy, the mesentery is an Organ (anatomy), organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall, consisting of a double fold of the peritoneum. It helps (among other functions) in storing Adipose tissue, fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines. The (the part of the mesentery that attaches the colon to the abdominal wall) was formerly thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopy, microscopic and electron microscope, electron microscopic histology, examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |