|
Oku No Hosomichi
, translated as ''The Narrow Road to the Deep North'' and ''The Narrow Road to the Interior'', is a major work of ''haibun'' by the List of Japanese language poets, Japanese poet Matsuo Bashō, considered one of the major texts of Japanese literature of the Edo period. The first edition was published posthumously in 1702. The text is written in the form of a prose and Verse (poetry), verse Travel literature, travel diary and was penned as Bashō made an epic and dangerous journey on foot through the Edo period, Edo Japan of the late 17th century. While the Poetry, poetic work became seminal of its own account, the poet's travels in the text have since inspired many people to follow in his footsteps and trace his journey for themselves. In one of its most memorable passages, Bashō suggests that "every day is a journey, and the journey itself home". The text was also influenced by the works of Du Fu, who was highly revered by Bashō. Of ''Oku no Hosomichi'', Kenji Miyazawa once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirakawa, Fukushima
is a city located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 59,393 in 23,546 households and a population density of 190 persons per km2. The total area of the city was . Geography Shirakawa is located in south-central Fukushima prefecture facing the Nasu plateau, and extending to the lowland Shirakawa Basin. *Rivers: Abukuma River Neighboring municipalities * Fukushima Prefecture ** Asakawa ** Ishikawa ** Izumizaki ** Nakajima ** Nishigō ** Tanagura ** Ten'ei ** Yabuki *Tochigi Prefecture ** Nasu Climate Shirakawa has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Shirakawa is 11.4 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1377 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 25.0 °C, and lowest in January, at around 0.3 °C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Tale Of The Heike
is an epic account compiled prior to 1330 of the struggle between the Taira clan and Minamoto clan for control of Japan at the end of the 12th century in the Genpei War (1180–1185). It has been translated into English at least five times. The first translation was by Arthur Lindsay Sadler, in 1918–1921. A complete translation in nearly 800 pages by Hiroshi Kitagawa & Bruce T. Tsuchida was published in 1975. It was also translated by Helen McCullough in 1988. An abridged translation by Burton Watson was published in 2006. In 2012, Royall Tyler completed his translation, which, he says, seeks to be mindful of the performance style for which the work was originally intended. Historical novelist Eiji Yoshikawa published a prose rendering in the '' Asahi Weekly'' in 1950, under the title ' (''Shin Heike Monogatari''). Background Title Heike () refers to the Taira (), ''hei'' being the ''on'yomi'' reading of the first ''kanji'' and "ke" () meaning "family". However, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
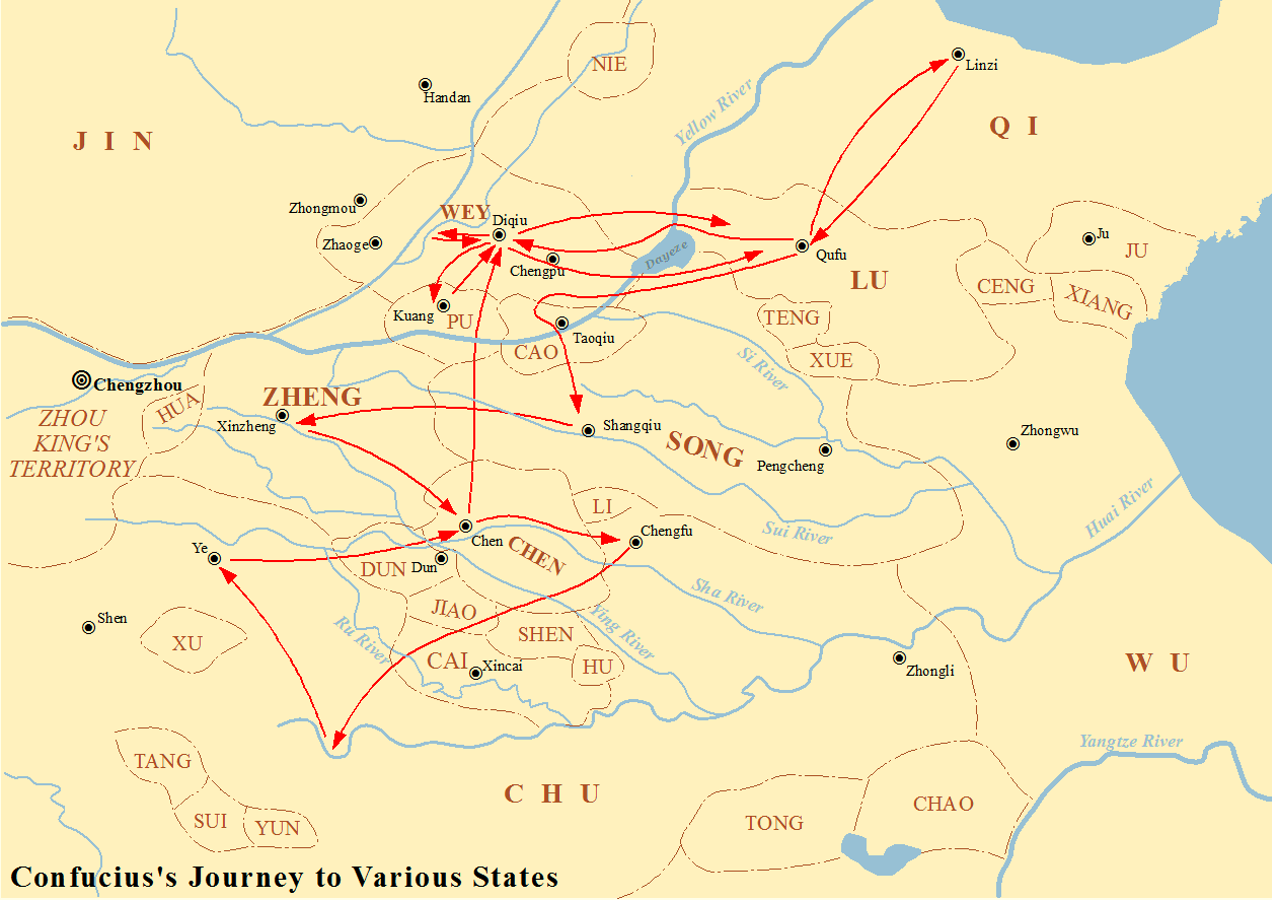
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiku
is a type of short form poetry that originated in Japan. Traditional Japanese haiku consist of three phrases composed of 17 Mora (linguistics), morae (called ''On (Japanese prosody), on'' in Japanese) in a 5, 7, 5 pattern; that include a ''kireji'', or "cutting word"; and a ''kigo'', or seasonal reference. However, haiku by classical Japanese poets, such as Matsuo Bashō, also deviate from the 17-''on'' pattern and sometimes do not contain a ''kireji''. Similar poems that do not adhere to these rules are generally classified as ''senryū''. Haiku originated as an opening part of a larger Japanese genre of poetry called renga. These haiku written as an opening stanza were known as ''hokku'' and over time they began to be written as stand-alone poems. Haiku was given its current name by the Japanese writer Masaoka Shiki at the end of the 19th century. Originally from Japan, haiku today are written by authors worldwide. Haiku in English and Haiku in languages other than Japanese, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetic Diary
or is a Japanese Japanese literature, literary genre, dating back to Ki no Tsurayuki's ''Tosa Nikki'', compiled in roughly 935. Nikki bungaku is a genre including prominent works such as the ''Tosa Nikki'', ''Kagerō Nikki'', and ''The Murasaki Shikibu Diary, Murasaki Shikibu Nikki''. While diaries began as records imitating daily logs kept by Chinese government officials, private and literary diaries emerged and flourished during the Heian period (794–1192 AD). The English term ''poetic diary'' was used by the Princeton University scholar/translator Earl Miner in his book, ''Japanese Poetic Diaries''. Traditionally, composed of a series of poems held together by prose sections, the poetic diary has often taken the form of a pillow book or a travel journal. Since World War II, Beat Generation writers in the United States such as Gary Snyder, Jack Kerouac, Philip Whalen, and Joanne Kyger, as well as post-beat writers such as Andrew Schelling and Michael Rothenberg have studied a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (poetry)
is a type of poetry in classical Japanese literature. Although ''waka'' in modern Japanese is written as , in the past it was also written as (see Wa (Japan), Wa, an old name for Japan), and a variant name is . Etymology The word ''waka'' has two different but related meanings: the original meaning was "poetry in Japanese" and encompassed several genres such as ''chōka'' and ''sedōka'' (discussed below); the later, more common definition refers to poetry in a tanka, 5-7-5-7-7 metre. Up to and during the compilation of the in the eighth century, the word ''waka'' was a general term for poetry composed in Japanese, and included several genres such as , , and . However, by the time of the ''Kokinshūs compilation at the beginning of the tenth century, all of these forms except for the ''tanka'' and ''chōka'' had effectively gone extinct, and ''chōka'' had significantly diminished in prominence. As a result, the word ''waka'' became effectively synonymous with ''tanka'', and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saigyō
was a Japanese poet of the late Heian and early Kamakura period. Biography Born in Kyoto to a noble family, he lived during the traumatic transition of power between the old court nobles and the new samurai warriors. After the start of the age of Mappō, Buddhism was considered to be in decline and no longer as effective a means of salvation. These cultural shifts during his lifetime led to a sense of melancholy in his poetry. As a youth, he worked as a guard to retired Emperor Toba, but in 1140 at age 22, for reasons now unknown, he quit worldly life to become a monk, taking the religious name . He later took the pen name , meaning "Western Journey", a reference to Amida Buddha and the Western paradise. He lived alone for long periods in his life in Saga, Mt. Koya, Mt. Yoshino, Ise, and many other places, but he is more known for the many long, poetic journeys he took to Northern Honshū that would later inspire Bashō in his '' Narrow Road to the Interior''. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most populous urban areas in the world. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo and parts of six neighboring Prefectures of Japan, prefectures, is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, with 41 million residents . Lying at the head of Tokyo Bay, Tokyo is part of the Kantō region, on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. It is Japan's economic center and the seat of the Government of Japan, Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers Tokyo's central Special wards of Tokyo, 23 special wards, which formerly made up Tokyo City; various commuter towns and suburbs in Western Tokyo, its western area; and two outlying island chains, the Tokyo Islands. Although most of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buson OKUnoHOSOMICHI
was a Japanese poet and painter of the Edo period. He lived from 1716 – January 17, 1784. Along with Matsuo Bashō and Kobayashi Issa, Buson is considered among the greatest poets of the Edo Period. He is also known for completing haiga as a style of art, working with haibun prose, and experimenting with a mixed Chinese-Japanese style of poetry. Biography Early life, training, and travels Buson was born in the village of Kema in Settsu Province (present-day Kema, Miyakojima Ward, Osaka). His original family name was Taniguchi. Buson scarcely discussed his childhood, but it is commonly thought that he was the illegitimate son of the village head and a migrant worker from Yoza. According to the Taniguchi family in Yosano, Kyoto, Buson was the son of a servant woman named Gen, who had come to work in Osaka and had a child with her master. A grave of Gen survives in Yosano. There is an oral tradition that the young Buson had been cared for at the Seyaku-ji temple in Yosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oku No Hosomichi- Separate At Yamanaka
Oku or OKU may refer to: * Oku, Cameroon, subdivision in the Northwest Region of Cameroon ** Lake Oku, a crater lake on the Bamenda Plateau in the Northwest Region of Cameroon ** Mount Oku, the largest volcano in the Oku Massif, in the Cameroon Volcanic Line * Oku language, a Grassfields Bantu language of Cameroon * Oku people (Sierra Leone), an ethnic group of Yoruba descent in Sierra Leone. * Ökü, a village in Azerbaijan * Oku District, Okayama, a former district located in Okayama Prefecture, Japan ** Oku, Okayama, a former town in the district, merged with other towns to create the city of Setouchi * Oku (surname), a common Japanese surname * Princess Ōku Ōku (Japanese: or ) (February 12, 661 – January 29, 702) was a Japanese princess during the Asuka period in Japanese history. She was the daughter of Emperor Tenmu and sister of Prince Ōtsu. As a young girl, she witnessed the Jinshin War. ... (661–702), a Japanese princess during the Asuka period in Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |