|
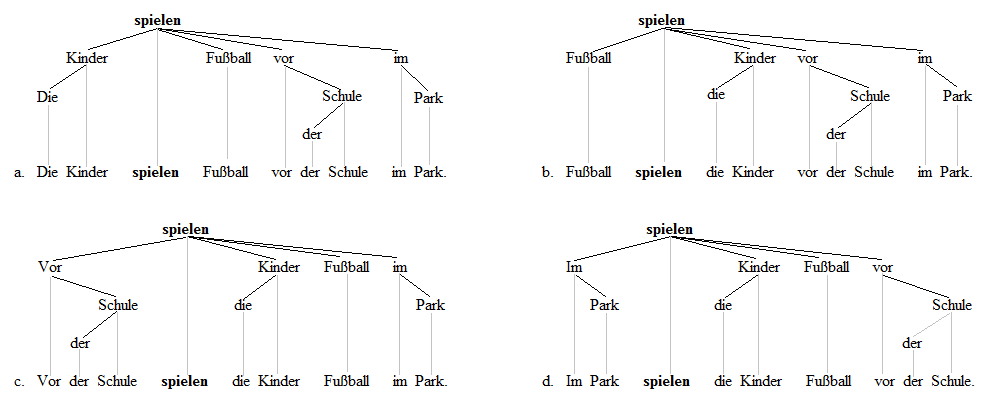
V2 Word Order
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words (a single constituent). Examples of V2 in English include (brackets indicating a single constituent): * "Neither do I", " ever in my lifehave I seen such things" If English used V2 in all situations, then it would feature such sentences as: * " * n schoollearned I about animals", " * hen she comes home from worktakes she a nap" V2 word order is common in the Germanic languages and is also found in Northeast Caucasian Ingush, Uto-Aztecan O'odham, and fragmentarily across Rhaeto-Romance varieties and Finno-Ugric Estonian. Of the Germanic family, English is exceptional in having predominantly SVO order instead of V2, although there are vestiges of the V2 phenomenon. Most Germanic languages do not normally use V2 order in embedded clauses, with a few except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew language, Hebrew (notably Mishnaic Hebrew, Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish has traditionally been written using the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, there were 11–13 million speakers. 85% of the approximately 6 million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hamburg: Buske, 1984), p. 3. leading to a massive decline in the use of the language. Jewish ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specifier (linguistics)
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase structure and a theory of syntactic category formation that proposes a universal schema for how phrases are organized. It suggests that all phrases share a common underlying structure, regardless of their specific category (noun phrase, verb phrase, etc.). This structure, known as the X-bar schema, is based on the idea that every phrase (XP, X phrase) has a Head (linguistics), head, which determines the type (syntactic category) of the phrase (X). The theory was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ''Reading in English Transformational Grammar'', 184–221. Waltham: Ginn. reformulating the ideas of Zellig Harris (1951), and further developed by Ray Jackendoff (1974, 1977a, 1977bJackendoff, Ray (1977b) Constraints on Phrase Structure Rules, in P. W. Culicover, T. Wasow & A. Akmajian (eds.), ''Formal Syntax'', Academic Press, New York, pp. 249– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nynorsk
Nynorsk (; ) is one of the two official written standards of the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. From 12 May 1885, it became the state-sanctioned version of Ivar Aasen's standard Norwegian language (''Landsmål''), parallel to the Dano-Norwegian written standard known as Riksmål. The name Nynorsk was introduced in 1929. After a series of reforms, it is still the written standard closer to , whereas Bokmål is closer to Riksmål and Danish. Between 10 and 15 percent of Norwegians (primarily in the west around the city of Bergen) have Nynorsk as their official language form, estimated by the number of students attending secondary schools. Nynorsk is also taught as a mandatory subject in both high school and middle school for all Norwegians who do not have it as their own language form. History Norway had its own written and oral language—Old Norse, Norwegian. After the Kalmar Union, Norway became a Denmark–Norway, less important part of Denmark. At that time, Dani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bokmål
Bokmål () (, ; ) is one of the official written standards for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is by far the most used written form of Norwegian today, as it is adopted by 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. There is no countrywide standard or agreement on the pronunciation of Bokmål and the Norwegian dialects, spoken dialects vary greatly. Bokmål is regulated by the governmental Language Council of Norway. A related, more conservative Orthography, orthographic standard, commonly known as ''Riksmål'', is regulated by the non-governmental Norwegian Academy for Language and Literature. The written standard is a Norwegianised variety of the Danish language. The first Bokmål orthography was officially adopted in 1907 under the name ''Riksmål'' after being under development since 1879. The architects behind the reform were Marius Nygaard (academic), Marius Nygaard and Jacob Jonathan Aars. It was an adaptation of Danish orthography, written Danish- commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkerdansk
Perkerdansk, Immigrant Danish or Gadedansk is a multi-ethnolect spoken in Denmark, a variety of Danish associated primarily with youth of Middle Eastern ethnic background. It is a contact variety that includes features of Danish as well as Arabic, Turkish, English and other immigrant languages. Particularly common in urban areas with high densities of immigrant populations, its features have also spread to general youth language in Denmark. The term ''perkerdansk'' may be perceived as offensive, just as ''perker'' may be offensive slang for immigrants and descendants of primarily Middle-eastern origin. However, it may also be used as an endonym. The following is an example of Danish spoken by two youth in Copenhagen. Speaker A speaks Berber as a first language and speaker B's first language is Kurdish. Nonetheless, their Danish includes elements of Arabic ('' wallah'' 'I swear') and Turkish (''kız'' 'girl', ''para'' 'money'), and English (''I got'' 'I have', -s plural ending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-finite Verb
Non-finite verbs, are verb forms that do not show tense, person, or number. They include: # Infinitives (e.g., to go, to see) - They often function as nouns or the base form of a verb # Gerunds (e.g., going, seeing) - These act as nouns but are derived from verbs # Participles (e.g., gone, seen) - These can function as adjectives or part of verb tenses (like has gone) Nonfinite verbs are used in constructions where there's no need to express tense directly. They help in creating sentences like "I want to go," where "to go" is nonfinite. In the English language, a non-finite verb cannot perform action as the main verb of an independent clause. Non-finite verb forms in some other languages include converbs, gerundives and supines. The categories of mood, tense, and or voice may be absent from non-finite verb forms in some languages. Because English lacks most inflectional morphology, the finite and the non-finite forms of a verb may appear the same in a given context. Exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Pronoun
Personal pronouns are pronouns that are associated primarily with a particular grammatical person – first person (as ''I''), second person (as ''you''), or third person (as ''he'', ''she'', ''it''). Personal pronouns may also take different forms depending on number (usually singular or plural), grammatical or natural gender, case, and formality. The term "personal" is used here purely to signify the grammatical sense; personal pronouns are not limited to people and can also refer to animals and objects (as the English personal pronoun ''it'' usually does). The re-use in some languages of one personal pronoun to indicate a second personal pronoun with formality or social distance – commonly a second person plural to signify second person singular formal – is known as the T–V distinction, from the Latin pronouns and . Examples are the majestic plural in English and the use of in place of in French. For specific details of the personal pronouns used in the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a Nominal group (functional grammar), nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the Dative case, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( ) is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (linguistics)
In linguistics, inversion is any of several grammatical constructions where two expressions switch their typical or expected order of appearance, that is, they invert. There are several types of subject-verb inversion in English: ''locative inversion'', ''directive inversion'', ''copular inversion'', and ''quotative inversion''. The most frequent type of inversion in English language, English is subject–auxiliary inversion in which an English auxiliaries, auxiliary verb changes places with its subject (grammar), subject; it often occurs in questions, such as ''Are you coming?'', with the subject ''you'' being switched with the auxiliary ''are''. In many other languages, especially those with a freer word order than that of English, inversion can take place with a variety of verbs (not just auxiliaries) and with other syntactic categories as well. When a layered phrase structure grammar, constituency-based analysis of sentence structure is used, inversion often results in the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |