|
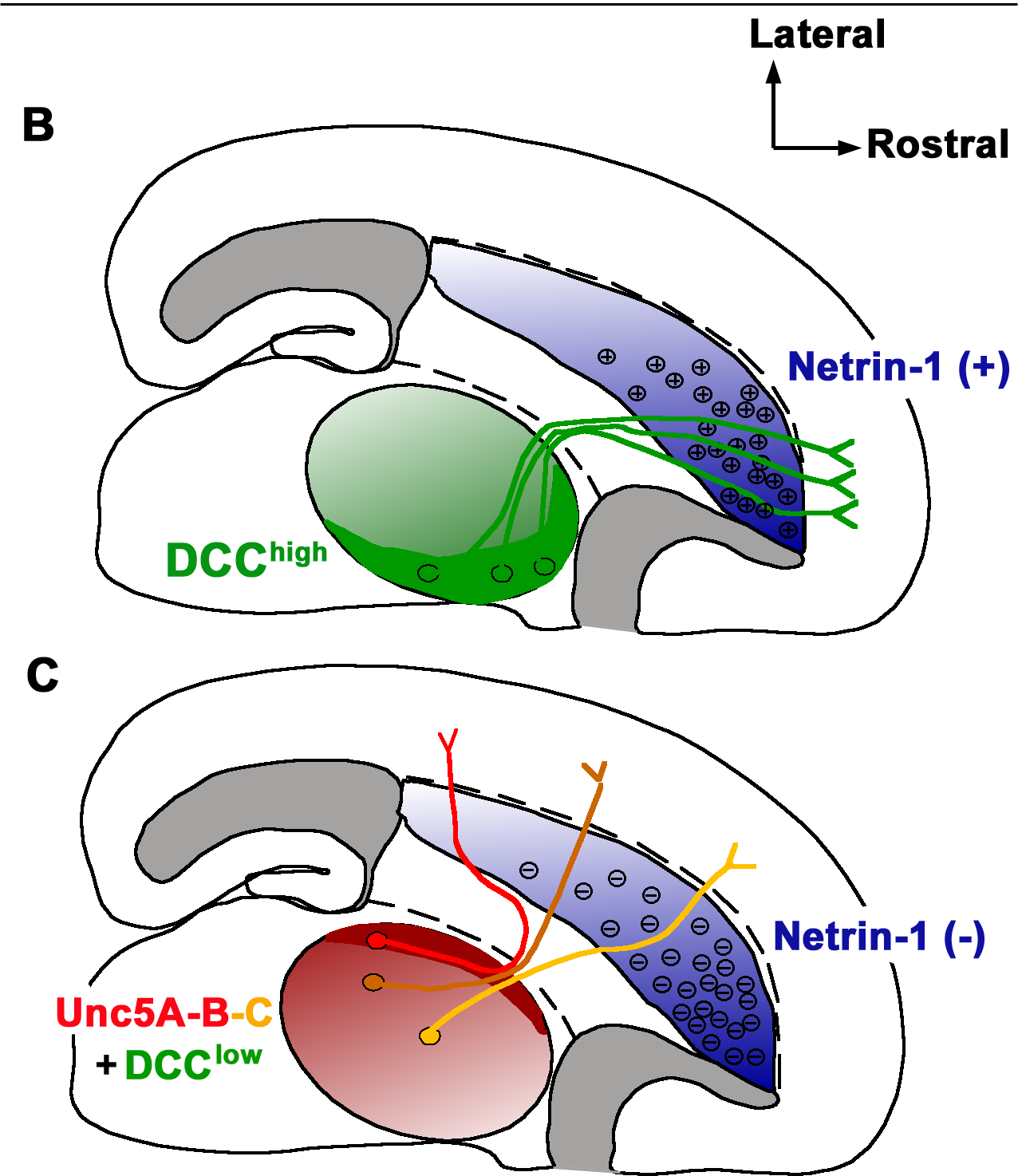
Netrin-1
Netrin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTN1'' gene. Netrin is included in a family of laminin-related secreted proteins. The function of this gene has not yet been defined; however, netrin is thought to be involved in axon guidance and cell migration during development. Mutations and loss of expression of netrin suggest that variation in netrin may be involved in cancer development. Interactions NTN1 has been shown to interact with Deleted in Colorectal Cancer, and components of the extracellular matrix and the tumor microenvironment. Midline crossing of commissural axons During the development of the central nervous system, when the dorsal and ventral signaling is being established, the floor plate is an important site for crossing for groups of neural processes at the dorsal midline. Once crossed through the floor plate, these groups are now referred to as commissural axons. These neuronal cell bodies are signaled by Netrin 1 to be attracted to the floor pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netrins
Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. They are named after the Sanskrit word "netr", which means "one who guides". Netrins are genetically conserved across nematode worms, fruit flies, frogs, mice, and humans. Structurally, netrin resembles the extracellular matrix protein laminin. Netrins are chemotropic; a growing axon will either move towards or away from a higher concentration of netrin. Though the detailed mechanism of axon guidance is not fully understood, it is known that netrin attraction is mediated through UNC-40/DCC cell surface receptors and repulsion is mediated through UNC-5 receptors. Netrins also act as growth factors, encouraging cell growth activities in target cells. Mice deficient in netrin fail to form the hippocampal comissure or the corpus callosum. A proposed model for netrin activity in the spinal column of developing human embryos is that netrins are released by the floor plate and then are picked up by receptor proteins embe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deleted In Colorectal Cancer
Netrin receptor DCC, also known as DCC, or colorectal cancer suppressor is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DCC'' gene. DCC has long been implicated in colorectal cancer and its previous name was ''Deleted in colorectal carcinoma''. Netrin receptor DCC is a single transmembrane receptor. Since it was first discovered in a colorectal cancer study in 1990, ''DCC'' has been the focus of a significant amount of research. ''DCC'' held a controversial place as a tumour suppressor gene for many years, and is well known as an axon guidance receptor that responds to netrin-1. More recently DCC has been characterized as a dependence receptor, and many hypotheses have been put forward that have revived interest in ''DCCs candidacy as a tumour suppressor gene, as it may be a ligand-dependent suppressor that is frequently epigenetically silenced. Background Early studies of colorectal tumours found that allelic deletions of segments of chromosome 18q occur in a very high per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Mirror Movement Disorder
Congenital mirror movement disorder (CMM disorder) is a rare genetic neurological disorder which is characterized by mirrored movement, sometimes referred to as associated or synkinetic movement, most often in the upper extremity of the body. These movements are voluntary intentional movements on one, ipsilateral, side of the body that are mirrored simultaneously by involuntary movements on the contralateral side. The reproduction of involuntary movement usually happens along the head-tail axis, having a left-right symmetry. For example, if someone were to voluntarily make a fist with their left hand, their right hand would do the same. In most cases, the accompanying contralateral involuntary movements are much weaker than the ipsilateral voluntary ones, although the extent and magnitude of the mirrored movement vary across patients. This disorder has not yet been found to be associated with any other neurologic disease or cognitive disability, and currently, no cures nor means t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they manage to find their way so accurately is an area of ongoing research. Axon growth takes place from a region called the growth cone and reaching the axon target is accomplished with relatively few guidance molecules. Growth cone receptors respond to the guidance cues. Mechanisms Growing axons have a highly motile structure at the growing tip called the growth cone, which responds to signals in the extracellular environment that instruct the axon in which direction to grow. These signals, called guidance cues, can be fixed in place or diffusible; they can attract or repel axons. Growth cones contain receptors that recognize these guidance cues and interpret the signal into a chemotropic response. The general theoretical framework is that wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryogenesis, embryonic development, wound healing and immune system, immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular directions to specific locations. Cells often migrate in response to specific external signals, including chemotaxis, chemical signals and mechanotaxis, mechanical signals. Errors during this process have serious consequences, including intellectual disability, cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, tumor, tumor formation and metastasis. An understanding of the mechanism by which cells migrate may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for controlling, for example, invasive tumour cells. Due to the highly viscous environment (low Reynolds number), cells need to continuously produce forces in order to move. Cells achieve active movement by very different mechanisms. Many less complex prokaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnès Bernet
Agnès Bernet, (born 1968) is a French cell biologist and professor of cancer biology at the University Claude Bernard Lyon I. A co-founder of NETRIS Pharma, she has led within the Laboratory of Apoptosis, Cancer and Development, the research team that validated the use of interference ligand/dependence receptors as novel targeted therapies for cancer. Life and work Bernet earned her PhD at University Claude Bernard Lyon I in 1994 with the thesis ''Etude, par recombinaison homologue, de régions régulatrices de l'expression des gènes de globine alpha humains (Study, by homologous recombination, of regulatory regions of the expression of human alpha globin genes). Her'' research focused on the study of two regions that may be involved in the activation of human alpha globin genes during erythroid differentiation. In 2008, she co-founded the company Netris Pharma SAS, where she serves as scientific director and coordinates numerous research projects concerning clinical therap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |