|
Octoechos (liturgy)
The book Octoechos (from the Greek language, Greek: ; from wikt:οκτώ, ὀκτώ 'eight' and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος 'sound, mode' called echos; , from wikt:осмь, о́смь 'eight' and wikt:гласъ, гласъ 'voice, sound') is a liturgical book containing a repertoire of hymns ordered in eight parts according to eight echoi (Musical mode, tones or modes). Originally created in the Monastery of Stoudios during the 9th century as a hymnal complete with musical notation, it is still used in many Christian liturgy, rites of Eastern Christianity. The book with similar function in the Western Christianity, Western Church is the tonary, and both contain the melodic models of an Hagiopolitan Octoechos, octoechos system; however, while the tonary serves simply for a modal classification, the octoechos is organized as a cycle of eight weeks of services. The word itself can also refer to the repertoire of hymns sung during the celebrations of the Liturgy of the Hours, Sunda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kontakion
A kontakion (Greek , ''kondákion'', plural κοντάκια, ''kondákia'') is a form of hymn in the Byzantine liturgical tradition. The kontakion form originated in Syriac hymnography and gained prominence in Byzantium during the 6th century, particularly through the work of St. Romanos the Melodist of Emesa. Kontakia have a number of strophes (''oikoi'' or ''ikoi'', stanzas; singular ''oikos'' or ''ikos'') and begin with a prologue (the ''prooimoion'' or ''koukoulion''). A kontakion sometimes has a biblical theme and may feature a dialogue between biblical characters. The only kontakion that is used in full length today is the Akathist to the Theotokos. Etymology The word ''kontakion'' derives from the Greek κόνταξ (''kóntax''), which means "rod" or "stick" and refers specifically to the rod around which a scroll is wound. While the genre dates to at least the 6th century, the word itself is attested only in the 9th century. The name is likely a reference to the fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menaion
The Menaion (; Slavonic: Минїѧ, ''Miniya'', "of the month") is the liturgical book used by the Eastern Orthodox Churchand those Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite containing the propers for fixed dates of the calendar year, ''i.e.'' entities not dependent on the date of Easter. The Menaion is the largest volume of the propers for the Byzantine Rite and is used at nearly all the daily services. Editions The complete Menaion is published in twelve volumes, one for each month; the first volume is for September which commences the Byzantine liturgical year. The Festal Menaion is an abridged version containing texts for those great feasts falling on the fixed cycle, some editions also containing feasts of the major saints. The General Menaion contains services for each type of celebration ( apostles, martyrs, etc.) with blank spaces for the name of the saint(s) commemorated. Originating before the invention of printing when the enormous volume of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Notation
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music. Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods. For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves, time signatures, key signatures, and noteheads for writing and deciphering pieces. But even so, there are far more systems just that, for instance in professional country music, the Nashville Number System is the main method, and for string instruments such as guitar, it is quite common for tablature to be used by player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiomelon
(Medieval Greek: from , 'unique' and , 'melody'; Church Slavonic: , )—pl. ''idiomela''—is a type of sticheron found in the liturgical books used in the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite, and many other Orthodox communities like Old Believers. are unique compositions, while or —sing. , or (Medieval Greek: , Church Slavonic: , )—were used to create other hymns by a composition over the 's melody and following the poetic meter provided by the musical rhythm. The genre composed over these was characterised as or (Medieval Greek: 'similar to', Church Slavonic: , ). Definition of ''idiomelon'', ''avtomelon'' and ''prosomoion'' The hymn category can only be understood in comparison with and . Already in the older book Tropologion each melody of a certain hymn was classified by a modal signature of the Byzantine music, Byzantine Hagiopolitan Octoechos, octoechos—the eight-mode system as it had developed in Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valaam Monastery
The Valaam Monastery (; ) is a stauropegic Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox monastery in Russian Republic of Karelia, Karelia, located on Valaam, the largest island in Lake Ladoga, the largest lake in Europe. History It is not clear when the monastery was founded, as the cloister is not mentioned in documents before the 16th century. Dates from the 10th to the 15th centuries having been suggested. According to one tradition, the monastery was founded by a 10th-century Greek monk, Sergius of Valaam, and his Karelian companion, Herman of Valaam. Heikki Kirkinen dated the foundation of the monastery to the 12th century. Contemporary historians consider even this date too early. According to the scholarly consensus, the monastery was founded at some point towards the end of the 14th century. John H. Lind and Michael C. Paul date the founding to between 1389 and 1393 based on various sources, including the "Tale of the Valamo Monastery", a sixteenth-century manuscript discovered in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automelon
(Medieval Greek: from , 'unique' and , 'melody'; Church Slavonic: , )—pl. ''idiomela''—is a type of sticheron found in the liturgical books used in the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite, and many other Orthodox communities like Old Believers. are unique compositions, while or —sing. , or (Medieval Greek: , Church Slavonic: , )—were used to create other hymns by a composition over the 's melody and following the poetic meter provided by the musical rhythm. The genre composed over these was characterised as or (Medieval Greek: 'similar to', Church Slavonic: , ). Definition of ''idiomelon'', ''avtomelon'' and ''prosomoion'' The hymn category can only be understood in comparison with and . Already in the older book Tropologion each melody of a certain hymn was classified by a modal signature of the Byzantine octoechos—the eight-mode system as it had developed in Constantinople, Damascus, Jerusalem, and in ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymn Tune
A hymn tune is the melody of a musical composition to which a hymn text is sung. Musically speaking, a hymn is generally understood to have four-part (or more) harmony, a fast harmonic rhythm (chords change frequently), with or without refrain or chorus. From the late sixteenth century in England and Scotland, when most people were not musically literate and learned melodies by rote, it was a common practice to sing a new text to a hymn tune the singers already knew which had a suitable meter and character. There are many hymn tunes which might fit a particular hymn: a hymn in Long Metre might be sung to any hymn tune in Long Metre, but the tunes might be as different as those tunes that have been used for centuries with hymns such as '' Te lucis ante terminum'', on one hand, and an arrangement of the calypso tune used with '' Jamaica Farewell'', on the other. Hymnal editors Editors bring extensive knowledge of theology, poetry, and music to the process of compiling a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
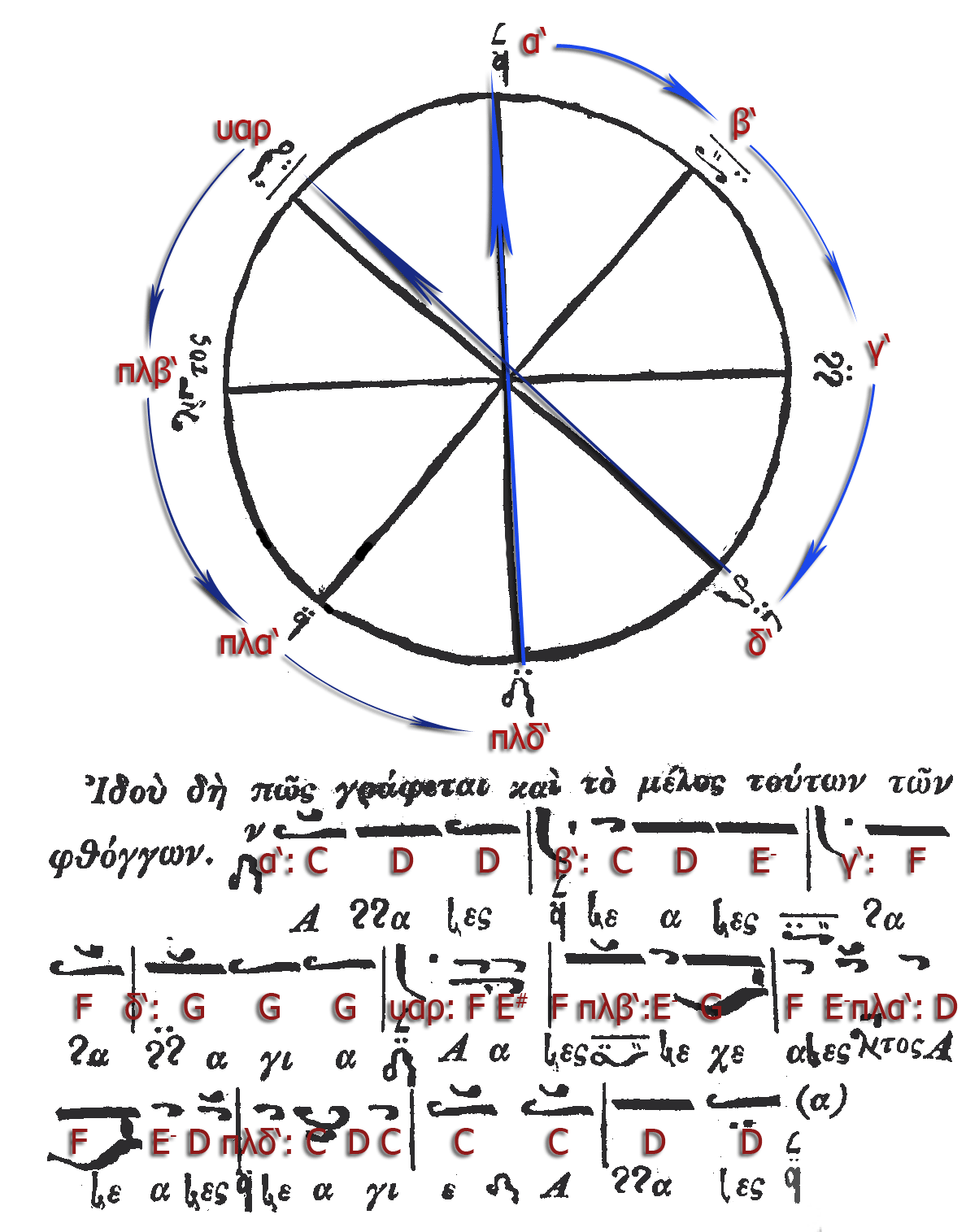
Neobyzantine Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed "Octoechos"; Greek language, Greek: ; from wikt:ὀκτώ, ὀκτώ "eight" and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Church Slavonic, Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from wikt:осмь, о́смь "eight" and wikt:гласъ, гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight musical mode, mode system used for the composition of religious chant in Byzantine, Syriac, Armenian, Georgian, Latin and Slavic churches since the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today. From a Phanariotes, Phanariot point of view, the re-formulation of the Octoechos and its melodic models according to the New Method was neither a simplification of the Byzantine tradition nor an adaption to Western tonality and its method of an heptaphonic solfeggio, just based on one tone system (σύστημα κατὰ ἑπταφωνίαν). Quite the opposite, as a u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |