|
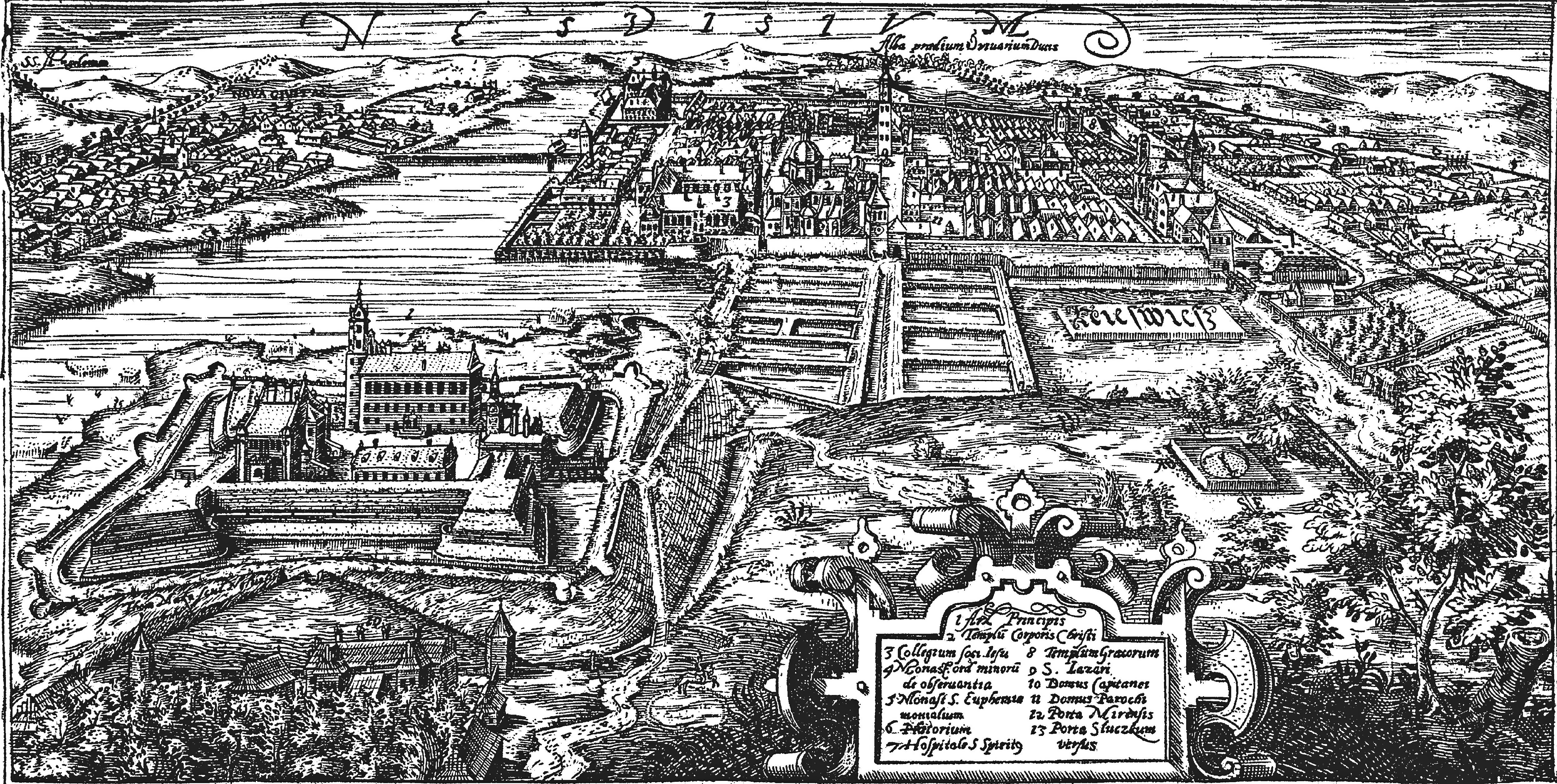
Nesvizh
Nyasvizh or Nesvizh is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Nyasvizh District. Nyasvizh is the site of Nesvizh Castle, a World Heritage Site. In 2009, its population was 14,300. As of 2025, it has a population of 15,909. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin alphabet, Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('':pl:Biblia nieświeska, Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Bible translations into Polish, Polish translations of the Bible, also by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radziwiłł Family
The House of Radziwiłł (; ; ; ) is a Polish princely family of Lithuanian origin, and one of the most powerful magnate families originating from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later also prominent in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. Part of the representatives of the Radziwiłł family were known for their persistent and consistent struggle for the independence of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and for their crucial role in preserving the Grand Duchy of Lithuania as a separate state in the 16th and 17th centuries. The family was founded by Radvila Astikas, but over time it split into many branches, such as the Biržai-Dubingiai and Goniądz-Meteliai lines. However, most of the branches became extinct by the 18th century, with only the Nesvizh-Kleck-Ołyka line surviving to this day. Their descendants were highly prominent for centuries, first in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Kingdom of Prussia. The family produced man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nesvizh Castle
Nesvizh Castle or Nyasvizh Castle (; ; ; ) is a residential castle of the Radziwiłł family in Nyasvizh (Nesvizh), Belarus. It is above sea level. Built in the 16th and 17th centuries, and maintained by the Radziwiłł family until 1939, the castle and the nearby Corpus Christi Church, Nesvizh, Corpus Christi Church were instrumental in the development of Central European and Russian architecture. In 2005, the castle, church, and surrounding environment were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage Site, World Heritage List. History The estate was owned by the Radziwiłł magnate family from 1533, when it was awarded to Mikołaj Krzysztof "the Orphan" Radziwiłł, Mikołaj Radziwiłł and his brother Jan Radziwiłł after the extinction of the Kiszka family. Since the Radziwiłłs were one of the most important and wealthy clans of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, it was there that the Lithuanian Metrica was moved in 1551. In 1586 the estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symon Budny
Szymon Budny or Symon Budny (, , ; c.1533, Budne – 13 January 1593, Vishnyeva) was a Polish- Belarusian humanist, educator, Hebraist, Bible translator, Protestant reformer, philosopher, sociologist and historian, active in the territory of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He was one of the first to promote the development of Belarusian culture in the Belarusian language. He was one of the leaders of the Polish Brethren. Place of birth Little is known about his place of birth. Though the common assumption is that he was born in Budne, Podlaskie Voivodeship, it is known that there were over 140 places with a similar name on the territory of Belarus. Though what is known is that he was familiar with the Belarusian culture first-hand and dedicated a big part of his life to promoting it. The family he was born into was a minor Belarusian szlachta. Symon Budny originally identified himself as a Litvin, which then was the term used mostly to describe Belarusians. Christo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest, most populated countries of 16th- to 18th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned approximately and supported a multi-ethnic population of around 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish language, Polish and Latin Language, Latin, with Catholic Church, Catholicism as the state religion. The Union of Lublin established the Commonwealth as a single entity on 1 July 1569. The two nations had previously been in a personal union since the Union of Krewo, Krewo Agreement of 1385 (Polish–Lithuanian union) and the subsequent marriage of Queen Jadwiga of Poland to Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania, who was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Belarus
This is a list of cities and towns in Belarus. Neither the Belarusian nor the Russian language makes a distinction between "city" and "town" as English does; the word ''horad'' ( ) or ''gorod'' ( ) is used for both. Overview Belarusian legislation uses a three-level hierarchy of town classifications. According to the Law under May 5, 1998, the categories of the most developed urban localities in Belarus are as follows: * ''capital'' — Minsk; * ''city of regional subordinance'' (; ) — urban locality with a population of not less than 50,000 people; it has its own body of self-government, known as ''Council of Deputies'' (; ) and an executive committee (; ), which stand on the level with these of a ''raion'' (). * ''city of district subordinance'' (; ) — urban locality with a population of more than 6,000 people; it may have its own body of self-government (; ) and an executive committee (; ), which belong to the same level as these of rural councils and of s.c. ''haradski p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into Regions of Belarus, six regions. Minsk is the capital and List of cities and largest towns in Belarus, largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the Partitions of Poland, 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Belarusian history in the Russian Empire, Russian Empire for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible Translations Into Polish
The earliest Bible translations into Polish language, Polish date to the 13th century. The first full ones were completed in the 16th. Background The history of translation of books of the Bible into Polish language, Polish begins with the Psalter. The earliest recorded translations date to the 13th century, around 1280; however, none of these survive. ks. prof. dr Jan SzerudGeneza i charakter Biblii Gdańskiej The oldest surviving Polish translation of the Bible is the St. Florian's Psalter (''Psałterz floriański''), assumed to be a copy of that translation, itself a manuscript of the second half of the 14th century, in the abbey of Saint Florian, near Linz, in Latin, Polish and German.Bernard Wodecki, ''Polish Translations of Bible'', in A critical edition of the Polish part of the St. Florian's Psalter was published by Wladysław Nehring (''Psalterii Florianensis pars Polonica'', Poznań, 1883) with a very instructive introduction. Slightly more recent than the St. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Time
Moscow Time (MSK; ) is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia, after the non-continguous Kaliningrad enclave. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011. Moscow Time is used to schedule trains, ships, etc. throughout Russia, but air transport in Russia is scheduled using local time. Time in Russia is often announced throughout the country's other timezones on radio stations as Moscow Time, which is also registered in telegrams, etc. Descriptions of time zones in Russia are often based on Moscow Time rather than UTC; for example, Yakutsk ( UTC+09:00) is said to be MSK+6 in Russia. History Until the October Revolution, the official time in Moscow corresponded to GMT+02:30:17 (according to the longitude of the Astronomical Observatory of Moscow State U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Occupation Of Byelorussia During World War II
The Operation Barbarossa, German invasion of the Soviet Union started on 22 June 1941 and led to a German military occupation of Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussia until it was fully liberated in August 1944 as a result of Operation Bagration. The western parts of Byelorussia became part of the Reichskommissariat Ostland in 1941, and in 1943, the German authorities allowed local Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, collaborators to set up a regional government, the Belarusian Central Rada, that lasted until the Soviet Union, Soviets reestablished control over the region. Altogether, more than two million people were killed in Belarus during the three years of Nazi occupation, around a quarter of the region's population, or even as high as three million killed or thirty percent of the population, including 500,000 to 550,000 Jews as part of the The Holocaust in Byelorussia, Holocaust in Belarus. In total, on the territory of modern Belarus, more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Belarus
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a republic is most often a single sovereign state, subnational state entities that have governments that are republican in nature may be referred to as republics. Representation in a republic may or may not be freely elected by the general citizenry. In many historical republics, representation has been based on personal status and the role of elections has been limited. This remains true today; among the 159 states that use ''republic'' in their official names , and other states formally constituted as republics, are states that narrowly constrain both the right of representation and the process of election. The term developed its modern meaning in reference to the constitution of the ancient Roman Republic, lasting from the overthrow o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six regions and one capital city. The six regions are oblasts (also known as ''voblastsi''), while the city of Minsk has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk also serves as the administrative center of Minsk Region. At the second level, the regions are divided into districts (raions). The layout and extent of the regions were set in 1960 when Belarus (then the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic) was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union. History At the start of the 20th century, the boundaries of the Belarusian lands within the Russian Empire were still being defined. In 1900 it was contained within all of the Minsk and Mogilev governorates, most of Grodno Governorate, parts of Vitebsk Governorate, and parts of Vilna Governorate. World War I, the independence of Poland, as well as the 1920–1921 Polish–Soviet War affected the boundaries. In 1921, Belarus had what is now all of Minsk Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |