|
Nickel Bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
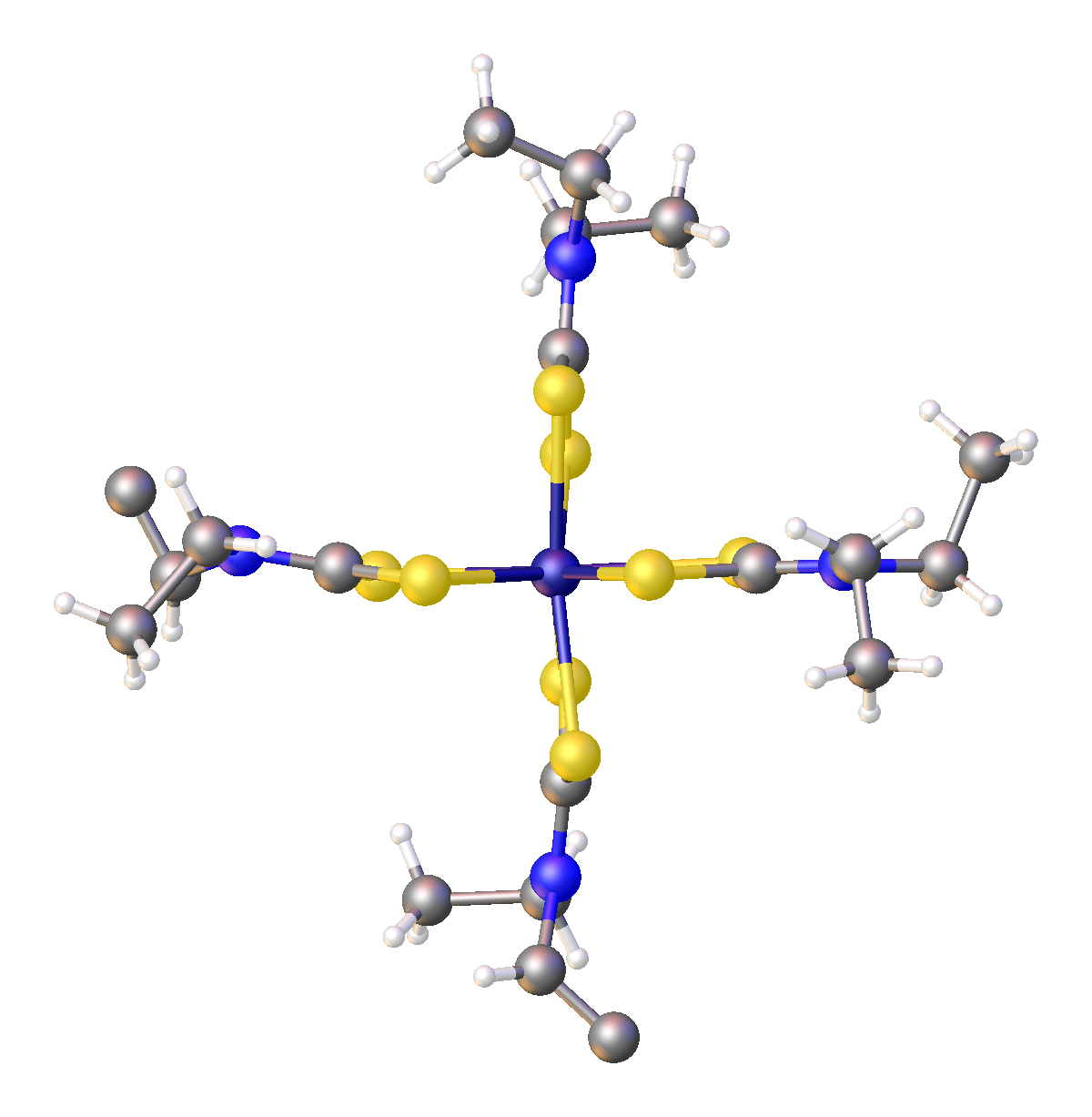
Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex on nickel and dimethyldithiocarbamate, with the formula Ni(S2CNMe2)2 (Me = methyl). It is the prototype for a large number of square planar bis(dialkhyldithiocarbamate)s of nickel(II), which feature diverse organic substituents. Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) has been marketed as a fungicide, and related complexes are used as stabilizers in polymers. Preparation and structure The compound precipitates as a light green solid upon combining aqueous solutions of nickel(II) salts and sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate. In terms of structure and bonding, the nickel is square planar, and the complex is diamagnetic. The structure of the closely related nickel bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) has been determined by X-ray crystallography. Oxidation of nickel bis(dieethyldithiocarbamate) gives the red-brown nickel(IV) complex .{{cite journal , last1=Mazumder , first1=Md. Motiur R. , last2=Dalpati , first2=Niharika , last3=Pokk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyldithiocarbamate
Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate is the organosulfur compound with the formula . It is one of the simplest organic dithiocarbamates. It is a white or pale yellow, water soluble solid. The compound is a precursor to fungicides and rubber chemicals. Preparation Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate typically crystallizes from water as the dihydrate NaS2CN(CH3)2.2H2O. The anhydrous salt and the trihydrate are often used interchangeably. Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate is obtained by treating carbon disulfide with dimethylamine in the presence of sodium hydroxide: :CS2 + HN(CH3)2 + NaOH → NaS2CN(CH3)2 + H2O Other dithiocarbamates can be prepared similarly from secondary amines and carbon disulfide. They are used as chelating agents for transition metal ions and as precursors to herbicides and vulcanization reagents. Uses left, 222px, Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) (Fe(S2CNMe2)3) is illustrative of hundreds of known dithiocarbamate complexes. It is a component of various pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
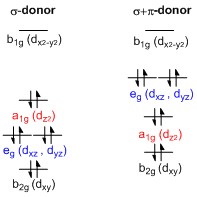
Square Planar Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, the square planar molecular geometry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners. Examples Numerous compounds adopt this geometry, examples being especially numerous for transition metal complexes. The noble gas compound xenon tetrafluoride adopts this structure as predicted by VSEPR theory. The geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d8 configuration, which includes Rh(I), Ir(I), Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III). Notable examples include the anticancer drugs cisplatin, tCl2(NH3)2 and carboplatin. Many homogeneous catalysts are square planar in their resting state, such as Wilkinson's catalyst and Crabtree's catalyst. Other examples include Vaska's complex and Zeise's salt. Certain ligands (such as porphyrins) stabilize this geometry. Splitting of d-orbitals A general d-orbital splitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Dimethyldithiocarbamate
Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate is the organosulfur compound with the formula . It is one of the simplest organic dithiocarbamates. It is a white or pale yellow, water soluble solid. The compound is a precursor to fungicides and rubber chemicals. Preparation Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate typically crystallizes from water as the dihydrate NaS2CN(CH3)2.2H2O. The anhydrous salt and the trihydrate are often used interchangeably. Sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate is obtained by treating carbon disulfide with dimethylamine in the presence of sodium hydroxide: :CS2 + HN(CH3)2 + NaOH → NaS2CN(CH3)2 + H2O Other dithiocarbamates can be prepared similarly from secondary amines and carbon disulfide. They are used as chelating agents for transition metal ions and as precursors to herbicides and vulcanization reagents. Uses left, 222px, Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) (Fe(S2CNMe2)3) is illustrative of hundreds of known dithiocarbamate complexes. It is a component of various pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Planar
In chemistry, the square planar molecular geometry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds. As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners. Examples Numerous compounds adopt this geometry, examples being especially numerous for transition metal complexes. The noble gas compound xenon tetrafluoride adopts this structure as predicted by VSEPR theory. The geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d8 configuration, which includes Rh(I), Ir(I), Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III). Notable examples include the anticancer drugs cisplatin, tCl2(NH3)2 and carboplatin. Many homogeneous catalysts are square planar in their resting state, such as Wilkinson's catalyst and Crabtree's catalyst. Other examples include Vaska's complex and Zeise's salt. Certain ligands (such as porphyrins) stabilize this geometry. Splitting of d-orbitals A general d-orbital splitting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dithiocarbamate Complexes
193px, Structure of iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate). Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3. Ligand characteristics Dithiocarbamate anions are bidentate ligands that are classified as L-X ligand in the Covalent bond classification method. In the usual electron counting method, they are three-electron ligands. With respect to HSAB theory, they are classified as soft. Because of the pi-donor properties of the amino substituent, the two sulfur centers show enhanced basicity relative to dithiocarboxylates. This situation is represented by the zwitterionic resonance structure that depicts a positive charge on N and negative charges on both sulfurs. This N to C pi-bonding results in partial double bond character for the C-N bond. Consequently, barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Bis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Nickel bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex ok nickel(II) and diethyldithiocarbamate, with the formula Ni(S2CNEt2)2 (Et = ethyl). It is one a large number of square planar bis(dialkhyldithiocarbamate)s of nickel(II). The closely related nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) has been marketed as a fungicide. R related complexes are used as stabilizers in polymers. Preparation, structure, reactions The compound precipitates as a greenish solid upon combining aqueous solutions of nickel(II) salts and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate. In terms of structure and bonding, the nickel is square planar, and the complex is diamagnetic. The planar structure has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. Oxidation of nickel bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) gives the red-brown nickel(IV) complex .{{cite journal , last1=Fackler , first1=John P. , last2=Avdeef , first2=Alex. , last3=Fischer , first3=R. G. , title=Sulfur chelates. XVI. Chemical Properties of Oxidized Nickel(II) Dithioc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Dimethyldithiocarbamate
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications. Applications Known as ziram in agriculture, it was introduced in the United States in 1960 as a broad-spectrum fungicide. It was used to address scab on apples and pears, leaf curl in peaches, and anthracnose and blight in tomatoes. In 1981, additional uses for ziram were approved, including the prevention of leaf blight and scab on almonds, shot-hole in apricots, brown rot and leaf spot in cherries, and scab and anthracnose in pecans. Ziram also began to be used on residential ornaments as a bird and mammal repellent. As a protectant fungicide, it is active on the plant’s surface where it forms a chemical barrier between the plant and a fungus. A protectant fungicide is not absorbed into the plant and must be applied prior to infection. Ziram can either be direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with dimethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNMe2)3 (Me = methyl). It is marketed as a fungicide. Synthesis, structure, bonding Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typically are prepared by salt metathesis reactions. Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is an octahedral coordination complex of iron(III) with D3 symmetry. Spin crossover (SCO) was first observed in 1931 by Cambi ''et al.'' who discovered anomalous magnetic behavior for the tris(N,N-dialkyldithiocarbamatoiron(III) complexes. The spin states of these complexes are sensitive to the nature of the amine substituents. Reactions Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s react with nitric oxide to give a nitrosyl complex: : This efficient chemical trapping reaction provides a means to detect NO. Reflecting the strongly donating properties of dithiocarbamate ligands, iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s oxidize at relatively mild potentials to give isolable iron(IV) deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |