|
OxMetrics Technologies
OxMetrics is an econometric software including the Ox programming language for econometrics and statistics, developed by Jurgen Doornik and David Hendry. OxMetrics originates from PcGive, one of the first econometric software for personal computers, initiated by David Hendry in the 1980s at the London School of Economics. OxMetrics builds on the Ox programming language of Jurgen Doornik developed at University of Oxford. describes the history of econometric software packages. OxMetrics is a family of software packages for the econometric and financial analysis of time series, forecasting, econometric model selection and for the statistical analysis of cross-sectional data and panel data. The main modules apart from ''PcGive'' for dynamic econometric models (ARDL, VAR, GARCH, Switching, Autometrics), panel data models (DPD), limited dependent models, are ''STAMP'' for structural time series modelling, "SsfPack" for State space methods and "G@RCH" for financial volati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometrics Software
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of statistical analysis packages. General information Operating system support ANOVA Support for various ANOVA methods Regression Support for various regression methods. Time series analysis Support for various time series analysis methods. Charts and diagrams Support for various statistical charts and diagrams. Other abilities See also * Comparison of computer algebra systems * Comparison of deep learning software * Comparison of numerical-analysis software * Comparison of survey software * Comparison of Gaussian process software * List of scientific journals in statistics * List of statistical packages Footnotes References Further reading * * * * * {{Statistical software Statistical packages Statistical software are specialized computer programs for analysis in statistics and econometrics. Open-source * ADaMSoft – a generalized statistical software with data m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Series Analysis
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements. Time series ''analysis'' comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series ''fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
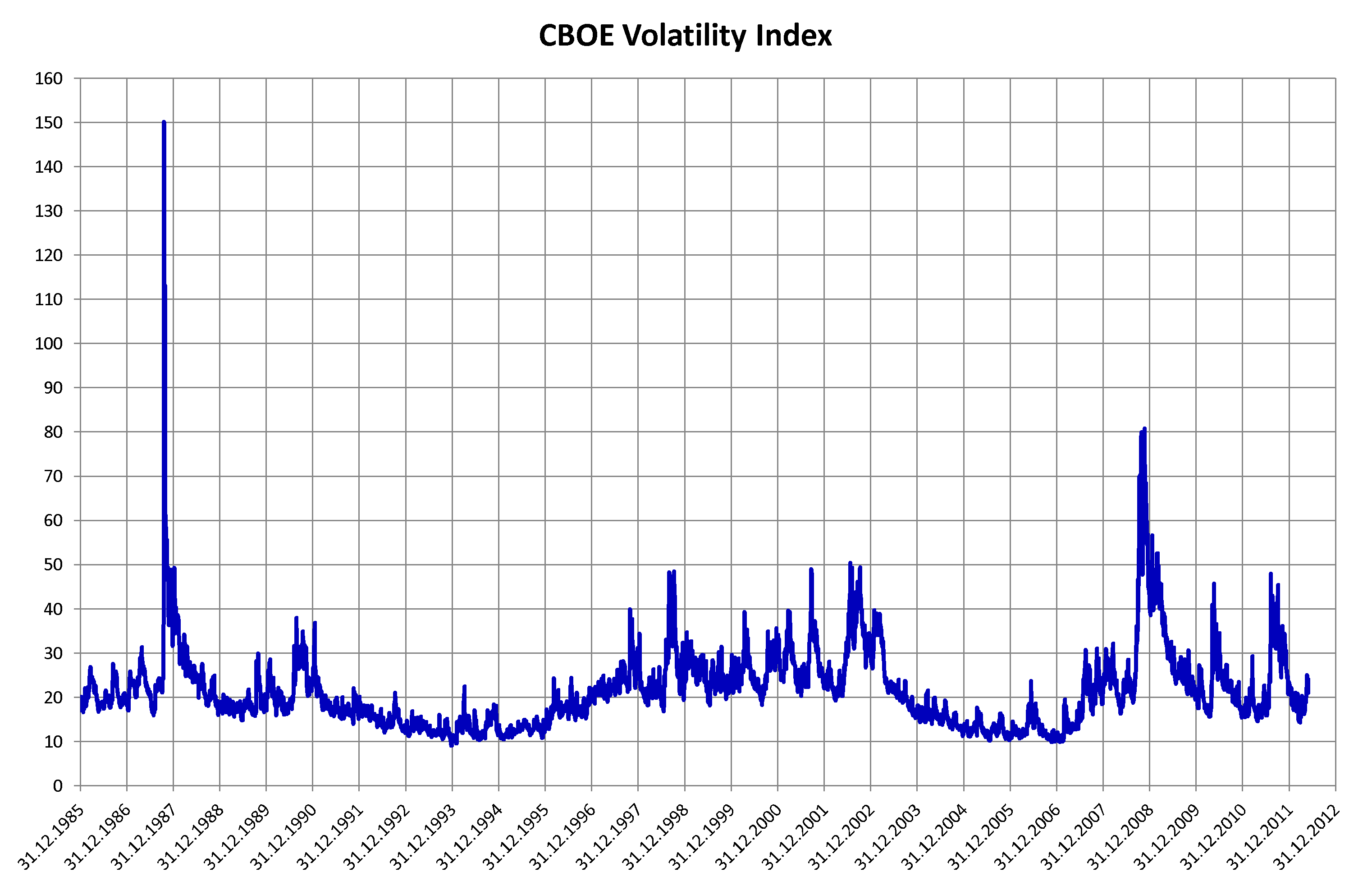
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn calculated using the sum of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Space
A state space is the set of all possible configurations of a system. It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory. For instance, the toy problem Vacuum World has a discrete finite state space in which there are a limited set of configurations that the vacuum and dirt can be in. A "counter" system, where states are the natural numbers starting at 1 and are incremented over time has an infinite discrete state space. The angular position of an undamped pendulum is a continuous (and therefore infinite) state space. Definition In the theory of dynamical systems, the state space of a discrete system defined by a function ''ƒ'' can be modeled as a directed graph where each possible state of the dynamical system is represented by a vertex with a directed edge from ''a'' to ''b'' if and only if ''ƒ''(''a'') = ''b''. This is known as a state diagram. For a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panel Data
In statistics and econometrics, panel data and longitudinal data are both multi-dimensional data involving measurements over time. Panel data is a subset of longitudinal data where observations are for the same subjects each time. Time series and cross-sectional data can be thought of as special cases of panel data that are in one dimension only (one panel member or individual for the former, one time point for the latter). A study that uses panel data is called a longitudinal study or panel study. Example In the multiple response permutation procedure (MRPP) example above, two datasets with a panel structure are shown and the objective is to test whether there's a significant difference between people in the sample data. Individual characteristics (income, age, sex) are collected for different persons and different years. In the first dataset, two persons (1, 2) are observed every year for three years (2016, 2017, 2018). In the second dataset, three persons (1, 2, 3) are obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-sectional Data
Cross-sectional data, or a cross section of a study population, in statistics and econometrics, is a type of data collected by observing many subjects (such as individuals, firms, countries, or regions) at the one point or period of time. The analysis might also have no regard to differences in time. Analysis of cross-sectional data usually consists of comparing the differences among selected subjects. For example, if we want to measure current obesity levels in a population, we could draw a sample of 1,000 people randomly from that population (also known as a cross section of that population), measure their weight and height, and calculate what percentage of that sample is categorized as obese. This cross-sectional sample provides us with a snapshot of that population, at that one point in time. Note that we do not know based on one cross-sectional sample if obesity is increasing or decreasing; we can only describe the current proportion. Cross-sectional data differs from time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Selection
Model selection is the task of selecting a statistical model from a set of candidate models, given data. In the simplest cases, a pre-existing set of data is considered. However, the task can also involve the design of experiments such that the data collected is well-suited to the problem of model selection. Given candidate models of similar predictive or explanatory power, the simplest model is most likely to be the best choice (Occam's razor). state, "The majority of the problems in statistical inference can be considered to be problems related to statistical modeling". Relatedly, has said, "How hetranslation from subject-matter problem to statistical model is done is often the most critical part of an analysis". Model selection may also refer to the problem of selecting a few representative models from a large set of computational models for the purpose of decision making or optimization under uncertainty. Introduction In its most basic forms, model selection is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual results. Prediction is a similar but more general term. Forecasting might refer to specific formal statistical methods employing time series, cross-sectional or longitudinal data, or alternatively to less formal judgmental methods or the process of prediction and resolution itself. Usage can vary between areas of application: for example, in hydrology the terms "forecast" and "forecasting" are sometimes reserved for estimates of values at certain specific future times, while the term "prediction" is used for more general estimates, such as the number of times floods will occur over a long period. Risk and uncertainty are central to forecasting and prediction; it is generally considered a good practice to indicate the degree of uncertai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |