|
Outbound Systems
Outbound Systems, Inc., was an American computer company based in Boulder, Colorado. Founded by Warren Conner in 1989, the company offered Macintosh clone computer systems in various Portable computer, portable form factors between 1989 and 1991. It left the Mac conversion business in 1992 to build Microsoft Windows, Windows-based desktop computers before going bankrupt in 1993. Wallaby laptop The company's first product, the Wallaby, was a Mac clone laptop. It is powered by a 15-MHz Motorola 68000 processor. Later versions increased the clock speed to 20 MHz. The Wallaby laptop was introduced in 1989 and was significantly lighter, at just over 4 kg, and easier to carry than Apple's own Macintosh Portable released at around the same time. Due to Apple's refusal to license the Macintosh Toolbox in read-only memory (ROM), Wallaby users had to install a Mac ROM to make the computer work. The ROM was typically removed from an older Mac, a process that would render the donor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Home rule municipality, home rule city in Boulder County, Colorado, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the most populous city in the county and the List of municipalities in Colorado, 12th-most populous city in Colorado. It is the principal city of the Boulder metropolitan statistical area, which had 330,758 residents in 2020 and is part of the Front Range Urban Corridor. Boulder is located at the base of the foothills of the Rocky Mountains, at an elevation of above sea level. The city is northwest of the Colorado state capital of Denver. Boulder is a college town, hosting the University of Colorado Boulder, the flagship and largest campus of the University of Colorado system as well as numerous research institutes. Starting in 2027, Boulder will become the new home of the Sundance Film Festival. History Archaeological evidence shows that Boul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Matrix Addressing
Passive matrix addressing is an Display addressing scheme, addressing scheme used in early liquid crystal displays, liquid crystal displays (LCDs). It is a matrix addressing scheme, meaning that only ''m'' + ''n'' control signals are required to address an ''m'' × ''n'' display. A pixel in a passive matrix must maintain its state without active driving circuitry until it can be refreshed again. The Wiktionary:signal, signal is divided into a row or ''select signal'' and a column or ''video signal''. The select voltage determines the row that is being addressed and all ''n'' pixels on a row are addressed simultaneously. When pixels on a row are being addressed, a ''Vsel'' potential is applied, and all other rows are unselected with a ''Vunsel'' potential. The video signal or column potential is then applied with a potential for each ''m'' columns individually. An on-switched (lit) pixel corresponds to a ''Von'', an off-switched (unlit) corresponds to a ''Vof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Companies Disestablished In 1991
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
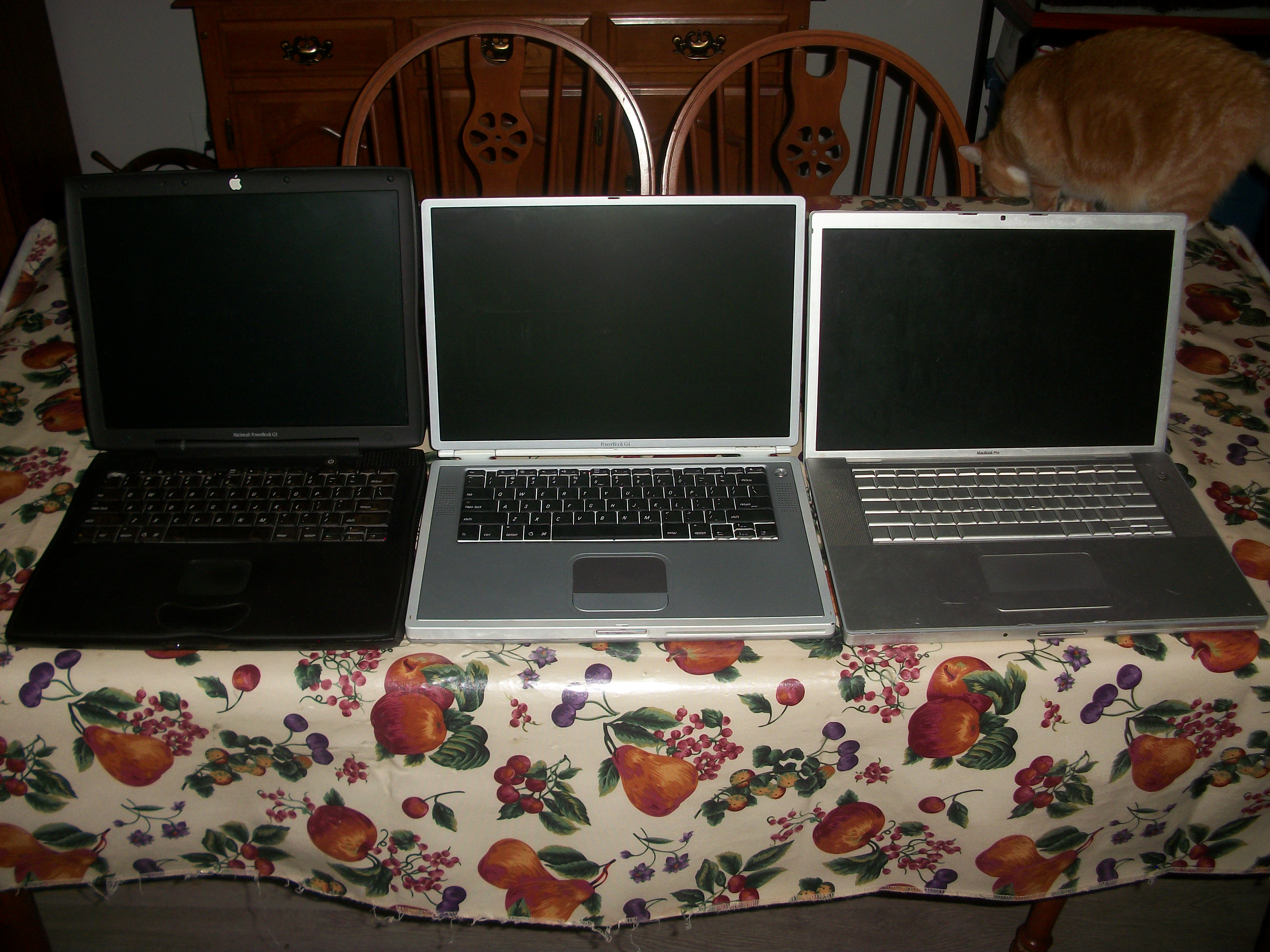
PowerBook
The PowerBook (known as Macintosh PowerBook before 1997) is a family of Macintosh-type laptop computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from 1991 to 2006. It was targeted at the professional market; in 1999, the line was supplemented by the home and education-focused iBook family. During its lifetime, the PowerBook went through several major revisions and redesigns, often being the first to incorporate features that would later become standard in competing laptops. The PowerBook was replaced by the MacBook Pro in 2006 as part of the Mac transition to Intel processors. 680x0-based models PowerBook 100 series In October 1991, Apple released the first three PowerBooks: the low-end PowerBook 100, the more powerful PowerBook 140, and the high end PowerBook 170, the only one with an active matrix display. These machines caused a stir in the industry with their compact dark grey cases, built-in trackball, and the innovative positioning of the keyboard tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAM Disk
A RAM drive (also called a RAM disk) is a block of random-access memory ( primary storage or volatile memory) that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive (secondary storage). RAM drives provide high-performance temporary storage for demanding tasks and protect non-volatile storage devices from wearing down, since RAM is not prone to wear from writing, unlike non-volatile flash memory. It is sometimes referred to as a virtual RAM drive or software RAM drive to distinguish it from a hardware RAM drive that uses separate hardware containing RAM, which is a type of battery-backed solid-state drive. Historically primary storage based mass storage devices were conceived to bridge the performance gap between internal memory and secondary storage devices. In the advent of solid-state devices this advantage lost most of its appeal. However, solid-state devices do suffer from wear from frequent writing. Primary memory writes do not so or in far lesser eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System 7
System 7 (later named Mac OS 7) is the seventh major release of the classic Mac OS operating system for Macintosh computers, made by Apple Computer. It was launched on May 13, 1991, to succeed System 6 with virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, TrueType fonts, the Force Quit dialog, and an improved user interface. It was code-named "Big Bang" in development and the initial release was named "The System" or "System" like all earlier versions. With version 7.5.1, the name "Mac OS" debuted on the boot screen, and the operating system was officially renamed to Mac OS in 1997 with version 7.6. The Mac OS 7 line was the longest-lasting major version of the Classic Mac OSes due to the troubled development of Copland, an operating system intended to be the successor to OS 7 before its cancellation and replacement with Mac OS 8. Development By 1988, the Macintosh had been on the market for four years. Some aspects of the operating system were beginning to fall behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
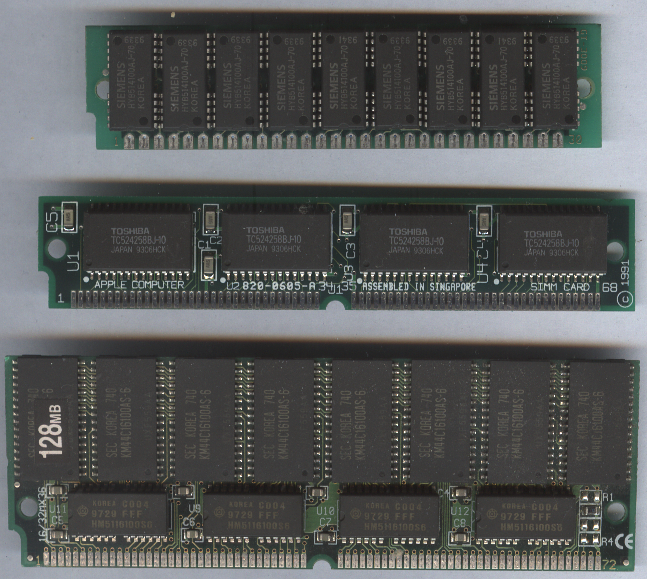
SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or both sides. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards ( 8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1983 by James E. ClaytonClayton, James E. (1983)Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daughtercard
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus slot) on a computer's motherboard (see also backplane) to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most (or all) of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard. Expansion cards allow the capabilities and interfaces of a computer system to be extended or supplemented in a way appropriate to the tasks it will perform. For example, a high-speed multi-channel data acquisition system would be of no use in a personal computer used for bookkeeping, but might be a key part of a system used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
68882
The Motorola 68881 and Motorola 68882 are floating-point units (FPUs) used in some computer systems in conjunction with Motorola's 32-bit 68020 or 68030 microprocessors. These coprocessors are external chips, designed before floating point math became standard on CPUs. The Motorola 68881 was introduced in 1984. The 68882 is a higher performance version produced later. Overview The 68020 and 68030 CPUs were designed with the separate 68881 chip in mind. Their instruction sets reserved the "F-line" instructions – that is, all opcodes beginning with the hexadecimal digit "F" could either be forwarded to an external coprocessor or be used as "traps" which would throw an exception, handing control to the computer's operating system. If an FPU is not present in the system, the OS would then either call an FPU emulator to execute the instruction's equivalent using 68020 integer-based software code, return an error to the program, terminate the program, or crash and require a reb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced in the 1980s and has seen widespread use on servers and high-end workstations, with new SCSI standards being published as recently as SAS-4 in 2017. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and optical disc drives, although not all controllers can handle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |