Musical notation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods.
For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves,
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods.
For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves,
 The earliest form of musical notation can be found in a
The earliest form of musical notation can be found in a 

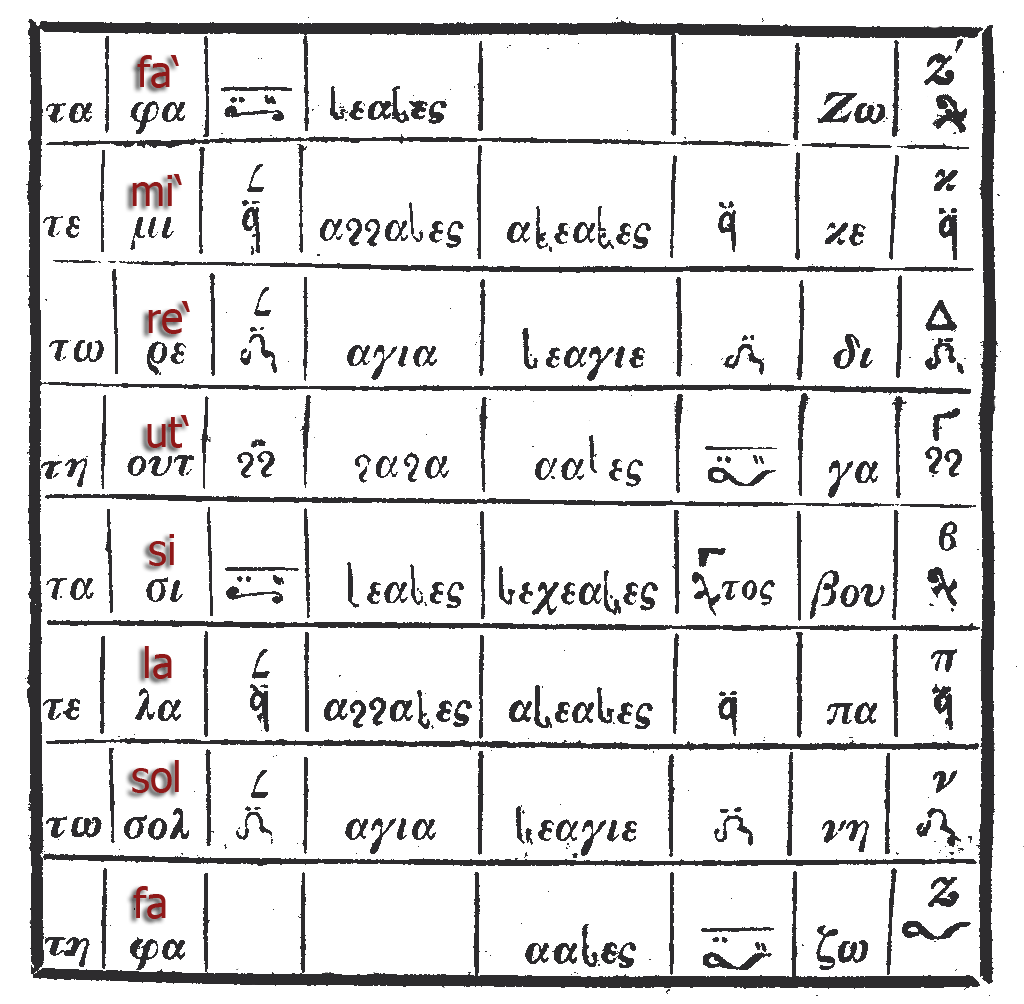 Since Chrysanthos of Madytos there are seven standard note names used for "solfège" (''parallagē'') ''pá, vú, ghá, dhi, ké, zō, nē'', while the older practice still used the four enechemata or intonation formulas of the four echoi given by the modal signatures, the authentic or ''kyrioi'' in ascending direction, and the plagal or ''plagioi'' in descending direction ( Papadic Octoechos). With exception of ''vú and zō'' they do roughly correspond to Western solmization syllables as ''re, mi, fa, sol, la, si, do''. Byzantine music uses the eight natural, non-tempered scales whose elements were identified by ''Ēkhoi'', "sounds", exclusively, and therefore the absolute pitch of each note may slightly vary each time, depending on the particular ''Ēkhos'' used. Byzantine notation is still used in many Orthodox Churches. Sometimes cantors also use transcriptions into Western or Kievan staff notation while adding non-notatable embellishment material from memory and "sliding" into the natural scales from experience, but even concerning modern neume editions since the reform of Chrysanthos a lot of details are only known from an oral tradition related to traditional masters and their experience.
Since Chrysanthos of Madytos there are seven standard note names used for "solfège" (''parallagē'') ''pá, vú, ghá, dhi, ké, zō, nē'', while the older practice still used the four enechemata or intonation formulas of the four echoi given by the modal signatures, the authentic or ''kyrioi'' in ascending direction, and the plagal or ''plagioi'' in descending direction ( Papadic Octoechos). With exception of ''vú and zō'' they do roughly correspond to Western solmization syllables as ''re, mi, fa, sol, la, si, do''. Byzantine music uses the eight natural, non-tempered scales whose elements were identified by ''Ēkhoi'', "sounds", exclusively, and therefore the absolute pitch of each note may slightly vary each time, depending on the particular ''Ēkhos'' used. Byzantine notation is still used in many Orthodox Churches. Sometimes cantors also use transcriptions into Western or Kievan staff notation while adding non-notatable embellishment material from memory and "sliding" into the natural scales from experience, but even concerning modern neume editions since the reform of Chrysanthos a lot of details are only known from an oral tradition related to traditional masters and their experience.
 The scholar and music theorist Isidore of Seville, while writing in the early 7th century, considered that "unless sounds are held by the memory of man, they perish, because they cannot be written down." By the middle of the 9th century, however, a form of neumatic notation began to develop in monasteries in Europe as a
The scholar and music theorist Isidore of Seville, while writing in the early 7th century, considered that "unless sounds are held by the memory of man, they perish, because they cannot be written down." By the middle of the 9th century, however, a form of neumatic notation began to develop in monasteries in Europe as a  Notation had developed far enough to notate melody, but there was still no system for notating rhythm. A mid-13th-century treatise, '' De Mensurabili Musica'', explains a set of six rhythmic modes that were in use at the time, although it is not clear how they were formed. These rhythmic modes were all in triple time and rather limited rhythm in chant to six different repeating patterns. This was a flaw seen by German music theorist Franco of Cologne and summarised as part of his treatise ''Ars Cantus Mensurabilis'' (the art of measured chant, or
Notation had developed far enough to notate melody, but there was still no system for notating rhythm. A mid-13th-century treatise, '' De Mensurabili Musica'', explains a set of six rhythmic modes that were in use at the time, although it is not clear how they were formed. These rhythmic modes were all in triple time and rather limited rhythm in chant to six different repeating patterns. This was a flaw seen by German music theorist Franco of Cologne and summarised as part of his treatise ''Ars Cantus Mensurabilis'' (the art of measured chant, or
 Modern music notation is used by musicians of many different genres throughout the world. The staff (or stave, in British English) consists of 5 parallel horizontal lines which acts as a framework upon which pitches are indicated by placing oval note-heads on (ie crossing) the staff lines, between the lines (ie in the spaces) or above and below the staff using small additional lines called ledger lines. Notation is read from left to right, which makes setting music for right-to-left scripts difficult. The pitch of a note is indicated by the vertical position of the note-head within the staff, and can be modified by accidentals. The duration (note length or note value) is indicated by the form of the note-head or with the addition of a note-stem plus beams or flags. A stemless hollow oval is a whole note or semibreve, a hollow rectangle or stemless hollow oval with one or two vertical lines on both sides is a double whole note or breve. A stemmed hollow oval is a half note or minim. Solid ovals always use stems, and can indicate quarter notes (crotchets) or, with added beams or flags, smaller subdivisions. Additional symbols such as dots and ties can lengthen the duration of a note.
A staff of written music generally begins with a clef, which indicates the pitch-range of the staff. The treble clef or G clef was originally a letter G and it identifies the second line up on the five line staff as the note G above middle C. The bass clef or F clef identifies the second line down as the note F below middle C. While the treble and bass clef are the most widely used, other clefs, which identify middle C, are used for some instruments, such as the alto clef (for viola and alto trombone) and the tenor clef (used for some
Modern music notation is used by musicians of many different genres throughout the world. The staff (or stave, in British English) consists of 5 parallel horizontal lines which acts as a framework upon which pitches are indicated by placing oval note-heads on (ie crossing) the staff lines, between the lines (ie in the spaces) or above and below the staff using small additional lines called ledger lines. Notation is read from left to right, which makes setting music for right-to-left scripts difficult. The pitch of a note is indicated by the vertical position of the note-head within the staff, and can be modified by accidentals. The duration (note length or note value) is indicated by the form of the note-head or with the addition of a note-stem plus beams or flags. A stemless hollow oval is a whole note or semibreve, a hollow rectangle or stemless hollow oval with one or two vertical lines on both sides is a double whole note or breve. A stemmed hollow oval is a half note or minim. Solid ovals always use stems, and can indicate quarter notes (crotchets) or, with added beams or flags, smaller subdivisions. Additional symbols such as dots and ties can lengthen the duration of a note.
A staff of written music generally begins with a clef, which indicates the pitch-range of the staff. The treble clef or G clef was originally a letter G and it identifies the second line up on the five line staff as the note G above middle C. The bass clef or F clef identifies the second line down as the note F below middle C. While the treble and bass clef are the most widely used, other clefs, which identify middle C, are used for some instruments, such as the alto clef (for viola and alto trombone) and the tenor clef (used for some

 *
*
 The Samaveda text (1200 BCE – 1000 BCE) contains notated melodies, and these are probably the world's oldest surviving ones.Bruno Nettl, Ruth M. Stone, James Porter and Timothy Rice (1999), The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music, Routledge, , pages 242–245 The musical notation is written usually immediately above, sometimes within, the line of Samaveda text, either in syllabic or a numerical form depending on the Samavedic ''Sakha'' (school). The Indian scholar and musical theorist Pingala (c. 200 BCE), in his ''Chanda Sutra'', used marks indicating long and short syllables to indicate meters in Sanskrit poetry.
A rock inscription from circa 7th–8th century CE at Kudumiyanmalai, Tamil Nadu contains an early example of a musical notation. It was first identified and published by archaeologist/epigraphist D. R. Bhandarkar. Written in the Pallava-grantha script of the 7th century, it contains 38 horizontal lines of notations inscribed on a rectangular rock face (dimension of around 13 by 14 feet). Each line of the notation contains 64 characters (characters representing musical notes), written in groups of four notes. The basic characters for the seven notes, 'sa ri ga ma pa dha ni', are seen to be suffixed with the vowels a, i, u, e. For example, in the place of 'sa', any one of 'sa', 'si', 'su' or 'se' is used. Similarly, in place of ri, any one of 'ra', 'ri', 'ru' or 're' is used. Horizontal lines divide the notation into 7 sections. Each section contains 4 to 7 lines of notation, with a title indicating its musical 'mode'. These modes may have been popular at least from the 6th century CE and were incorporated into the Indian 'raga' system that developed later. But some of the unusual features seen in this notation have been given several non-conclusive interpretations by scholars.
In the notation of Indian rāga, a solfege-like system called sargam is used. As in Western solfege, there are names for the seven basic pitches of a major scale (Shadja, Rishabha, Gandhara, Madhyama, Panchama, Dhaivata and Nishada, usually shortened to Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni). The tonic of any scale is named Sa, and the dominant Pa. Sa is fixed in any scale, and Pa is fixed at a fifth above it (a Pythagorean fifth rather than an equal-tempered fifth). These two notes are known as achala swar ('fixed notes').
Each of the other five notes, Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni, can take a 'regular' (shuddha) pitch, which is equivalent to its pitch in a standard major scale (thus, shuddha Re, the second degree of the scale, is a whole-step higher than Sa), or an altered pitch, either a half-step above or half-step below the shuddha pitch. Re, Ga, Dha and Ni all have altered partners that are a half-step lower (Komal-"flat") (thus, komal Re is a half-step higher than Sa).
Ma has an altered partner that is a half-step higher (-"sharp") (thus, Ma is an augmented fourth above Sa). Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni are called ('movable notes'). In the written system of Indian notation devised by Ravi Shankar, the pitches are represented by Western letters. Capital letters are used for the achala swar, and for the higher variety of all the vikrut swar. Lowercase letters are used for the lower variety of the vikrut swar.
Other systems exist for non-twelve-tone
The Samaveda text (1200 BCE – 1000 BCE) contains notated melodies, and these are probably the world's oldest surviving ones.Bruno Nettl, Ruth M. Stone, James Porter and Timothy Rice (1999), The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music, Routledge, , pages 242–245 The musical notation is written usually immediately above, sometimes within, the line of Samaveda text, either in syllabic or a numerical form depending on the Samavedic ''Sakha'' (school). The Indian scholar and musical theorist Pingala (c. 200 BCE), in his ''Chanda Sutra'', used marks indicating long and short syllables to indicate meters in Sanskrit poetry.
A rock inscription from circa 7th–8th century CE at Kudumiyanmalai, Tamil Nadu contains an early example of a musical notation. It was first identified and published by archaeologist/epigraphist D. R. Bhandarkar. Written in the Pallava-grantha script of the 7th century, it contains 38 horizontal lines of notations inscribed on a rectangular rock face (dimension of around 13 by 14 feet). Each line of the notation contains 64 characters (characters representing musical notes), written in groups of four notes. The basic characters for the seven notes, 'sa ri ga ma pa dha ni', are seen to be suffixed with the vowels a, i, u, e. For example, in the place of 'sa', any one of 'sa', 'si', 'su' or 'se' is used. Similarly, in place of ri, any one of 'ra', 'ri', 'ru' or 're' is used. Horizontal lines divide the notation into 7 sections. Each section contains 4 to 7 lines of notation, with a title indicating its musical 'mode'. These modes may have been popular at least from the 6th century CE and were incorporated into the Indian 'raga' system that developed later. But some of the unusual features seen in this notation have been given several non-conclusive interpretations by scholars.
In the notation of Indian rāga, a solfege-like system called sargam is used. As in Western solfege, there are names for the seven basic pitches of a major scale (Shadja, Rishabha, Gandhara, Madhyama, Panchama, Dhaivata and Nishada, usually shortened to Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni). The tonic of any scale is named Sa, and the dominant Pa. Sa is fixed in any scale, and Pa is fixed at a fifth above it (a Pythagorean fifth rather than an equal-tempered fifth). These two notes are known as achala swar ('fixed notes').
Each of the other five notes, Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni, can take a 'regular' (shuddha) pitch, which is equivalent to its pitch in a standard major scale (thus, shuddha Re, the second degree of the scale, is a whole-step higher than Sa), or an altered pitch, either a half-step above or half-step below the shuddha pitch. Re, Ga, Dha and Ni all have altered partners that are a half-step lower (Komal-"flat") (thus, komal Re is a half-step higher than Sa).
Ma has an altered partner that is a half-step higher (-"sharp") (thus, Ma is an augmented fourth above Sa). Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni are called ('movable notes'). In the written system of Indian notation devised by Ravi Shankar, the pitches are represented by Western letters. Capital letters are used for the achala swar, and for the higher variety of all the vikrut swar. Lowercase letters are used for the lower variety of the vikrut swar.
Other systems exist for non-twelve-tone
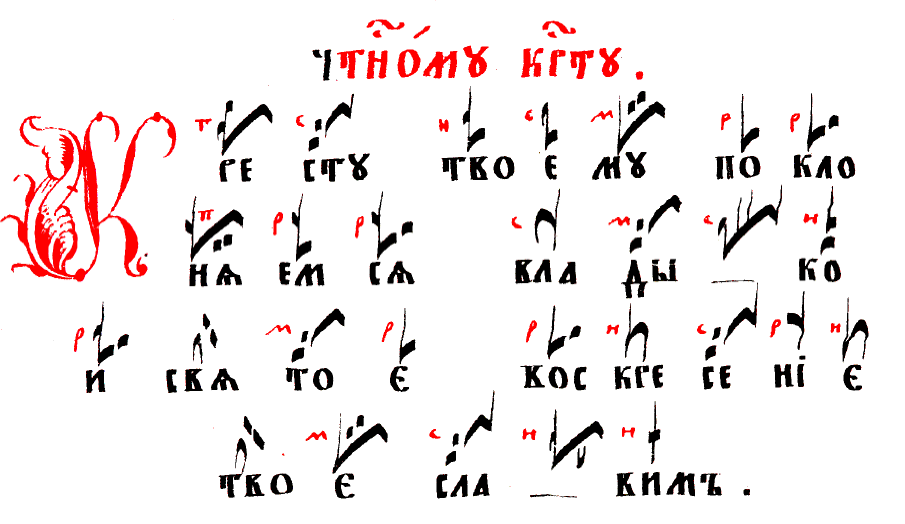
 Znamenny Chant is a singing tradition used in the Russian Orthodox Church which uses a "hook and banner" notation. Znamenny Chant is
Znamenny Chant is a singing tradition used in the Russian Orthodox Church which uses a "hook and banner" notation. Znamenny Chant is
 The earliest known examples of text referring to music in China are inscriptions on musical instruments found in the Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng (d. 433 B.C.). Sets of 41 chimestones and 65 bells bore lengthy inscriptions concerning pitches, scales, and transposition. The bells still sound the pitches that their inscriptions refer to. Although no notated musical compositions were found, the inscriptions indicate that the system was sufficiently advanced to allow for musical notation. Two systems of pitch nomenclature existed, one for relative pitch and one for absolute pitch. For relative pitch, a solmization system was used.
Gongche notation used Chinese characters for the names of the scale.
The earliest known examples of text referring to music in China are inscriptions on musical instruments found in the Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng (d. 433 B.C.). Sets of 41 chimestones and 65 bells bore lengthy inscriptions concerning pitches, scales, and transposition. The bells still sound the pitches that their inscriptions refer to. Although no notated musical compositions were found, the inscriptions indicate that the system was sufficiently advanced to allow for musical notation. Two systems of pitch nomenclature existed, one for relative pitch and one for absolute pitch. For relative pitch, a solmization system was used.
Gongche notation used Chinese characters for the names of the scale.
 Japanese music is highly diversified, and therefore requires various systems of notation. In Japanese
Japanese music is highly diversified, and therefore requires various systems of notation. In Japanese
Image:Surakarta gamelan notation slendro.png, A short melody in slendro notated using the Surakarta method.
Image:Yogyakarta gamelan notation slendro.png, The same notated using the Yogyakarta method or 'chequered notation'.
Image:Kepatihan gamelan notation slendro.png, The same notated using Kepatihan notation.
Image:Western gamelan notation slendro.png, The same approximated using Western notation.
 Ancient Jewish texts include a series of marks assigning musical cantillation notes. Known in Hebrew as Ta'amim and Yiddish as Trope, there are records of these marks from the 6th and 7th centuries, having been passed down as a tradition for Jewish prayers and texts. Traditionally a series of marks written above and around the accompanying Hebrew texts, Trope marks represent a short musical motif. Throughout the Jewish diaspora there are variations in the accompanying melodies. There are three main systems of Hebrew cantillation: The Babylonian System, The Palestinian System, and the Tiberian System.
Ancient Jewish texts include a series of marks assigning musical cantillation notes. Known in Hebrew as Ta'amim and Yiddish as Trope, there are records of these marks from the 6th and 7th centuries, having been passed down as a tradition for Jewish prayers and texts. Traditionally a series of marks written above and around the accompanying Hebrew texts, Trope marks represent a short musical motif. Throughout the Jewish diaspora there are variations in the accompanying melodies. There are three main systems of Hebrew cantillation: The Babylonian System, The Palestinian System, and the Tiberian System.
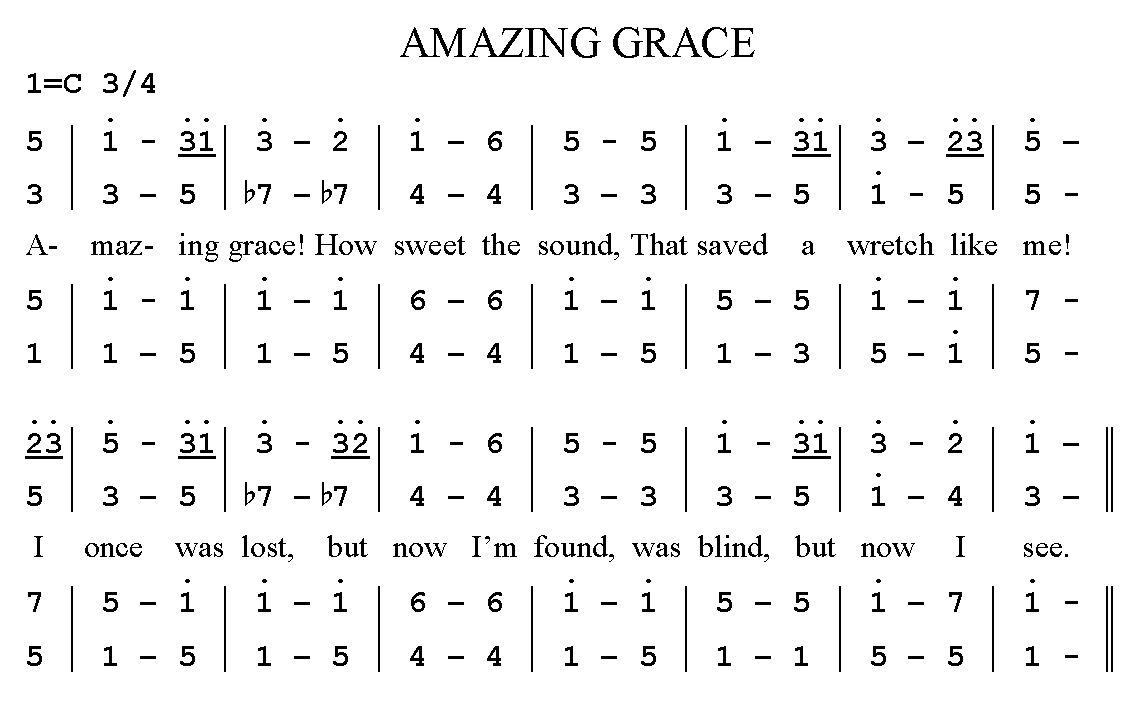 Cipher notation systems assigning Arabic numerals to the major scale degrees have been used at least since the Iberian organ tablatures of the 16th-century and include such exotic adaptations as '' Siffernotskrift''. The one most widely in use today is the Chinese ''Jianpu'', discussed in the main article. Numerals can also be assigned to different scale systems, as in the Javanese '' kepatihan'' notation described above.
Cipher notation systems assigning Arabic numerals to the major scale degrees have been used at least since the Iberian organ tablatures of the 16th-century and include such exotic adaptations as '' Siffernotskrift''. The one most widely in use today is the Chinese ''Jianpu'', discussed in the main article. Numerals can also be assigned to different scale systems, as in the Javanese '' kepatihan'' notation described above.
Byzantine Music Notation
Contains a Guide to Byzantine Music Notation (neumes).
CCARH—Center for Computer Assisted Research in the Humanities
Information on Stanford University Course on music representation. Links page shows examples of different notations.
Music Markup Language
XML-based language for music notation. *
* Gehrkens, Karl Wilson ttps://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/19499 ''Music Notation and Terminology'' Project Gutenberg. * Gilbert, Nina.
Glossary of U.S. and British English musical terms
" Posted 17 June 1998; updated 7 September 2000. {{DEFAULTSORT:Musical Notation Mathematical notation
 Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods.
For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves,
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods.
For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves, time signature
A time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, and measure signature) is an indication in music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type fit into each measure ( bar). The time signature indicates th ...
s, key signatures, and noteheads for writing and deciphering pieces. But even so, there are far more systems just that, for instance in professional country music
Country (also called country and western) is a popular music, music genre originating in the southern regions of the United States, both the American South and American southwest, the Southwest. First produced in the 1920s, country music is p ...
, the Nashville Number System is the main method, and for string instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play some ...
s such as guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, it is quite common for tablature to be used by players.
The symbols used include ancient symbols and modern symbols made upon any media such as symbols cut into stone, made in clay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian language, Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay t ...
s, made using a pen on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
or parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared Tanning (leather), untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves and goats. It has been used as a writing medium in West Asia and Europe for more than two millennia. By AD 400 ...
or manuscript paper; printed using a printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
(), a computer printer () or other printing or modern copying technology.
Although many ancient cultures used symbols to represent melodies and rhythms, none of them were particularly comprehensive, which has limited today's understanding of their music. The direct ancestor of the modern Western system of notation emerged in medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
, in the context of the Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus Christ. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a syn ...
's attempts to standardize the performance of plainsong melodies so that chants could be standardized across different areas. Notation developed further during the Renaissance and Baroque music eras. In the classical period (1750–1820) and the Romantic music era (1820–1900), notation continued to develop as the technology for musical instruments developed. In the contemporary classical music
Contemporary classical music is Western art music composed close to the present day. At the beginning of the 21st-century classical music, 21st century, it commonly referred to the post-1945 Modernism (music), post-tonal music after the death of ...
of the 20th and 21st centuries, music notation has continued to develop, with the introduction of graphical notation by some modern composers and the use, since the 1980s, of computer-based scorewriter programs for notating music. Music notation has been adapted to many kinds of music, including classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
, popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
, and traditional music.
History
Ancient Near East
 The earliest form of musical notation can be found in a
The earliest form of musical notation can be found in a cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
tablet that was created at Nippur, in Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
(today's Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
), in about 1400 BCE. The tablet represents fragmentary instructions for performing music, that the music was composed in harmonies of thirds, and that it was written using a diatonic scale.
A tablet from about 1250 BCE shows a more developed form of notation. Although the interpretation of the notation system is still controversial, it is clear that the notation indicates the names of strings on a lyre, the tuning of which is described in other tablets. Research indicates these notations had dual purposes for liturgical and secular musical pieces since music was essential in both religious ceremonies and courtly activities. Although they are fragmentary, these tablets represent the earliest notated melodies found anywhere in the world.

Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
musical notation was in use from at least the 6th century BCE until approximately the 4th century CE; only one complete composition ( Seikilos epitaph) and a number of fragments using this notation survive.
The notation for sung music consists of letter symbols for the pitches, placed above text syllables. Rhythm is indicated in a rudimentary way only, with long and short symbols. The Seikilos epitaph has been variously dated between the 2nd century BCE to the 2nd century CE.
Three hymns by Mesomedes of Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
exist in manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has ...
. The Delphic Hymns, dated to the 2nd century BCE also use this notation, but they are not completely preserved.
Ancient Greek notation appears to have fallen out of use around the time of the decline of the Western Roman Empire.
Byzantine Empire

Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
music once included music for court ceremonies, but has only survived as vocal church music within various Orthodox traditions of monodic ( monophonic) chant written down in Byzantine round notation (see Macarie's '' anastasimatarion'' with the Greek text translated into Romanian and transliterated into its corresponding Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, C ...
).
Since the 6th century, Greek theoretical categories (''melos'', ''genos'', ''harmonia
In Greek mythology, Harmonia (; /Ancient Greek phonology, harmoˈnia/, "harmony", "agreement") is the goddess of harmony and concord. Her Greek opposite is Eris (mythology), Eris and her Roman mythology, Roman counterpart is Concordia (mythol ...
'', ''systema'') played a key role to understand and transmit Byzantine music, especially the tradition of Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
had a strong impact on the pre-Islamic Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
comparable to the impact coming from Persian music. The earliest evidence are papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
fragments of Greek tropologia. These fragments just present the hymn text following a modal signature or key (like "" for ''echos plagios protos'' or "" for ''echos devteros'').
Unlike Western notation, Byzantine neumes used since the 10th century were always related to modal steps (same modal degree, one degree lower, two degrees higher, etc.) in relation to such a clef or modal key ( modal signatures). Originally this key or the incipit of a common melody was enough to indicate a certain melodic model given within the echos. Next to ekphonetic notation, only used in lectionaries to indicate formulas used during scriptural lessons, melodic notation developed not earlier than between the 9th and the 10th century, when a ''theta'' (), ''oxeia'' () or ''diple'' () were written under a certain syllable of the text, whenever a longer melisma was expected. This primitive form was called "theta" or "diple notation".
Today, one can study the evolution of this notation in Greek monastic chant books like those of the sticherarion and the heirmologion (Chartres notation was rather used on Mount Athos and Constantinople, Coislin notation within the patriarchates of Jerusalem and Alexandria), while there was another gestic notation originally used for the ''asmatikon'' (choir book) and kontakarion (book of the soloist or monophonaris) of the Constantinopolitan cathedral rite. The earliest books which have survived, are "kondakars" in Slavonic translation which already show a notation system known as Kondakarian notation. Like the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
notational signs are ordered left to right (though the direction could be adapted like in certain Syriac manuscripts). The question of rhythm was entirely based on ''cheironomia'' (the interpretation of so-called great signs which derived from different chant books). These great signs () indicated well-known melodic phrases given by gestures of the choirleaders of the cathedral rite. They existed once as part of an oral tradition, developed Kondakarian notation and became, during the 13th century, integrated into Byzantine round notation as a kind of universal notation system.
Today the main difference between Western and Eastern neumes is that Eastern notation symbols are "differential" rather than absolute, i.e., they indicate pitch steps (rising, falling or at the same step), and the musicians know to deduce correctly, from the score and the note they are singing presently, which correct interval is meant. These step symbols themselves, or better "phonic neumes", resemble brush strokes and are colloquially called ''gántzoi'' ('hooks') in modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
.
Notes as pitch classes or modal keys (usually memorised by modal signatures) are represented in written form only between these neumes (in manuscripts usually written in red ink). In modern notation they simply serve as an optional reminder and modal and tempo directions have been added, if necessary. In Papadic notation medial signatures usually meant a temporary change into another echos.
The so-called "great signs" were once related to cheironomic signs; according to modern interpretations they are understood as embellishments and microtonal attractions (pitch changes smaller than a semitone), both essential in Byzantine chant.
 Since Chrysanthos of Madytos there are seven standard note names used for "solfège" (''parallagē'') ''pá, vú, ghá, dhi, ké, zō, nē'', while the older practice still used the four enechemata or intonation formulas of the four echoi given by the modal signatures, the authentic or ''kyrioi'' in ascending direction, and the plagal or ''plagioi'' in descending direction ( Papadic Octoechos). With exception of ''vú and zō'' they do roughly correspond to Western solmization syllables as ''re, mi, fa, sol, la, si, do''. Byzantine music uses the eight natural, non-tempered scales whose elements were identified by ''Ēkhoi'', "sounds", exclusively, and therefore the absolute pitch of each note may slightly vary each time, depending on the particular ''Ēkhos'' used. Byzantine notation is still used in many Orthodox Churches. Sometimes cantors also use transcriptions into Western or Kievan staff notation while adding non-notatable embellishment material from memory and "sliding" into the natural scales from experience, but even concerning modern neume editions since the reform of Chrysanthos a lot of details are only known from an oral tradition related to traditional masters and their experience.
Since Chrysanthos of Madytos there are seven standard note names used for "solfège" (''parallagē'') ''pá, vú, ghá, dhi, ké, zō, nē'', while the older practice still used the four enechemata or intonation formulas of the four echoi given by the modal signatures, the authentic or ''kyrioi'' in ascending direction, and the plagal or ''plagioi'' in descending direction ( Papadic Octoechos). With exception of ''vú and zō'' they do roughly correspond to Western solmization syllables as ''re, mi, fa, sol, la, si, do''. Byzantine music uses the eight natural, non-tempered scales whose elements were identified by ''Ēkhoi'', "sounds", exclusively, and therefore the absolute pitch of each note may slightly vary each time, depending on the particular ''Ēkhos'' used. Byzantine notation is still used in many Orthodox Churches. Sometimes cantors also use transcriptions into Western or Kievan staff notation while adding non-notatable embellishment material from memory and "sliding" into the natural scales from experience, but even concerning modern neume editions since the reform of Chrysanthos a lot of details are only known from an oral tradition related to traditional masters and their experience.
13th-century Near East
In 1252, Safi al-Din al-Urmawi developed a form of musical notation, where rhythms were represented by geometric representation. Many subsequent scholars of rhythm have sought to develop graphical geometrical notations. For example, a similar geometric system was published in 1987 by Kjell Gustafson, whose method represents a rhythm as a two-dimensional graph. Rhythmic notation during its early stages developed Eastern musical traditions while simultaneously establishing concepts that Western music used to build its notation systems later on.Early Europe
 The scholar and music theorist Isidore of Seville, while writing in the early 7th century, considered that "unless sounds are held by the memory of man, they perish, because they cannot be written down." By the middle of the 9th century, however, a form of neumatic notation began to develop in monasteries in Europe as a
The scholar and music theorist Isidore of Seville, while writing in the early 7th century, considered that "unless sounds are held by the memory of man, they perish, because they cannot be written down." By the middle of the 9th century, however, a form of neumatic notation began to develop in monasteries in Europe as a mnemonic
A mnemonic device ( ), memory trick or memory device is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval in the human memory, often by associating the information with something that is easier to remember.
It makes use of e ...
device for Gregorian chant, using symbols known as neumes; the earliest surviving musical notation of this type is in the ''Musica Disciplina'' of Aurelian of Réôme, from about 850. There are scattered survivals from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
before this time, of a type of notation known as Visigothic neumes, but its few surviving fragments have not yet been deciphered. The problem with this notation was that it only showed melodic contours and consequently the music could not be read by someone who did not know the music already.
mensural notation
Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphony, polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measur ...
). He suggested that individual notes could have their own rhythms represented by the shape of the note. Not until the 14th century did something like the present system of fixed note lengths arise. The use of regular measures (bars) became commonplace by the end of the 17th century.
The founder of what is now considered the standard music staff was Guido d'Arezzo, an Italian Benedictine monk who lived from about 991 until after 1033. He taught the use of solmization syllables based on a hymn to Saint John the Baptist, which begins Ut Queant Laxis and was written by the Lombard historian Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon ( 720s 13 April in 796, 797, 798, or 799 AD), also known as ''Paulus Diaconus'', ''Warnefridus'', ''Barnefridus'', or ''Winfridus'', and sometimes suffixed ''Cassinensis'' (''i.e.'' "of Monte Cassino"), was a Benedictine monk, sc ...
. The first stanza is:
# Ut queant laxis
# resonare fibris,
# Mira gestorum
# famuli tuorum,
# Solve polluti
# labii reatum,
# Sancte Iohannes.
Guido used the first syllable of each line, Ut, Re, Mi, Fa, Sol, La, and Si, to read notated music in terms of hexachords; they were not note names, and each could, depending on context, be applied to any note. In the 17th century, Ut was changed in most countries except France to the easily singable, open syllable Do, believed to have been taken either from the name of the Italian theorist Giovanni Battista Doni, or from the Latin word ''Dominus'', meaning ''Lord''.
Christian monks developed the first forms of modern European musical notation in order to standardize liturgy throughout the worldwide Church, and an enormous body of religious music has been composed for it through the ages. This led directly to the emergence and development of European classical music, and its many derivatives. The Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
style, which encompassed music, art, and architecture, was particularly encouraged by the post-Reformation Catholic Church as such forms offered a means of religious expression that was stirring and emotional, intended to stimulate religious fervor.
Modern staff notation
 Modern music notation is used by musicians of many different genres throughout the world. The staff (or stave, in British English) consists of 5 parallel horizontal lines which acts as a framework upon which pitches are indicated by placing oval note-heads on (ie crossing) the staff lines, between the lines (ie in the spaces) or above and below the staff using small additional lines called ledger lines. Notation is read from left to right, which makes setting music for right-to-left scripts difficult. The pitch of a note is indicated by the vertical position of the note-head within the staff, and can be modified by accidentals. The duration (note length or note value) is indicated by the form of the note-head or with the addition of a note-stem plus beams or flags. A stemless hollow oval is a whole note or semibreve, a hollow rectangle or stemless hollow oval with one or two vertical lines on both sides is a double whole note or breve. A stemmed hollow oval is a half note or minim. Solid ovals always use stems, and can indicate quarter notes (crotchets) or, with added beams or flags, smaller subdivisions. Additional symbols such as dots and ties can lengthen the duration of a note.
A staff of written music generally begins with a clef, which indicates the pitch-range of the staff. The treble clef or G clef was originally a letter G and it identifies the second line up on the five line staff as the note G above middle C. The bass clef or F clef identifies the second line down as the note F below middle C. While the treble and bass clef are the most widely used, other clefs, which identify middle C, are used for some instruments, such as the alto clef (for viola and alto trombone) and the tenor clef (used for some
Modern music notation is used by musicians of many different genres throughout the world. The staff (or stave, in British English) consists of 5 parallel horizontal lines which acts as a framework upon which pitches are indicated by placing oval note-heads on (ie crossing) the staff lines, between the lines (ie in the spaces) or above and below the staff using small additional lines called ledger lines. Notation is read from left to right, which makes setting music for right-to-left scripts difficult. The pitch of a note is indicated by the vertical position of the note-head within the staff, and can be modified by accidentals. The duration (note length or note value) is indicated by the form of the note-head or with the addition of a note-stem plus beams or flags. A stemless hollow oval is a whole note or semibreve, a hollow rectangle or stemless hollow oval with one or two vertical lines on both sides is a double whole note or breve. A stemmed hollow oval is a half note or minim. Solid ovals always use stems, and can indicate quarter notes (crotchets) or, with added beams or flags, smaller subdivisions. Additional symbols such as dots and ties can lengthen the duration of a note.
A staff of written music generally begins with a clef, which indicates the pitch-range of the staff. The treble clef or G clef was originally a letter G and it identifies the second line up on the five line staff as the note G above middle C. The bass clef or F clef identifies the second line down as the note F below middle C. While the treble and bass clef are the most widely used, other clefs, which identify middle C, are used for some instruments, such as the alto clef (for viola and alto trombone) and the tenor clef (used for some cello
The violoncello ( , ), commonly abbreviated as cello ( ), is a middle pitched bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), tuned i ...
, bassoon, tenor trombone, and double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
music). Some instruments use mainly one clef, such as violin and flute which use treble clef, and double bass
The double bass (), also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched string instrument, chordophone in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding rare additions ...
and tuba which use bass clef. Some instruments, such as piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
and pipe organ, regularly use both treble and bass clefs.
Following the clef, the key signature is a group of 0 to 7 sharp ( ♯) or flat ( ♭) signs placed on the staff to indicate the key of the piece or song by specifying that certain notes are sharp or flat throughout the piece, unless otherwise indicated with accidentals added before certain notes. When a flat ( ♭) sign is placed before a note, the pitch of the note is lowered by one semitone. Similarly, a sharp sign ( ♯) raises the pitch by one semitone. For example, a sharp on the note D would raise it to D♯ while a flat would lower it to D♭. Double sharps and double flats are less common, but they are used. A double sharp is placed before a note to make it two semitones higher, a double flat - two semitones lower. A natural sign placed before a note renders that note in its "natural" form, which means that any sharp or flat applied to that note from the key signature or an accidental, is cancelled. Sometimes a courtesy accidental is used in music where it is not technically required, to remind the musician of what pitch is required.
Following the key signature is the time signature
A time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, and measure signature) is an indication in music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type fit into each measure ( bar). The time signature indicates th ...
. The time signature typically consists of two numbers, with one of the most common being . The top "4" indicates that there are four beats per measure (also called bar). The bottom "4" indicates that each of those beats are quarter notes. Measures divide the piece into groups of beats, and the time signatures specify those groupings. is used so often that it is also called " common time", and it may be indicated with rather than numbers. Other frequently used time signatures are (three beats per bar, with each beat being a quarter note); (two beats per bar, with each beat being a quarter note); (six beats per bar, with each beat being an eighth note) and (twelve beats per bar, with each beat being an eighth note; in practice, the eighth notes are typically put into four groups of three eighth notes. is a compound time type of time signature). Many other time signatures exist, such as or .
Many short classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
pieces from the classical era
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilization ...
and songs from traditional music and popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
are in one time signature for much or all of the piece. Music from the Romantic music era and later, particularly contemporary classical music
Contemporary classical music is Western art music composed close to the present day. At the beginning of the 21st-century classical music, 21st century, it commonly referred to the post-1945 Modernism (music), post-tonal music after the death of ...
and rock music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdo ...
genres such as progressive rock
Progressive rock (shortened as prog rock or simply prog) is a broad genre of rock music that primarily developed in the United Kingdom through the mid- to late 1960s, peaking in the early-to-mid-1970s. Initially termed " progressive pop", the ...
and the hardcore punk
Hardcore punk (commonly abbreviated to hardcore or hXc) is a punk rock music genre#subtypes, subgenre and subculture that originated in the late 1970s. It is generally faster, harder, and more aggressive than other forms of punk rock. Its roots ...
subgenre mathcore, may use mixed meter; songs or pieces change from one meter to another, for example alternating between bars of and .
Directions to the player regarding matters such as tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition ...
(e.g., Andante) and dynamics (e.g., forte) appear above or below the staff. Terms indicating the musical expression or "feel" to a song or piece are indicated at the beginning of the piece and at any points where the mood changes (e.g., "Gelassen") For vocal music, lyrics are written near the pitches of the melody. For short pauses (breaths), retakes (retakes are indicated with a ' mark) are added.
In music for ensembles, a " score" shows music for all players together, with the staves for the different instruments and/or voices stacked vertically. The conductor uses the score while leading an orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
, concert band, choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
or other large ensemble. Individual performers in an ensemble play from "parts" which contain only the music played by an individual musician. A score can be constructed from a complete set of parts and vice versa. The process was laborious and time consuming when parts were hand-copied from the score, but since the development of scorewriter computer software in the 1980s, a score stored electronically can have parts automatically prepared by the program and quickly and inexpensively printed out using a computer printer.
Variations on staff notation
Percussion notation
Percussion notation is a type of musical notation indicating Musical note, notes to be played by percussion instruments. As with other forms of musical notation, sounds are represented by symbols which are usually written onto a musical Staff (mu ...
conventions are varied because of the wide range of percussion instruments. Percussion instruments are generally grouped into two categories: pitched (e.g. glockenspiel or tubular bells) and non-pitched (e.g. bass drum and snare drum). The notation of non-pitched percussion instruments is less standardized. Pitched instruments use standard Western classical notation for the pitches and rhythms. In general, notation for unpitched percussion uses the five line staff, with different lines and spaces representing different drum kit
A drum kit or drum set (also known as a trap set, or simply drums in popular music and jazz contexts) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and sometimes other Percussion instrument, auxiliary percussion instruments set up to be played by one p ...
instruments. Standard Western rhythmic notation is used to indicate the rhythm.
* Figured bass
Figured bass is musical notation in which numerals and symbols appear above or below (or next to) a bass note. The numerals and symbols (often accidental (music), accidentals) indicate interval (music), intervals, chord (music), chords, and non- ...
notation originated in Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
basso continuo parts. It is also used extensively in accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German language, German ', from '—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a Reed (mou ...
notation. The bass notes of the music are conventionally notated, along with numbers and other signs that determine which chords the harpsichordist, organist or lutenist should improvise. It does not, however, specify the exact pitches of the harmony, leaving that for the performer to improvise.
* A lead sheet specifies only the melody, lyrics and harmony, using one staff with chord symbols placed above and lyrics below. It is used to capture the essential elements of a popular song without specifying how the song should be arranged or performed.
* A chord chart or "chart" contains little or no melodic or voice-leading information at all, but provides basic harmonic information about the chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
. Some chord charts also contain rhythmic information, indicated using slash notation for full beats and rhythmic notation for rhythms. This is the most common kind of written music used by professional session musicians playing jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
or other forms of popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
and is intended primarily for the rhythm section (usually containing piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, bass and drums).
* Simpler chord charts for songs may contain only the chord changes, placed above the lyrics where they occur. Such charts depend on prior knowledge of the melody, and are used as reminders in performance or informal group singing. Some chord charts intended for rhythm section accompanists contain only the chord progression.
* The shape note
Shape notes are a musical notation designed to facilitate congregational and Sing-along, social singing. The notation became a popular teaching device in American singing schools during the 19th century. Shapes were added to the noteheads in ...
system is found in some church hymnals, sheet music, and song books, especially in the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
. Instead of the customary elliptical note head, note heads of various shapes are used to show the position of the note on the major scale. ''The Sacred Harp'' is one of the most popular tune books using shape notes.
In various countries
Korea
''Jeongganbo'' is a traditional musical notation system created during the time of Sejong the Great that was the first East Asian system to represent rhythm, pitch, and time. Among various kinds of Korean traditional music, Jeong-gan-bo targets a particular genre, Jeong-ak (). Jeong-gan-bo specifies the pitch by writing the pitch's name down in a box called 'jeong-gan'. One jeong-gan is one beat each, and it can be split into two, three or more to hold half beats and quarter beats, and more. Also, there are many markings indicating things such as ornaments. Most of these were later created by Ki-su Kim.India
 The Samaveda text (1200 BCE – 1000 BCE) contains notated melodies, and these are probably the world's oldest surviving ones.Bruno Nettl, Ruth M. Stone, James Porter and Timothy Rice (1999), The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music, Routledge, , pages 242–245 The musical notation is written usually immediately above, sometimes within, the line of Samaveda text, either in syllabic or a numerical form depending on the Samavedic ''Sakha'' (school). The Indian scholar and musical theorist Pingala (c. 200 BCE), in his ''Chanda Sutra'', used marks indicating long and short syllables to indicate meters in Sanskrit poetry.
A rock inscription from circa 7th–8th century CE at Kudumiyanmalai, Tamil Nadu contains an early example of a musical notation. It was first identified and published by archaeologist/epigraphist D. R. Bhandarkar. Written in the Pallava-grantha script of the 7th century, it contains 38 horizontal lines of notations inscribed on a rectangular rock face (dimension of around 13 by 14 feet). Each line of the notation contains 64 characters (characters representing musical notes), written in groups of four notes. The basic characters for the seven notes, 'sa ri ga ma pa dha ni', are seen to be suffixed with the vowels a, i, u, e. For example, in the place of 'sa', any one of 'sa', 'si', 'su' or 'se' is used. Similarly, in place of ri, any one of 'ra', 'ri', 'ru' or 're' is used. Horizontal lines divide the notation into 7 sections. Each section contains 4 to 7 lines of notation, with a title indicating its musical 'mode'. These modes may have been popular at least from the 6th century CE and were incorporated into the Indian 'raga' system that developed later. But some of the unusual features seen in this notation have been given several non-conclusive interpretations by scholars.
In the notation of Indian rāga, a solfege-like system called sargam is used. As in Western solfege, there are names for the seven basic pitches of a major scale (Shadja, Rishabha, Gandhara, Madhyama, Panchama, Dhaivata and Nishada, usually shortened to Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni). The tonic of any scale is named Sa, and the dominant Pa. Sa is fixed in any scale, and Pa is fixed at a fifth above it (a Pythagorean fifth rather than an equal-tempered fifth). These two notes are known as achala swar ('fixed notes').
Each of the other five notes, Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni, can take a 'regular' (shuddha) pitch, which is equivalent to its pitch in a standard major scale (thus, shuddha Re, the second degree of the scale, is a whole-step higher than Sa), or an altered pitch, either a half-step above or half-step below the shuddha pitch. Re, Ga, Dha and Ni all have altered partners that are a half-step lower (Komal-"flat") (thus, komal Re is a half-step higher than Sa).
Ma has an altered partner that is a half-step higher (-"sharp") (thus, Ma is an augmented fourth above Sa). Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni are called ('movable notes'). In the written system of Indian notation devised by Ravi Shankar, the pitches are represented by Western letters. Capital letters are used for the achala swar, and for the higher variety of all the vikrut swar. Lowercase letters are used for the lower variety of the vikrut swar.
Other systems exist for non-twelve-tone
The Samaveda text (1200 BCE – 1000 BCE) contains notated melodies, and these are probably the world's oldest surviving ones.Bruno Nettl, Ruth M. Stone, James Porter and Timothy Rice (1999), The Garland Encyclopedia of World Music, Routledge, , pages 242–245 The musical notation is written usually immediately above, sometimes within, the line of Samaveda text, either in syllabic or a numerical form depending on the Samavedic ''Sakha'' (school). The Indian scholar and musical theorist Pingala (c. 200 BCE), in his ''Chanda Sutra'', used marks indicating long and short syllables to indicate meters in Sanskrit poetry.
A rock inscription from circa 7th–8th century CE at Kudumiyanmalai, Tamil Nadu contains an early example of a musical notation. It was first identified and published by archaeologist/epigraphist D. R. Bhandarkar. Written in the Pallava-grantha script of the 7th century, it contains 38 horizontal lines of notations inscribed on a rectangular rock face (dimension of around 13 by 14 feet). Each line of the notation contains 64 characters (characters representing musical notes), written in groups of four notes. The basic characters for the seven notes, 'sa ri ga ma pa dha ni', are seen to be suffixed with the vowels a, i, u, e. For example, in the place of 'sa', any one of 'sa', 'si', 'su' or 'se' is used. Similarly, in place of ri, any one of 'ra', 'ri', 'ru' or 're' is used. Horizontal lines divide the notation into 7 sections. Each section contains 4 to 7 lines of notation, with a title indicating its musical 'mode'. These modes may have been popular at least from the 6th century CE and were incorporated into the Indian 'raga' system that developed later. But some of the unusual features seen in this notation have been given several non-conclusive interpretations by scholars.
In the notation of Indian rāga, a solfege-like system called sargam is used. As in Western solfege, there are names for the seven basic pitches of a major scale (Shadja, Rishabha, Gandhara, Madhyama, Panchama, Dhaivata and Nishada, usually shortened to Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni). The tonic of any scale is named Sa, and the dominant Pa. Sa is fixed in any scale, and Pa is fixed at a fifth above it (a Pythagorean fifth rather than an equal-tempered fifth). These two notes are known as achala swar ('fixed notes').
Each of the other five notes, Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni, can take a 'regular' (shuddha) pitch, which is equivalent to its pitch in a standard major scale (thus, shuddha Re, the second degree of the scale, is a whole-step higher than Sa), or an altered pitch, either a half-step above or half-step below the shuddha pitch. Re, Ga, Dha and Ni all have altered partners that are a half-step lower (Komal-"flat") (thus, komal Re is a half-step higher than Sa).
Ma has an altered partner that is a half-step higher (-"sharp") (thus, Ma is an augmented fourth above Sa). Re, Ga, Ma, Dha and Ni are called ('movable notes'). In the written system of Indian notation devised by Ravi Shankar, the pitches are represented by Western letters. Capital letters are used for the achala swar, and for the higher variety of all the vikrut swar. Lowercase letters are used for the lower variety of the vikrut swar.
Other systems exist for non-twelve-tone equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencie ...
and non-Western music, such as the Indian '' Swaralipi''.
Russia
 Znamenny Chant is a singing tradition used in the Russian Orthodox Church which uses a "hook and banner" notation. Znamenny Chant is
Znamenny Chant is a singing tradition used in the Russian Orthodox Church which uses a "hook and banner" notation. Znamenny Chant is unison
Unison (stylised as UNISON) is a Great Britain, British trade union. Along with Unite the Union, Unite, Unison is one of the two largest trade unions in the United Kingdom, with over 1.2 million members who work predominantly in public servic ...
, melismatic liturgical singing that has its own specific notation, called the ''stolp'' notation. The symbols used in the stolp notation are called ' (, 'hooks') or ' (, 'banners'). Often the names of the signs are used to refer to the stolp notation. Znamenny melodies are part of a system, consisting of Eight Modes (intonation structures; called glasy); the melodies are characterized by fluency and well-balancedness. There exist several types of Znamenny Chant: the so-called ''Stolpovoy'', ''Malyj'' (Little) and ''Bolshoy'' (Great) Znamenny Chant. Ruthenian Chant ( Prostopinije) is sometimes considered a sub-division of the Znamenny Chant tradition, with the Muscovite Chant (Znamenny Chant proper) being the second branch of the same musical continuum.
Znamenny Chants are not written with notes (the so-called linear notation), but with special signs, called ''Znamëna'' (Russian for "marks", "banners") or ''Kryuki'' ("hooks"), as some shapes of these signs resemble hooks. Each sign may include the following components: a large black hook or a black stroke, several smaller black 'points' and 'commas' and lines near the hook or crossing the hook. Some signs may mean only one note, some 2 to 4 notes, and some a whole melody of more than 10 notes with a complicated rhythmic structure. The stolp notation was developed in Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
as an East Slavic refinement of the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
neumatic musical notation.
The most notable feature of this notation system is that it records transitions of the melody, rather than notes. The signs also represent a mood and a gradation of how this part of melody is to be sung (tempo, strength, devotion, meekness, etc.) Every sign has its own name and also features as a spiritual symbol. For example, there is a specific sign, called "little dove" (Russian: голубчик ''(golubchik)''), which represents two rising sounds, but which is also a symbol of the Holy Ghost. Gradually the system became more and more complicated. This system was also ambiguous, so that almost no one, except the most trained and educated singers, could sing an unknown melody at sight. The signs only helped to reproduce the melody, not coding it in an unambiguous way.
(See Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
)
China
 The earliest known examples of text referring to music in China are inscriptions on musical instruments found in the Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng (d. 433 B.C.). Sets of 41 chimestones and 65 bells bore lengthy inscriptions concerning pitches, scales, and transposition. The bells still sound the pitches that their inscriptions refer to. Although no notated musical compositions were found, the inscriptions indicate that the system was sufficiently advanced to allow for musical notation. Two systems of pitch nomenclature existed, one for relative pitch and one for absolute pitch. For relative pitch, a solmization system was used.
Gongche notation used Chinese characters for the names of the scale.
The earliest known examples of text referring to music in China are inscriptions on musical instruments found in the Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng (d. 433 B.C.). Sets of 41 chimestones and 65 bells bore lengthy inscriptions concerning pitches, scales, and transposition. The bells still sound the pitches that their inscriptions refer to. Although no notated musical compositions were found, the inscriptions indicate that the system was sufficiently advanced to allow for musical notation. Two systems of pitch nomenclature existed, one for relative pitch and one for absolute pitch. For relative pitch, a solmization system was used.
Gongche notation used Chinese characters for the names of the scale.
Japan
 Japanese music is highly diversified, and therefore requires various systems of notation. In Japanese
Japanese music is highly diversified, and therefore requires various systems of notation. In Japanese shakuhachi
A is a Japanese longitudinal, end-blown flute that is made of bamboo. The bamboo end-blown flute now known as the was developed in Japan in the 16th century and is called the .
music, for example, glissandos and timbres are often more significant than distinct pitches, whereas taiko
are a broad range of Traditional Japanese musical instruments, Japanese percussion instruments. In Japanese language, Japanese, the term refers to any kind of drum, but outside Japan, it is used specifically to refer to any of the various J ...
notation focuses on discrete strokes.
Ryukyuan sanshin music uses kunkunshi, a notation system of kanji
are logographic Chinese characters, adapted from Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script, used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are ...
with each character corresponding to a finger position on a particular string.
Indonesia
Notation plays a relatively minor role in the oral traditions ofIndonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
. However, in Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
and Bali
Bali (English:; Balinese language, Balinese: ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller o ...
, several systems were devised beginning at the end of the 19th century, initially for archival purposes. Today the most widespread are cipher notations ("not angka" in the broadest sense) in which the pitches are represented with some subset of the numbers 1 to 7, with 1 corresponding to either highest note of a particular octave, as in Sundanese gamelan
Gamelan (; ; , ; ) is the traditional musical ensemble, ensemble music of the Javanese people, Javanese, Sundanese people, Sundanese, and Balinese people, Balinese peoples of Indonesia, made up predominantly of percussion instrument, per ...
, or lowest, as in the kepatihan notation of Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
nese gamelan
Gamelan (; ; , ; ) is the traditional musical ensemble, ensemble music of the Javanese people, Javanese, Sundanese people, Sundanese, and Balinese people, Balinese peoples of Indonesia, made up predominantly of percussion instrument, per ...
.
Notes in the ranges outside the central octave are represented with one or more dots above or below the each number. For the most part, these cipher notations are mainly used to notate the skeletal melody (the balungan) and vocal parts ( gerongan), although transcriptions of the elaborating instrument variations are sometimes used for analysis and teaching. Drum parts are notated with a system of symbols largely based on letters representing the vocables used to learn and remember drumming patterns; these symbols are typically laid out in a grid underneath the skeletal melody for a specific or generic piece.
The symbols used for drum notation (as well as the vocables represented) are highly variable from place to place and performer to performer. In addition to these current systems, two older notations used a kind of staff: the Solo
Solo or SOLO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Characters
* Han Solo, a ''Star Wars'' character
* Jacen Solo, a Jedi in the non-canonical ''Star Wars Legends'' continuity
* Kylo Ren (Ben Solo), a ''Star Wars'' character
* Napoleon Solo, fr ...
nese script could capture the flexible rhythms of the pesinden with a squiggle on a horizontal staff, while in Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta is the capital city of the Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by Hamengkubuwono, a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an importan ...
a ladder-like vertical staff allowed notation of the balungan by dots and also included important drum strokes. In Bali, there are a few books published of Gamelan gender wayang pieces, employing alphabetical notation in the old Balinese script.
Composers and scholars both Indonesian and foreign have also mapped the slendro and pelog tuning systems of gamelan onto the western staff, with and without various symbols for microtones. The Dutch composer Ton de Leeuw also invented a three line staff for his composition ''Gending''. However, these systems do not enjoy widespread use.
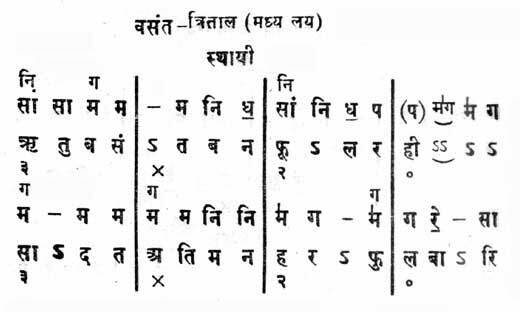
In the second half of the twentieth century, Indonesian musicians and scholars extended cipher notation to other oral traditions, and a diatonic scale cipher notation has become common for notating western-related genres (church hymns, popular songs, and so forth). Unlike the cipher notation for gamelan music, which uses a "fixed Do" (that is, 1 always corresponds to the same pitch, within the natural variability of gamelan tuning), Indonesian diatonic cipher notation is "moveable-Do" notation, so scores must indicate which pitch corresponds to the number 1 (for example, "1=C").
Judea
Other systems and practices
Cipher notation
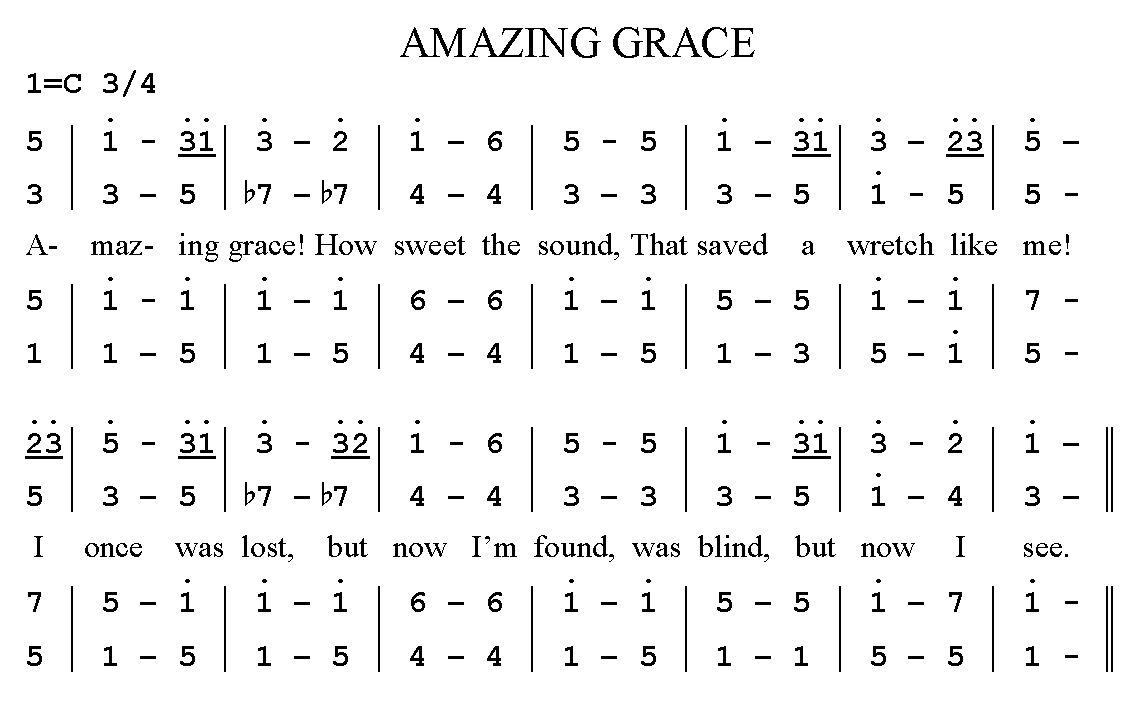 Cipher notation systems assigning Arabic numerals to the major scale degrees have been used at least since the Iberian organ tablatures of the 16th-century and include such exotic adaptations as '' Siffernotskrift''. The one most widely in use today is the Chinese ''Jianpu'', discussed in the main article. Numerals can also be assigned to different scale systems, as in the Javanese '' kepatihan'' notation described above.
Cipher notation systems assigning Arabic numerals to the major scale degrees have been used at least since the Iberian organ tablatures of the 16th-century and include such exotic adaptations as '' Siffernotskrift''. The one most widely in use today is the Chinese ''Jianpu'', discussed in the main article. Numerals can also be assigned to different scale systems, as in the Javanese '' kepatihan'' notation described above.
Solfège
Solfège is a way of assigning syllables to names of the musical scale. In order, they are today: ''Do Re Mi Fa Sol La Ti Do'' (for the octave). The classic variation is: ''Do Re Mi Fa Sol La Si Do''. The first Western system of functional names for the musical notes was introduced by Guido of Arezzo (c. 991 – after 1033), using the beginning syllables of the first six musical lines of the Latin hymn Ut queant laxis. The original sequence was ''Ut Re Mi Fa Sol La'', where each verse started a scale note higher. "Ut" later became "Do". The equivalent syllables used in Indian music are: ''Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni''. See also: solfège, sargam, Kodály hand signs. Tonic sol-fa is a type of notation using the initial letters of solfège.Letter notation
The notes of the 12-tone scale can be written by their letter names A–G, possibly with a trailing accidental, such as A or B.ABC
ABC notation
ABC notation is a shorthand form of musical notation for computers. In basic form it uses the letter notation with –, –, and , to represent the corresponding notes and rests, along with other elements used to place added value on these – ...
is a compact format using plain text characters, readable by computers and by humans. More than 100,000 tunes are now transcribed in this format.
Tablature
Tablature was first used in theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
for organ music and later in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
for lute music. In most lute tablatures, a staff is used, but instead of pitch values, the lines of the staff represent the strings of the instrument. The frets to finger are written on each line, indicated by letters or numbers. Rhythm is written separately with one or another variation of standard note values indicating the duration of the fastest moving part. Few seem to have remarked on the fact that tablature combines in one notation system both the physical and technical requirements of play (the lines and symbols on them and in relation to each other representing the actual performance actions) with the unfolding of the music itself (the lines of tablature taken horizontally represent the actual temporal unfolding of the music). In later periods, lute and guitar music was written with standard notation. Tablature caught interest again in the late 20th century for popular guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
music and other fretted instruments, being easy to transcribe and share over the internet in ASCII format.
Piano-roll-based notations
Some chromatic systems have been created taking advantage of the layout of black and white keys of the standard piano keyboard. The "staff" is most widely referred to as " piano roll", created by extending the black and white piano keys.Klavar notation
(sometimes shortened to klavar) is a music notation system that was introduced in 1931 by the Dutchman Cornelis Pot. The name means "keyboard writing" inEsperanto
Esperanto (, ) is the world's most widely spoken Constructed language, constructed international auxiliary language. Created by L. L. Zamenhof in 1887 to be 'the International Language' (), it is intended to be a universal second language for ...
. It differs from conventional music notation in a number of ways and is intended to be easily readable. Many klavar readers are from the Netherlands.
Chromatic staff notations
Over the past three centuries, hundreds of music notation systems have been proposed as alternatives to traditional western music notation. Many of these systems seek to improve upon traditional notation by using a "chromatic staff" in which each of the 12 pitch classes has its own unique place on the staff. An example is Jacques-Daniel Rochat's Dodeka music notation. These notation systems do not require the use of standard key signatures, accidentals, or clef signs. They also represent interval relationships more consistently and accurately than traditional notation, e.g. major 3rds appear wider than minor 3rds. Many of these systems are described and illustrated in Gardner Read's "Source Book of Proposed Music Notation Reforms".Graphic notation
The term "graphic notation" refers to the contemporary use of non-traditional symbols and text to convey information about the performance of a piece of music. Composers such as Johanna Beyer, Christian Wolff, Carmen Barradas, Earle Brown, Yoko Ono, Anthony Braxton,John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and Extended technique, non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one ...
, Morton Feldman, Cathy Berberian, Graciela Castillo, Krzysztof Penderecki, Cornelius Cardew
Cornelius Cardew (7 May 193613 December 1981) was an English experimental music composer, and founder (with Howard Skempton and Michael Parsons) of the Scratch Orchestra, an experimental performing ensemble. He later rejected experimental mu ...
, Pauline Oliveros and Roger Reynolds are among the early generation of composers who innovated forms of graphic notation beginning in the mid-twentieth century. The book Notations, edited by John Cage and Alison Knowles and published by Something Else Press in 1969, compiles many examples of this kind of notation.
Simplified music notation
Simplified Music Notation is an alternative form of musical notation designed to makesight-reading
In music, sight-reading, also called ''a prima vista'' (Italian language, Italian meaning, "at first sight"), is the practice of reading and performing of a piece in a music notation that the performer has not seen or learned before. Sight-singi ...
easier. It is based on classical staff notation, but incorporates sharps and flats into the shape of the note heads. Notes such as double sharps and double flats are written at the pitch they are actually played at, but preceded by symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
s called ''history signs'' that show they have been transposed.
Modified Stave Notation
Modified Stave Notation (MSN) is an alternative way of notating music for people who cannot easily read ordinary musical notation even if it is enlarged.Parsons code
Parsons code is used to encode music so that it can be easily searched.Braille music
Braille music is a complete, well developed, and internationally accepted musical notation system that has symbols and notational conventions quite independent of print music notation. It is linear in nature, similar to a printed language and different from the two-dimensional nature of standard printed music notation. To a degree Braille music resembles musical markup languages such as MusicXML or NIFF.Integer notation
In integer notation, or theinteger
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
model of pitch, all pitch classes and intervals between pitch classes are designated using the numbers 0 through 11.
Rap notation
The standard form of rap notation is the "flow diagram", where rappers line up their lyrics underneath "beat numbers". Hip-hop scholars also make use of the same flow diagrams that rappers use: the books ''How to Rap'' and ''How to Rap 2'' extensively use the diagrams to explain rap's triplets, flams, rests, rhyme schemes, runs of rhyme, and breaking rhyme patterns, among other techniques. Similar systems are used by musicologists Adam Krims in his book ''Rap Music and the Poetics of Identity'' and Kyle Adams in his work on rap's flow. As rap usually revolves around a strong 4/4 beat, with certain syllables aligned to the beat, all the notational systems have a similar structure: they all have four beat numbers at the top of the diagram, so that syllables can be written in-line with the beat.Tin Whistle Fingering Charts
It is being used for six-hole woodwind instruments, basically for Irish folk songs. Tin whistle tabs are particularly useful for those unfamiliar with sheet music notation.Music notation on computers
Unicode
The Musical Symbols Unicode block encodes an extensive system of formal musical notation. The Miscellaneous Symbols block has a few of the more common symbols: * * * * * * * The Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs block has threeemoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
that may include depictions of musical notes:
*
*
*
Software
Various computer programs have been developed for creating music notation (called ''scorewriters'' or ''music notation software''). Music may also be stored in various digital file formats for purposes other than graphic notation output.Perspectives of musical notation in composition and musical performance
According to Philip Tagg and Richard Middleton, musicology and to a degree European-influenced musical practice suffer from a 'notational centricity', a methodology slanted by the characteristics of notation. A variety of 20th- and 21st-century composers have dealt with this problem, either by adapting standard Western musical notation or by using graphic notation. These include George Crumb, Luciano Berio, Krzystof Penderecki, Earl Brown,John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and Extended technique, non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one ...
, Witold Lutoslawski, and others.
See also
* List of musical symbols of modern notation. *Hebrew cantillation
Hebrew cantillation, trope, trop, or ''te'amim'' is the manner of chanting ritual readings from the Hebrew Bible in synagogue Jewish services, services. The chants are written and notated in accordance with the special signs or marks printed ...
* Helmholtz pitch notation
Helmholtz pitch notation is a system for naming musical notes of the Western chromatic scale. Fully described and normalized by the German scientist Hermann von Helmholtz, it uses a combination of upper and lower case letters (A to G), and t ...
* Colored music notation
* Eye movement in music reading
* Guido of Arezzo, inventor of modern musical notation
* History of music publishing
* List of scorewriters
* Mensural notation
Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphony, polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measur ...
* Modal notation
* Music engraving, drawing music notation for the purpose of mechanical reproduction
* Music OCR, the application of optical character recognition to interpret sheet music
* Neume ( plainchant notation)
* Pitch class
* Rastrum, a five-pointed writing implement used to draw parallel staff lines across a blank piece of sheet music
* Scorewriter
* Semasiography
* Sight-reading
In music, sight-reading, also called ''a prima vista'' (Italian language, Italian meaning, "at first sight"), is the practice of reading and performing of a piece in a music notation that the performer has not seen or learned before. Sight-singi ...
* Sheet music
* Time unit box system, a notation system useful for polyrhythms
* Tongan music notation, a subset of standard music notation
* Tonnetz
* Znamenny chant
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * English translation of "Kojak—50 sekunders tv-musik". * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Byzantine Music Notation
Contains a Guide to Byzantine Music Notation (neumes).
CCARH—Center for Computer Assisted Research in the Humanities
Information on Stanford University Course on music representation. Links page shows examples of different notations.
Music Markup Language
XML-based language for music notation. *
* Gehrkens, Karl Wilson ttps://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/19499 ''Music Notation and Terminology'' Project Gutenberg. * Gilbert, Nina.
Glossary of U.S. and British English musical terms
" Posted 17 June 1998; updated 7 September 2000. {{DEFAULTSORT:Musical Notation Mathematical notation