|
Nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins. Structures Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The tertiary structures and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy. Viruses Virus genomes (either DNA or RNA) are extremely tightly packed into the viral capsid. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins include influenza, rabies, Ebola, Bunyamwera, Schm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Nucleoprotein
Viral nucleoproteins (NPs) are essential RNA-binding protein, RNA-binding proteins encoded by many Virus, viruses, especially Negative-strand RNA virus, negative-sense single-stranded RNA (–ssRNA) viruses. They play crucial roles in Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis, encapsulating viral RNA, facilitating Viral replication, genome replication and Transcription (biology), transcription, organizing viral Nucleoprotein, ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) complexes, and Immune system, evading host immunity. Structure and function Key functions of viral NPs include: * RNA Encapsulation: NPs coat the viral genome in a sequence-independent manner, protecting it from Nuclease, nucleases and Pattern recognition receptor, host pattern recognition receptors such as RIG-I and MDA5. * RNP Assembly: NP-RNA complexes serve as templates for viral RNA synthesis by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). * Regulation of Replication: NP levels help determine the balance between Transcription (biology), tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as causing seasonal flu in humans. Mammals in which different strains of IAV circulate with sustained transmission are bats, pigs, horses and dogs; other mammals can occasionally become infected. IAV is an enveloped negative-sense RNA virus, with a segmented genome. Through a combination of mutation and genetic reassortment the virus can evolve to acquire new characteristics, enabling it to evade host immunity and occasionally to jump from one species of host to another. Subtypes of IAV are defined by the combination of the antigenic H and N proteins in the viral envelope; for example, "H1N1" designates an IAV subtype that has a type-1 hemagglutinin (H) protein and a type-1 neuraminidase (N) protein. Almost all possible combinations of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus
''Orthoebolavirus zairense'' or Zaire ebolavirus, more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the Western African Ebola virus epidemic, 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was List of Ebola outbreaks, first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies Virus
Rabies virus (''Lyssavirus rabies'') is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in animals, including humans. It can cause violence, hydrophobia, and fever. Rabies transmission can also occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. Rabies virus, like many Rhabdoviridae, rhabdoviruses, has an extremely wide host range. In the wild it has been found infecting many mammalian species, while in the laboratory it has been found that birds can be infected, as well as cell cultures from mammals, birds, reptiles and insects. Rabies is reported in more than 150 countries and on all continents except Antarctica. The main burden of disease is reported in Asia and Africa, but some cases have been reported also in Europe in the past 10 years, especially in returning travellers. Rabies virus has a cylindrical morphology and is a member of the ''Lyssavirus'' genus of the ''Rhabdoviridae'' family. These viruses are Viral envelope, enveloped and have a Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
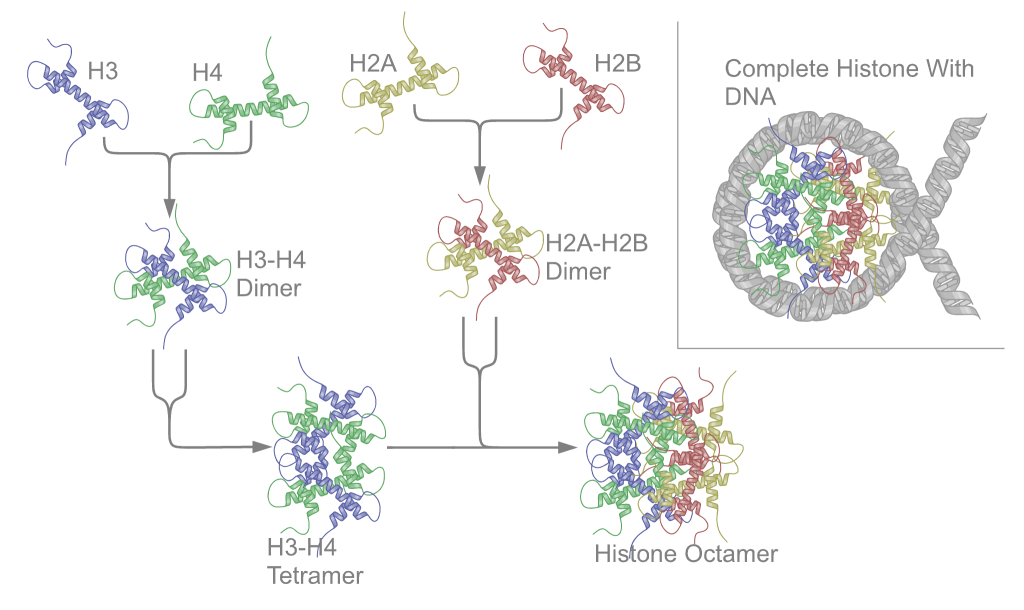
Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30- nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 9 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones, which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30 nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazara Virus
In 1954 the Hazara virus, one of the 34 tick-borne viruses of the genus '' Orthonairovirus'', was discovered in Pakistan in the ''Ixodes'' tick native to that region. Today this virus is studied in mice in an attempt to develop treatments for the highly pathogenic Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus. Characteristics Hazara virus is part of the genus ''Orthonairovirus'' of the '' Nairoviridae'' family of viruses, which are a family of enveloped negative-stranded RNA viruses with a genome split into three parts—Small (S), Middle (M) and Large (L). The L RNA segment encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L protein), the M RNA segment encodes two surface glycoproteins (Gc and Gn), and the S RNA segment encodes a nucleocapsid protein (N). The three genomic RNA segments are encapsidated by copies of the N protein in the form of ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes. The N protein is the most abundant viral protein in ''Bunyaviridae'' virus particles and infected cells and, therefore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protamine
Protamines are small, arginine-rich, nuclear proteins that replace histones late in the haploid phase of spermatogenesis and are believed essential for sperm head condensation and DNA stabilization. They may allow for denser packaging of DNA in the spermatozoon than histones, but they must be decompressed before the genetic data can be used for protein synthesis. However, part of the sperm's genome is packaged by histones (10-15% in humans and other primates) thought to bind genes that are essential for early embryonic development. Protamine and protamine-like (PL) proteins are collectively known as the sperm-specific nuclear basic proteins (SNBPs). The PL proteins are intermediate in structure between protamine and Histone H1. The C-terminal domain of PL could be the precursor of vertebrate protamine. Spermatogenesis During the formation of sperm, protamine binds to the phosphate backbone of DNA using the arginine-rich domain as an anchor. DNA is then folded into a toroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |