|
Congenital Mirror Movement Disorder
Congenital mirror movement disorder (CMM disorder) is a rare genetic neurological disorder which is characterized by mirrored movement, sometimes referred to as associated or synkinetic movement, most often in the upper extremity of the body. These movements are voluntary intentional movements on one, ipsilateral, side of the body that are mirrored simultaneously by involuntary movements on the contralateral side. The reproduction of involuntary movement usually happens along the head-tail axis, having a left-right symmetry. For example, if someone were to voluntarily make a fist with their left hand, their right hand would do the same. In most cases, the accompanying contralateral involuntary movements are much weaker than the ipsilateral voluntary ones, although the extent and magnitude of the mirrored movement vary across patients. This disorder has not yet been found to be associated with any other neurologic disease or cognitive disability, and currently, no cures nor means t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Disease
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, the term orphan disease describes a rare disease whose rarity results in little or no funding or research for treatments, without financial incentives from governments or other agencies. Orphan drugs are medications targeting orphan diseases. Most rare diseases are genetic in origin and thus are present throughout the person's entire life, even if symptoms do not immediately appear. Many rare diseases appear early in life, and about 30% of children with rare diseases will die before reaching their fifth birthdays. Fields condition is considered the rarest known disease, affecting three known individuals, two of whom are identical twins. With four diagnosed patients in 27 years, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase deficiency is considered the second rarest. While no single number has been agreed upon for which a disease is considered rare, several efforts have been undertaken to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
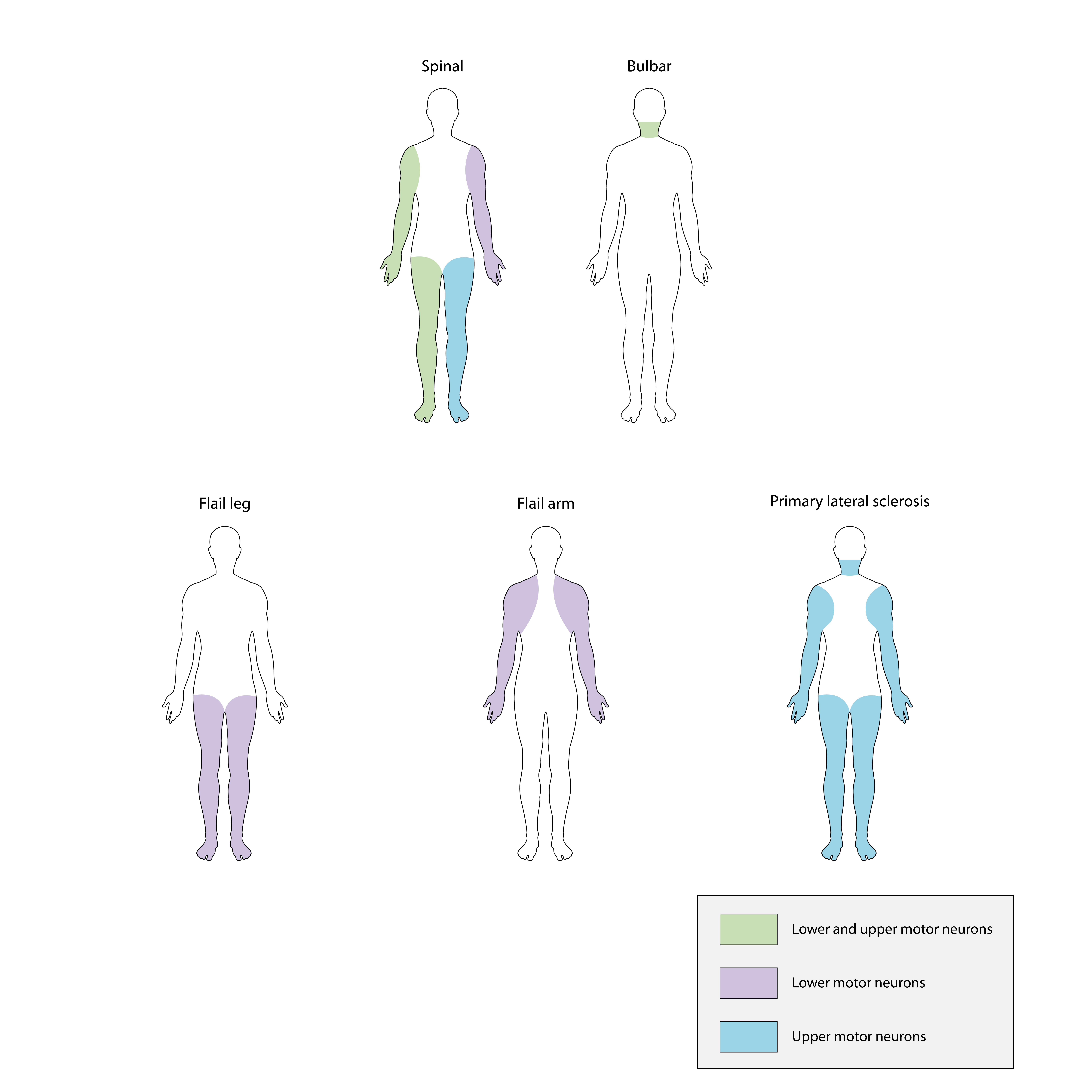
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of the organism's genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance, such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildervanck Syndrome
Wildervanck syndrome or cervico-oculo-acoustic syndrome comprises a triad of: * Duane syndrome Duane syndrome is a congenital rare type of strabismus most commonly characterized by the inability of the human eye, eye to move outward. The syndrome was first described by ophthalmologists Jakob Stilling (1887) and Siegmund Türk (1896), and s ... * Klippel-Feil anomaly (fused cervical vertebrae) * congenital hearing loss Wildervanck syndrome is a developmental disorder that may be characterized by accessory tragi. References External links Syndromes affecting hearing Medical triads Rare diseases {{Nervoussystem-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seckel Syndrome
Seckel syndrome, or microcephalic primordial dwarfism (also known as bird-headed dwarfism, Harper's syndrome, Virchow–Seckel dwarfism and bird-headed dwarf of Seckel) is an extremely rare congenital nanosomic disorder. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. It is characterized by intrauterine growth restriction and postnatal dwarfism with a small head, narrow bird-like face with a beak-like nose, large eyes with down-slanting palpebral fissures, receding mandible and intellectual disability. A mouse model has been developed. This mouse model is characterized by a severe deficiency of ATR protein. These mice have high levels of replicative stress and DNA damage. Adult Seckel mice display accelerated aging. These findings are consistent with the DNA damage theory of aging. Symptoms and signs Symptoms include: * intellectual disability (more than half of the patients have an IQ below 50) * microcephaly * sometimes pancytopenia (low blood counts) * cryptorchidism in males * low bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Möbius Syndrome
Möbius syndrome or Moebius syndrome is a rare congenital neurological disorder which is characterized by facial nerve paralysis, facial paralysis and the inability to move the eyes from side to side. Most people with Möbius syndrome are born with complete facial paralysis and cannot close their eyes or form facial expressions. Limb and chest wall abnormalities sometimes occur with the syndrome. People with Möbius syndrome have normal intelligence, although their lack of facial expression is sometimes incorrectly taken to be due to dullness or unfriendliness. It is named for Paul Julius Möbius, a German neurologist who first described the syndrome in 1888. In 1994, the "Moebius Syndrome Foundation" was founded, and later that year the first "Moebius Syndrome Foundation Conference" was held in Los Angeles. Signs and symptoms People with Möbius syndrome are born with facial paralysis and the inability to move their eyes laterally. Often, their upper lip is retracted due to muscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Hemiplegia
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many birth defects are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visible at birth or diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms Prodrome, develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorder, mood, anxiety disorder, anxiety, and substance use disorders, substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). About 0.3% to 0.7% of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |