|
Nikolai Antsiferov
Nikolai Pavlovich Antsiferov (russian: Николай Павлович Анциферов; – September 2, 1958) was a Soviet historian and scholar of culture and local lore. Biography Antsiferov was born in the estate of Count Potocki in Uman, Ukraine. His father, Pavel Grigor'evich Antsiferov (1815–1897) was a state counsellor and the son of a naval officer in Arkhangelsk, who took a post as an inspector of agriculture and horticulture at an institute in Uman, and later was the director of the Nikitsky Botanical Garden in Crimea from 1891. He was buried in the cemetery in Sofeiskaia Slobodka. His mother, Ekaterina Maksinovna née Petrova, was the daughter of a Tver peasant. She was born in 1853 in Saint Petersburg and died in 1933. Following the death of his father, Nikolai Antsiferov lived with his mother in Pulavy (in present-day Poland), and then in Kiev where he studied at the first Kiev Gymnasium. Beginning in 1908 he studied in Saint Petersburg from 1908, gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Potocki
The House of Potocki (; plural: Potoccy, male: Potocki, feminine: Potocka) was a prominent Polish noble family in the Kingdom of Poland and magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Potocki family is one of the wealthiest and most powerful aristocratic families in Poland. History The Potocki family originated from the small village of Potok Wielki; their family name derives from that place name. The family contributed to the cultural development and history of Poland's Eastern Borderlands (today Western Ukraine). The family is renowned for numerous Polish statesmen, military leaders, and cultural activists. The first known Potocki was Żyrosław z Potoka (born about 1136). The children of his son Aleksander (~1167) castelan of Sandomierz, were progenitors of new noble families such as the Moskorzewskis, Stanisławskis, Tworowskis, Borowskis, and Stosłowskis. Jakub Potocki (c. 1481-1551) was the progenitor of the magnate line of the Potocki family. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
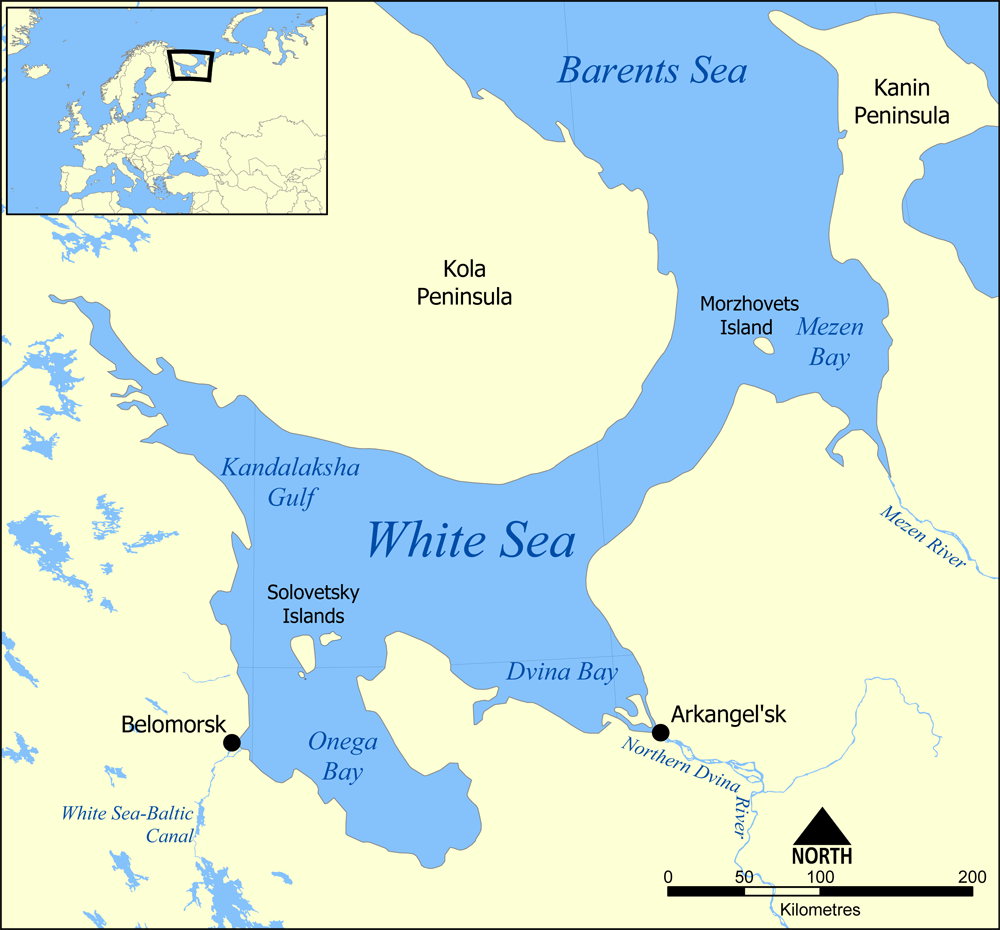
Solovetsky Islands
The Solovetsky Islands (russian: Солове́цкие острова́), or Solovki (), are an archipelago located in the Onega Bay of the White Sea, Russia. As an administrative division, the islands are incorporated as Solovetsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia.Law #65-5-OZ Within the framework of municipal divisions, they are incorporated as Solovetskoye Rural Settlement within Primorsky Municipal District.Law #258-vneoch.-OZ The administrative center of both divisions is the settlement of Solovetsky, located on Bolshoy Solovetsky Island. Almost all of the population of the islands lives in Solovetsky. As of the 2010 Census, the district had a population of 861 inhabitants. The Solovetsky Monastery (founded in 1436), in 1923 became the site of the first Gulag establishment, the Solovki prison camp. Geography The archipelago has a total area of and consists of six islands: * Bolshoy Solovetsky Island, * Anzersky Island (Anzer), * Bolshaya Muksalma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1889 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** The total solar eclipse of January 1, 1889 is seen over parts of California and Nevada. ** Paiute spiritual leader Wovoka experiences a vision, leading to the start of the Ghost Dance movement in the Dakotas. * January 4 – An Act to Regulate Appointments in the Marine Hospital Service of the United States is signed by President Grover Cleveland. It establishes a Commissioned Corps of officers, as a predecessor to the modern-day U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps. * January 5 – Preston North End F.C. is declared the winner of the inaugural Football League in England. * January 8 – Herman Hollerith receives a patent for his electric tabulating machine in the United States. * January 15 – The Coca-Cola Company is originally incorporated as the Pemberton Medicine Company in Atlanta, Georgia. * January 22 – Columbia Phonograph is formed in Washington, D.C. * January 30 – Rudolf, Crown Prince of Austria a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Historians
This list of Russian historians includes the famous historians, as well as archaeologists, paleographers, genealogists and other representatives of auxiliary historical disciplines from the Russian Federation, the Soviet Union, the Russian Empire and other predecessor states of Russia. Alphabetical list __NOTOC__ A *Friedrich von Adelung (1768-1843), historian and museologist, researched the European accounts of the Time of Troubles * Valery Alekseyev (1929-1991), anthropologist, proposed ''Homo rudolfensis'' * Mikhail Artamonov (1898-1972), historian and archaeologist, founder of modern Khazar studies, excavated a great number of Scythian and Khazar kurgans and settlements, including the fortress of Sarkel *Artemiy Artsikhovsky (1902-1978), archaeologist, discoverer of birch bark documents in Novgorod B *Vasily Bartold (1869-1930), turkologist, the ''"Gibbon of Turkestan"'', an archaeologist of Samarcand *Konstantin Bestuzhev-Ryumin (1829-1897), 19th-century historian and paleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushkin, Saint Petersburg
Pushkin (russian: Пу́шкин) is a municipal town in Pushkinsky District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, located south from the center of St. Petersburg proper, and its railway station, Tsarskoye Selo, is directly connected by railway to the Vitebsky Rail Terminal of the city. Population: Pushkin was founded in 1710 as an imperial residence named Tsarskoye Selo (russian: Ца́рское Село́, "Tsar's Village") and received status of a town in 1808. The first public railways in Russia, Tsarskoye Selo Railways, were opened here in 1837 and connected the town to the capital, St. Petersburg. After the October Revolution, the town was renamed to Detskoye Selo (russian: Де́тское Село́, "Children's Village"). Its name was further changed in 1937 to Pushkin to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the death of the Russian poet Alexander Pushkin. The town contains an ensemble of the 18th century "Tsarskoye Selo". This museum complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antsiferov Prize
Antsiferov (feminine form: Antsiferova) is a Russian-language surname derived from the archaic Russian first name "Antsifer" (Анцифер), in turn derived from "Onisifor" (Онисифор, Onesiphorus). People with the name include: * Alexei Antsiferov (born 1991), a Kazakhstani-Russian ice hockey player * Danila Antsiferov (died 1712), Russian explorer, after whom Antsiferov Island in the Kuril Islands is named * Nikolai Antsiferov (1889–1958), Russian historian See also * * {{surname Russian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorky Institute Of World Literature
The Gorky Institute of World Literature (IMLI; russian: Институт мировой литературы им. А. М. Горького РАН) is a research institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. Not to be confused with the Gorky Literary Institute, which is an institute of higher education that trains writers, the A. M. Gorky Institute of World Literature is a scientific research institute and part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. It was founded on 17 September 1932 for the 40th anniversary of Maxim Gorky's literary activity, and is located in the former estate of the Gagarin family in Moscow. The institute is organized into departments, each specializing in a specific region or genre of literature. These departments include, but are not limited to the Department of Literary Theory, Folklore, Old Slavic Literature, 19th Century Russian Literature, Contemporary Russian Literature and Russian Emigree Literature, Classical Western Literature and Comparative L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagankovo Cemetery
Vagankovo Cemetery (russian: Ваганьковское кладбище, Vagan'kovskoye kladbishche), established in 1771, is located in the Presnya district of Moscow. It started in the aftermath of the Moscow plague riot of 1771 outside the city proper, so as to prevent the contagion from spreading. Half a million people are estimated to have been buried at Vagankovo throughout its history. As of 2010, the existing cemetery contains more than 100,000 graves. The vast necropolis contains the mass graves from the Battle of Borodino, the Battle of Moscow, and the Khodynka Tragedy. It is the burial site for a number of people from the artistic and sports community of Russia and the old Soviet Union. William Taubman claims that during the Great Purge "alcohol-soused guards would execute weeping prisoners" after they had dug their graves in the cemetery. The cemetery is served by several Orthodox churches constructed between 1819 and 1823 in the Muscovite version of the Empire s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Soviet Writers
The Union of Soviet Writers, USSR Union of Writers, or Soviet Union of Writers (russian: Союз писателей СССР, translit=Soyuz Sovetstikh Pisatelei) was a creative union of professional writers in the Soviet Union. It was founded in 1934 on the initiative of the Central Committee of the Communist Party (1932) after disbanding a number of other writers' organizations, including Proletkult and the Russian Association of Proletarian Writers. The aim of the Union was to achieve party and state control in the field of literature. For professional writers, membership of the Union became effectively obligatory, and non-members had much more limited opportunities for publication. The result was that exclusion from the Union meant a virtual ban on publication. However, the history of the Union of Writers also saw cases of voluntary self-exclusion from its cadre. Thus, Vasily Aksenov, Semyon Lipkin, and Inna Lisnyanskaya left the Union of Writers in a show of solidarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamlag
Baikal Amur Corrective Labor Camp (Bamlag) (russian: Байка́ло-Аму́рский исправи́тельно-трудово́й ла́герь, Бамла́г) was a subdivision of GULAG which existed during 1932-1948. Its administration, headed by Naftaly Frenkel (1933-1938), was headquartered in the settlement of Svobodny, Amur Oblast. Its main activity was construction of the Baikal Amur Mainline and secondary railroad branches. Its peak headcount was about 201,000 (1938). In 1938 it was dismantled into several camps. Notable convicts * |
Solovki Prison Camp
The Solovki special camp (later the Solovki special prison), was set up in 1923 on the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea as a remote and inaccessible place of detention, primarily intended for socialist opponents of Soviet Russia's new Bolshevik regime. The first book on the Gulag, namely, ''In the Claws of the GPU'' (1934) by Francišak Aljachnovič, described the Solovki prison camp. At first, the Anarchists, Mensheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries enjoyed a special status there and were not made to work. Gradually, prisoners from the old regime (priests, gentry, and White Army officers) joined them and the guards and the ordinary criminals worked together to keep the "politicals" in order. This was the nucleus from which the entire Gulag grew, thanks to its proximity to the first great construction project of the Five-Year Plans, the White Sea–Baltic Canal. In one way, Solovki and the White Sea Canal broke a basic rule of the Gulag: they were both far too close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uman
Uman ( uk, Умань, ; pl, Humań; yi, אומאַן) is a city located in Cherkasy Oblast in central Ukraine, to the east of Vinnytsia. Located in the historical region of the eastern Podolia, the city rests on the banks of the Umanka River at around . Uman serves as the administrative center of Uman Raion (raion, district). It hosts the administration of Uman urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: Among Ukrainians, Uman is known for its depiction of the Haidamak rebellions in Taras Shevchenko's longest of poems, ''Haidamaky'' ("The Haidamaks", 1843). The city is also a pilgrimage site for Breslov (Hasidic group), Breslov Hasidic Jews and a major center of gardening research containing the Sofiyivsky Park, dendrological park Sofiyivka and the University of Gardening. Uman (Humań) was a private town, privately owned city of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. History Uman was first mentioned in historical documents in 1616, when it was unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |