|
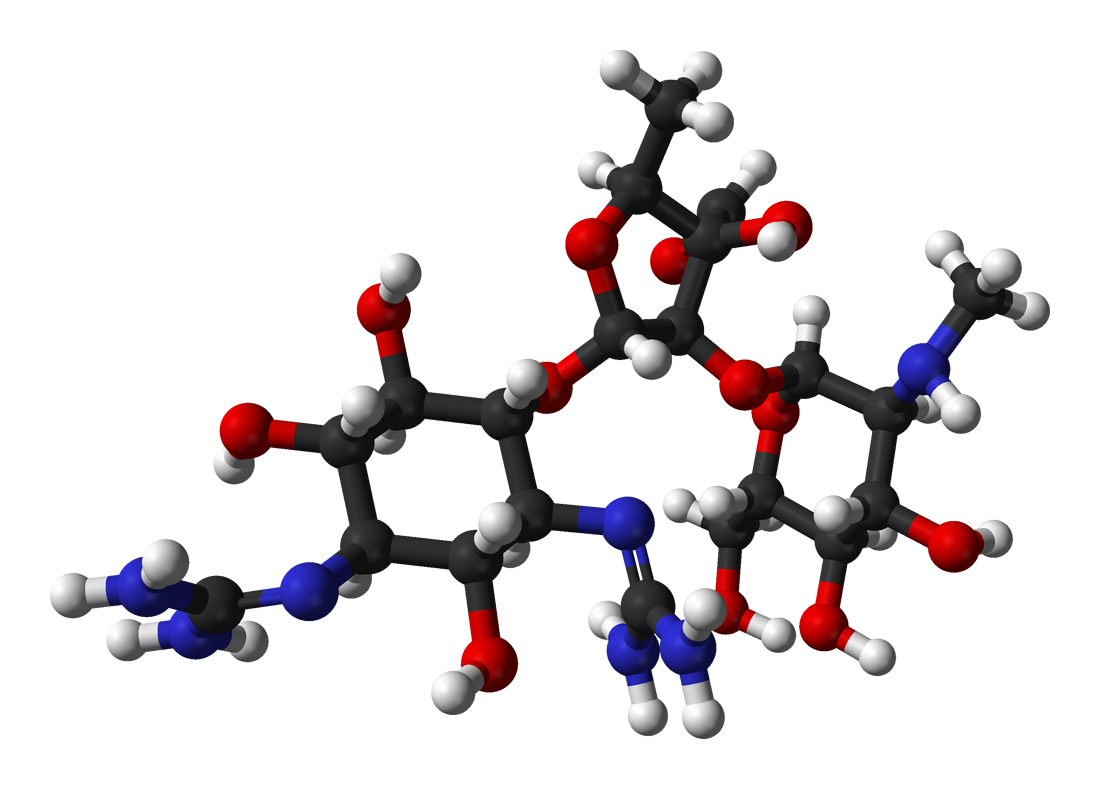
Nilofabicin
Nilofabicin (CG-400549) is an experimental antibiotic medication related to afabicin, which acts as an inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI). It is being researched as a potential treatment for infections by drug-resistant strains of bacteria such as ''Staphylococcus aureus'', ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' and ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...''. References {{reflist Antibiotics Thiophenes 2-Pyridones Anilines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afabicin
Afabicin (Debio 1450) is an experimental antibiotic developed by Debiopharm for the treatment of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' infections. It is a prodrug which is converted ''in vivo'' into the active form afabicin desphosphono (Debio 1452) which acts as an inhibitor of the staphylococcal enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI) enzyme. It has shown similar efficacy in clinical trials to established drugs such as vancomycin, but has not yet been approved for clinical use. See also * Mupirocin Mupirocin, sold under the brand name Bactroban among others, is a topical antibiotic useful against superficial skin infections such as impetigo or folliculitis. It may also be used to get rid of methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA) wh ... * Nilofabicin References {{reflist Antibiotics Acrylamides Benzofurans Naphthyridines Organophosphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoyl-acyl Carrier Protein Reductase
Enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (ENR or FabI) (), is a key enzyme of the type II fatty acid synthesis (FAS) system. ENR is an attractive target for narrow-spectrum antibacterial drug discovery because of its essential role in metabolism and its sequence conservation across many bacterial species. In addition, the bacterial ENR sequence and structural organization are distinctly different from those of mammalian fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes. : At lower concentrations, Triclosan and Triclocarban provide a bacteriostatic effect by binding to ENR. Atromentin and leucomelone possess antibacterial activity, inhibiting the enzyme in the bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, hemolysis (microbiology), alpha-hemolytic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. ''S. pneumoniae'' cells are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not f ...''. See also * Enoyl-(acyl-carrier-protein) reductase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose- fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar. Although found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines, it can cause destructive changes to human and animal lungs if aspirated, specifically to the alveoli, resulting in bloody, brownish or yellow colored jelly-like sputum. In the clinical setting, it is the most significant member of the genus ''Klebsiella'' of the Enterobacteriaceae. ''K. oxytoca'' and ''K. rhinoscleromatis'' have also been demonstrated in human clinical specimens. In recent years, ''Klebsiella'' species have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections. It naturally occurs in the soil, and about 30% of strains can fix nitrogen in anaerobic conditions. As a free-living diazotroph, its nitrogen-fixation system has been much-studied, and is of agricultural interest, as ''K. pneumoniae'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
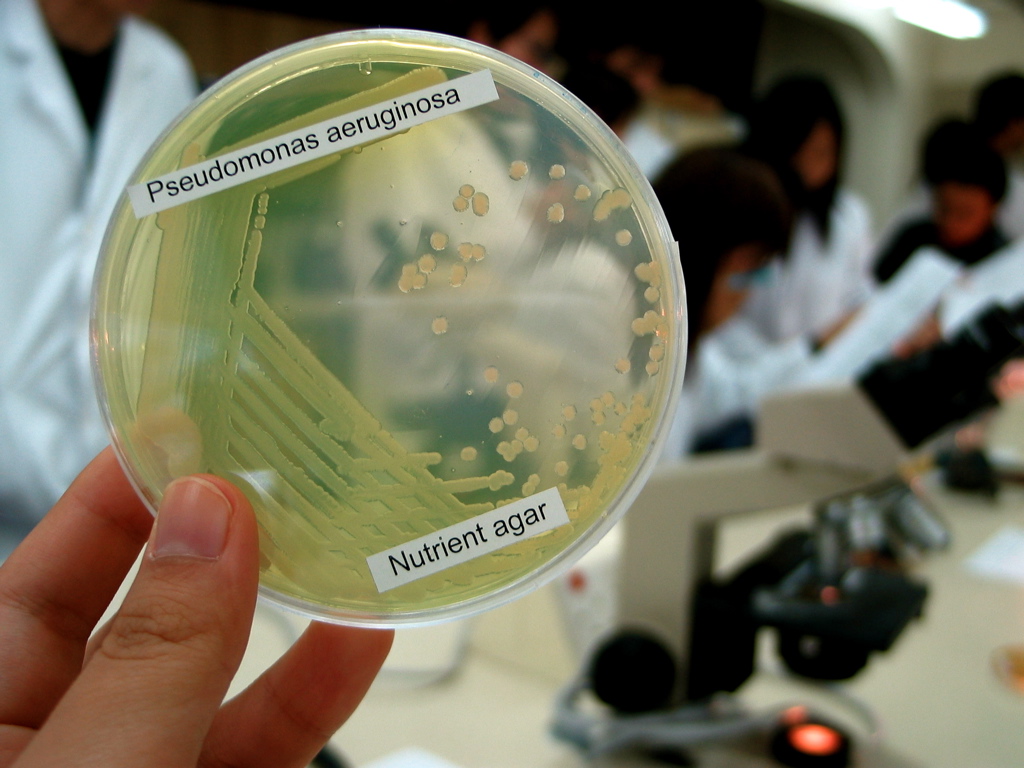
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophenes
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromaticity, aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring. Isolation and occurrence Thiophene was discovered by Viktor Meyer in 1882 as a contaminant in benzene. It was observed that isatin (an indole) forms a blue dye if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the blue indophenin had long been believed to be a reaction of benzene itself. Viktor Meyer was able to isolate thiophene as the actual substance responsible for this reaction. Thiophene and especially its derivatives occur in petroleum, sometimes in concentrations up to 1–3%. The thiophenic content of Petroleum, oil and coal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |