|
Old Gallo-Romance Language
Old Gallo-Romance is a Romance language spoken from around 600 to 900 AD. It evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken by the Gallo-Romans during the time of Clovis I's successors belonging to the Merovingian dynasty. Characteristics * Like other Romance languages, Old-Gallo Romance distinguished the masculine and feminine forms. * The noun forms in Old Gallo-Romance were reduced from the Latin six to two, as shown in Old Occitan and Old French, with the nominative ending being -s. * Old Gallo-Italic appears to have used V2 word order. Literature Old Gallo-Romance literature consists of a few texts, with them including the Oaths of Strasbourg (also written in Old High Frankish).''« Moyen Âge : l'affirmation des langues vulgaires »'' in the ''Encyclopædia univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallo-Romans
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire in Roman Gaul. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context. The well-studied meld of cultures in Gaul gives historians a model against which to compare and contrast parallel developments of Romanization in other less-studied Roman provinces. ''Interpretatio romana'' offered Roman names for Gaulish deities such as the smith-god Gobannus; however, of the Celtic deities, only the horse-patroness Epona penetrated Romanized cultures beyond the confines of Gaul. The barbarian invasions began in the late 3rd century and forced upon Gallo-Roman culture fundamental changes in politics, economic underpinning and military organization. The Gothic settlement of 418 offered a double loyalty, as Western Roman authority disintegrated at Rome. The plight of the highly-Romanized governing class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king, and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries. Clovis is important in the historiography of France as "the first king of what would become France." Clovis succeeded his father, Childeric I, as a king of the Salian Franks in 481, and eventually came to rule an area extending from what is now the southern Netherlands to northern France, corresponding in Roman terms to Gallia Belgica (northern Gaul). At the Battle of Soissons (486), he established his military dominance of the Domain of Soissons, rump state of the fragmenting Western Roman Empire, which was then under the command of Sya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Belgium
As a result of being in between Latin and Germanic Europe, and historically being split between different principalities, the nation has multiple official languages. The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch, French, and German. A number of non-official, minority languages and dialects are spoken as well. Official languages Legal status The Belgian Constitution guarantees, since the country's independence, freedom of language in the private sphere. Article 30 specifies that "the use of languages spoken in Belgium is optional; only the law can rule on this matter, and only for acts of the public authorities and for legal matters." For those public authorities, there is extensive language legislation concerning Dutch, French and German, even though the Belgian Constitution does not explicitly mention which languages enjoy official status. Article 4 divides the country into linguistic areas, which form the basis of the federal structure: "Belgium has four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of France
French is the sole official language in France according to the second article of the French Constitution. French, a Gallo-Romance language, is spoken by nearly the entire population of France. In addition to French, several regional languages are also spoken to varying degrees, such as Alsatian, a German dialect (specifically Alemannic; spoken by 1.44% of the national population); Basque, a language isolate; Breton, a Celtic language (spoken by 0.61%); Corsican, an Italo-Dalmatian language; and various other Gallo-Romance languages (Langues d'oïl 1.25%, Occitan 1.33%). Some of these languages are also spoken in neighbouring countries, such as Belgium, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Andorra, or Spain. Status The official language of the French Republic is French (art. 2 of the French Constitution) and the French government is, by law, compelled to communicate primarily in French. The government, furthermore, mandates that commercial advertising be available in Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian language, Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and Regional Italian, regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance languages, Romance group. The majority of languages often labeled as regional are distributed in a dialect continuum, continuum across the regions' administrative boundaries, with speakers from one locale within a single region being typically aware of the features distinguishing their own variety from others spoken nearby. The official and most widely spoken language across the country is Italian, which started off based on the medieval Tuscan dialect, Tuscan of Florence. In parallel, many Italians also communicate in one of the local languages, most of which, like Tuscan, are indigenous evolutions of Vulgar Latin. Some local languages do not stem from Latin, however, but belong to other Indo-European languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The German
Louis the German (German language, German: ''Ludwig der Deutsche''; c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany (German language, German: ''Ludwig II. von Deutschland''), was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the Pious, emperor of Francia, and his first wife, Ermengarde of Hesbaye, he received the appellation ''Germanicus'' shortly after his death, when East Francia became known as the kingdom of Germany. After protracted clashes with his father and his brothers, Louis received the East Frankish kingdom in the Treaty of Verdun (843). His attempts to conquer his half-brother Charles the Bald's West Frankish kingdom in 858–59 were unsuccessful. The 860s were marked by a severe crisis, with the East Frankish rebellions of the sons, as well as struggles to maintain supremacy over his realm. In the Treaty of Meerssen he acquired Lotharingia for the East Frankish kingdom in 87 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichenau Glossary
The Reichenau Glossary is a collection of Latin glosses likely compiled in the 8th century in northern France to assist local clergy in understanding certain words or expressions found in the Vulgate Bible. They constitute an important document in Romance linguistics, particularly Gallo-Romance. Background Over the centuries Jerome’s translation of the Bible () became more difficult to read for novice clergy as a result of the various grammatical, lexical, and phonological changes that Latin was experiencing in the course of its evolution into Romance. To facilitate interpretation, scribes would put together glossaries or collected explanations of words or phrases found in the Vulgate. The words used as glosses tended to be those that were destined to survive in Romance, whilst the words that needed glossing generally were not. What we now know as the Reichenau Glossary was compiled circa the eighth century at the Abbey of Corbie in Picardy. From there it eventually found its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel Conversations
Kassel conversations () is the conventional name of an early medieval text preserved in a manuscript from c. 810. It is held today in the university library of Kassel, Germany (Ms. 4° theol. 24). It contains several parts, among them an , an instructional theological text in Latin. The part that has been of most interest for modern scholarship is that of the so-called Kassel glosses, one of the earliest written documents of the Old High German language. The Kassel glosses are a collection of words and short phrases translated from Latin to Old High German. They appear to have been meant as a practical tool to help speakers of Romance languages to learn Old High German. Among them are everyday phrases such as orders given to servants ''("shave my beard"),'' questions and answers for basic communication ("do you understand? No, I don't"), and a few fragmentary grammar paradigms ("I understand, you understood, we understood"). The most famous entry, however, is a jocular jibe i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Hagège
Claude Hagège (; born 1 January 1936) is a French linguist. Biography He was elected to the Collège de France in 1988 and received several awards for his work, including the Prix de l'Académie Française and the CNRS Gold medal. Famous for being a polyglot, he speaks (or is knowledgeable about) fifty languages, including Italian, English, Arabic, Chinese, Hebrew, Russian, Greek, Guarani, Hungarian, Navajo, Nocte, Punjabi, Persian, Malay, Hindi, Malagasy, Fula, Quechua, Tamil, Tetela, Turkish and Japanese. Publications * ''La Langue mbum de nganha cameroun - phonologie - grammaire'', Paris, Klincksieck, 1970 * ''Le Problème linguistique des prépositions et la solution chinoise'', Paris, Société de linguistique de Paris, 1975 * ''La Phonologie panchronique'', Paris, PUF, 1978 * ''Le Comox lhaamen de Colombie britannique : présentation d'une langue amérindienne''. Amerindia, numéro spécial, Paris, Association d'Ethnolinguistique Amérindienne, 1981 * ''La Structure de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Cerquiglini
Bernard Cerquiglini (born 8 April 1947 in Lyon, France), is a French linguist. A Graduate of the École normale supérieure de Saint-Cloud, having received an agrégé and a doctorate in letters, he was a teacher of linguistics in University of Paris VII, former director of the National Institute for the French language, former vice-president of the '' Conseil supérieur de la langue française'' and president of the French National Reading Observatory. In 1995 Bernard Cerquiglini joined the Oulipo. He was in charge of a governmental studies on a French orthography reform and about national languages in France. He received the title Doctor Honoris Causa at ULIM. Biography Bernard Cerquiglini is, through his paternal lineage, of Italian heritage from the region of Umbria (Perugia). He notably served as the director of schooling (in other words, primary education) at the French Ministry of Education (1985–1987), as director of the Institut national de la langue français ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oaths Of Strasbourg
The Oaths of Strasbourg were a military pact made on 14 February 842 by Charles the Bald and Louis the German against their older brother Lothair I, the designated heir of Louis the Pious, the successor of Charlemagne. One year later the Treaty of Verdun would be signed, with major consequences for Western Europe's geopolitical landscape. Louis the German swore his oath in an early form of Old French so that the soldiers of Charles the Bald could understand him. Likewise, the latter recited his in Old High German so that Louis's soldiers would understand. The Romance section of the Oaths is of special importance to historical linguistics, as it is the oldest extant document in France that was written deliberately and consistently in a form of Romance languages, Romance. Context Centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Charlemagne, who had conquered much of its former territory, announced its Renovatio imperii Romanorum, restoration. Upon his death, he passed this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
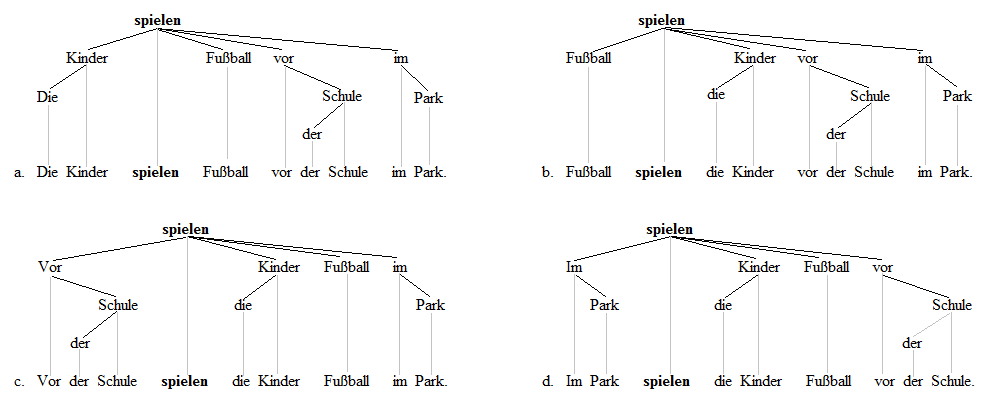
V2 Word Order
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words (a single constituent). Examples of V2 in English include (brackets indicating a single constituent): * "Neither do I", " ever in my lifehave I seen such things" If English used V2 in all situations, then it would feature such sentences as: * " * n schoollearned I about animals", " * hen she comes home from worktakes she a nap" V2 word order is common in the Germanic languages and is also found in Northeast Caucasian Ingush, Uto-Aztecan O'odham, and fragmentarily across Rhaeto-Romance varieties and Finno-Ugric Estonian. Of the Germanic family, English is exceptional in having predominantly SVO order instead of V2, although there are vestiges of the V2 phenomenon. Most Germanic languages do not normally use V2 order in embedded clauses, with a few except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |