|
Niya (kingdom)
Niya (also Niye, Niy, Nii, and Nihe) was a kingdom in Syria near the Orontes River in northern Syria next to Nuhasse. History Late Bronze In the Amarna letters correspondence of 1350- 1335 BC, ''Nii'' is referenced in two letters. The city of Tunip in the northern Levant had been trying to communicate to the Egyptian pharaoh for two decades, and resorted to another letter, EA 59: entitled: ''"From the citizens of Tunip"'', ( EA for 'el Amarna'). The city-state of Arqa also sent a letter to pharaoh, requesting aid (EA 100). The other letter referencing ''Nii'' concerns the individual Etakkama, his collusion with the Hittites, and the takeover of territory, 'city-states', and peoples in the northern and western Levant. Mitanni Period In the 15th century BC, the entire region came under the control of the Mitanni Empire. Amarna Archive, ''"Nii"'', 2--letters * EA 59, title: "From the citizens of Tunip" :"To the king of Egypt, our lord: Message of "the citizens of Tunip", yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizraim
Mizraim (; cf. ) is the Hebrew and Aramaic name for the land of Egypt and its people. Mizraim - king of Egypt Linguistic analysis '' Mizraim'' is the Hebrew cognate of a common Semitic source word for the land now known as Egypt. It is similar to '' Miṣr'' in modern Arabic, '' Misri'' in the 14th century B.C. Akkadian Amarna tablets, '' Mṣrm'' in Ugaritic, ''Mizraim'' in Neo-Babylonian texts, and ''Mu-ṣur'' in neo-Assyrian Akkadian (as seen on the Rassam cylinder). To this root is appended the dual suffix ''-āyim'', perhaps referring to the "two Egypts": Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. This word is similar in pronunciation and spelling to the Hebrew words '' matsór'' and '' meitsár'', meaning literally "siege" and " strait, distress" respectively, and may carry those connotations to Hebrew speakers. Biblical accounts According to Genesis 10, Mizraim, son of Ham was the younger brother of Cush and elder brother of Phut whose families together made up the Hamite bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
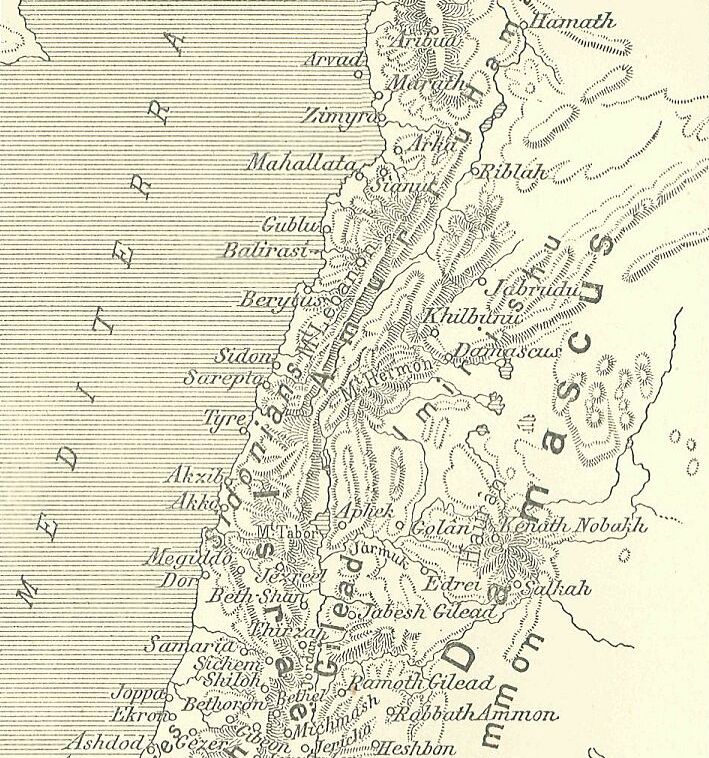
Ruhizzi
Ruhizzi, was a city, or city-state located in northern Canaan or southern Amurru territories, in the foothills of Mount Hermon during the time of the Amarna letters correspondence. During the 15-20 year Amarna letters of 1350- 1335 BC, Arsawuya was the 'mayor' of Ruhizzi and corresponded with the Egyptian pharaoh. According to EA 53, ( EA for 'el Amarna'), a letter concerning a warring Etakkama, Ruhizzi was associated with the problems of Upu in the region to the south at Damascus Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ..., (named Dimašqu), and in the region of Amqu, (the Beqaa), in the northwest. Ruhizzi is located near Kadesh-(''Qidšu''), and east of the Anti-Lebanon. See also * Arsawuya, mayor of Ruhizzi * Amarna letters References * Moran, William L. ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsawuya
Arsawuya was a 'mayor' of Ruhizzi, located east of ''Qidšu''-(Kadesh), and farther east beyond the Anti-Lebanon mountain range, during the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. He is referenced in five letters, two letters of which he wrote to the Egyptian pharaoh, letters EA 191, and 192, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). Arsawuya's second letter The complete topic of Arsawuya's second letter is missing because of a multi-sentence lacuna. EA 191, ''"Preparations for war"'' :To the king, my lord: Message of ''Arsawuya'', the ruler of Ruhizza. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord. The king, my lord, wrote to me to make preparations before the arrival of the archers of the king, my lord, and before the arrival of his many commissioners. :And could I think of not serving the king, my lord? :May I join up with the archers of the king and his commissioners so that, having everything prepared, I might follow them wherever they are at war against the king, my lord, and we capture the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qatna
Qatna (modern: , Tell al-Mishrifeh; also Tell Misrife or Tell Mishrifeh) was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an important center through most of the second millennium BC and in the first half of the first millennium BC. It contained one of the largest royal palaces of Bronze Age Syria and an intact royal tomb that has provided a great amount of archaeological evidence on the funerary habits of that period. First inhabited for a short period in the second half of the fourth millennium BC, it was repopulated around 2800 BC and continued to grow. By 2000 BC, it became the capital of a regional kingdom that spread its authority over large swaths of the central and southern Levant. The kingdom enjoyed good relations with Mari, but was engaged in constant warfare against Yamhad. By the 15th century BC, Qatna lost its hegemony and came under the authorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akizzi
Akizzi (Akk. ma-ki-iz-zi) was the King of Qatna around 1350-1345 BC. He is also known as a writer of several of the Amarna Letters, im which he requested aid from the pharaoh against invaders. He was a successor of Idanda. While Idanda is known from an archive in Qatna, no archive has been found within Qatna that contained letters belonging to Akizzi; instead, letters Akizzi sent were found in Amarna. It is unclear if Akizzi used the titles LU (man) or LUGAL (king) for himself. He used the former title for surrounding pettery rulers, and the latter title for himself in one letter (Amarna Letter EA 57). Reign As Tushratta of Mitanni lost control of the territory west of the Euphrates, the former vassal states were faced with trying to align themselves with Egypt or submit to Suppiluliuma I of Hatti. Akizzi wrote several letters of the Amarna letters correspondence. Here he pleaded for help from the Egyptians against the Hittite invasion into former Mitanni territory. Even earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zemar
Sumur (Biblical Hebrew: ollective noun denoting the city inhabitants Egyptian: ''Smr''; Akkadian: ''Sumuru''; Assyrian: ''Simirra'') was a Phoenician city in what is now Syria. It was a major trade center. The city has also been referred to in English publications as Simyra, Ṣimirra, Ṣumra, Sumura, Ṣimura, Zemar, and Zimyra. Sumur (or "Sumura") appears in the Amarna letters (mid-14th century BCE); Ahribta is named as its ruler. It was under the guardianship of Rib-Addi, king of Byblos, but was conquered by Abdi-Ashirta's expanding kingdom of Amurru. Pro-Egyptian factions may have seized the city again, but Abdi-Ashirta's son, Aziru, recaptured Sumur. Sumur became the capital of Amurru. It is likely, although not completely certain, that the "Sumur" of the Amarna letters is the same city later known as "Simirra." Simirra was claimed as part of the Assyrian empire by Tiglath-Pileser III in 738 BCE, but rebelled against Assyria in 721 at the beginning of the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 1950–1880 BC and are depicted on cylinder seals from Central Anatolia Region, Central Anatolia in Kültepe dated to c. 1900 BC. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more Equidae, equids (usually horses) that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Age, Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by Light cavalry, light and Heavy cavalry, heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aziru
Aziru (Akk. ma-zi-ra) was the Canaanite ruler of Amurru, modern Lebanon, in the 14th century BC. He was the son of Abdi-Ashirta, the previous Egyptian vassal of Amurru and a direct contemporary of Akhenaten. Reign Relations with Egypt The dealings of Aziru are well-known from the Amarna letters. While being a formal vassal of Egypt, he tried to expand his kingdom towards the Mediterranean coast and captured the city of Sumur (Simyrra). This was seen with alarm by his neighbouring states, particularly Rib-Hadda, the king of Gubla, (Byblos), who pleaded for Egyptian troops to be sent for their protection. Rib-Hadda was ultimately exiled—and probably not long afterwards killed—at the behest of Aziru. Rib-Hadda had left his city of Byblos for four months to conclude a treaty with the king of Beirut, Ammunira, but when he returned home, he learned that a palace coup led by his brother Ilirabih had unseated him from power. He temporarily sought refuge with Ammunira and unsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |