|
Neohormone
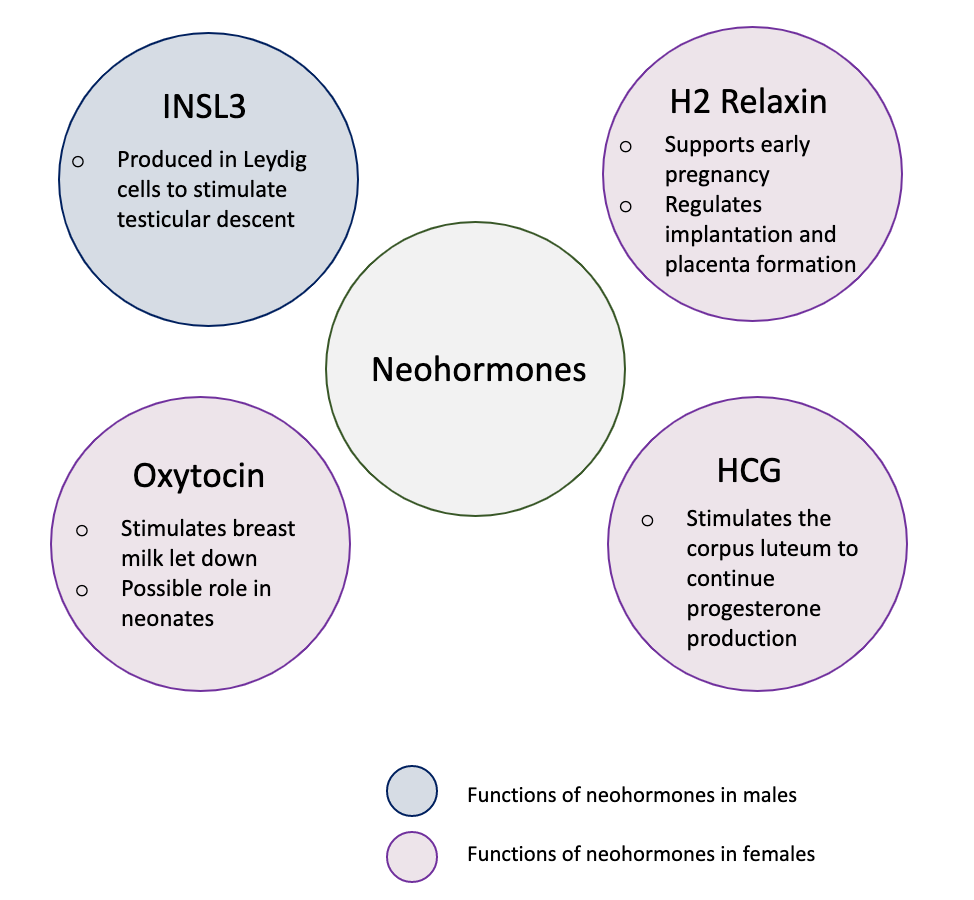
Neohormones are a group of recently evolved hormones primarily associated to the success of mammalian development. These hormones are specific to mammals and are not found in other vertebrates—this is because neohormones are evolved to enhance specific mammalian functions. In males, neohormones play important roles in regulating testicular descent (the testes descend into the scrotum during foetal development) and preparing the sperm for internal fertilisation (the sperm fertilizes the egg within the female). In females, neohormones are essential for regulating early pregnancy, mammary gland development lactation (secretion of milk from the mammary gland), and viviparity (allowing the fertilized egg to grow inside the female until they can exist independently). Neohormones superimpose their actions on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (a hormone system which regulates key reproductive functions in animals) and are not associated with other core bodily functions. Pre-nata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
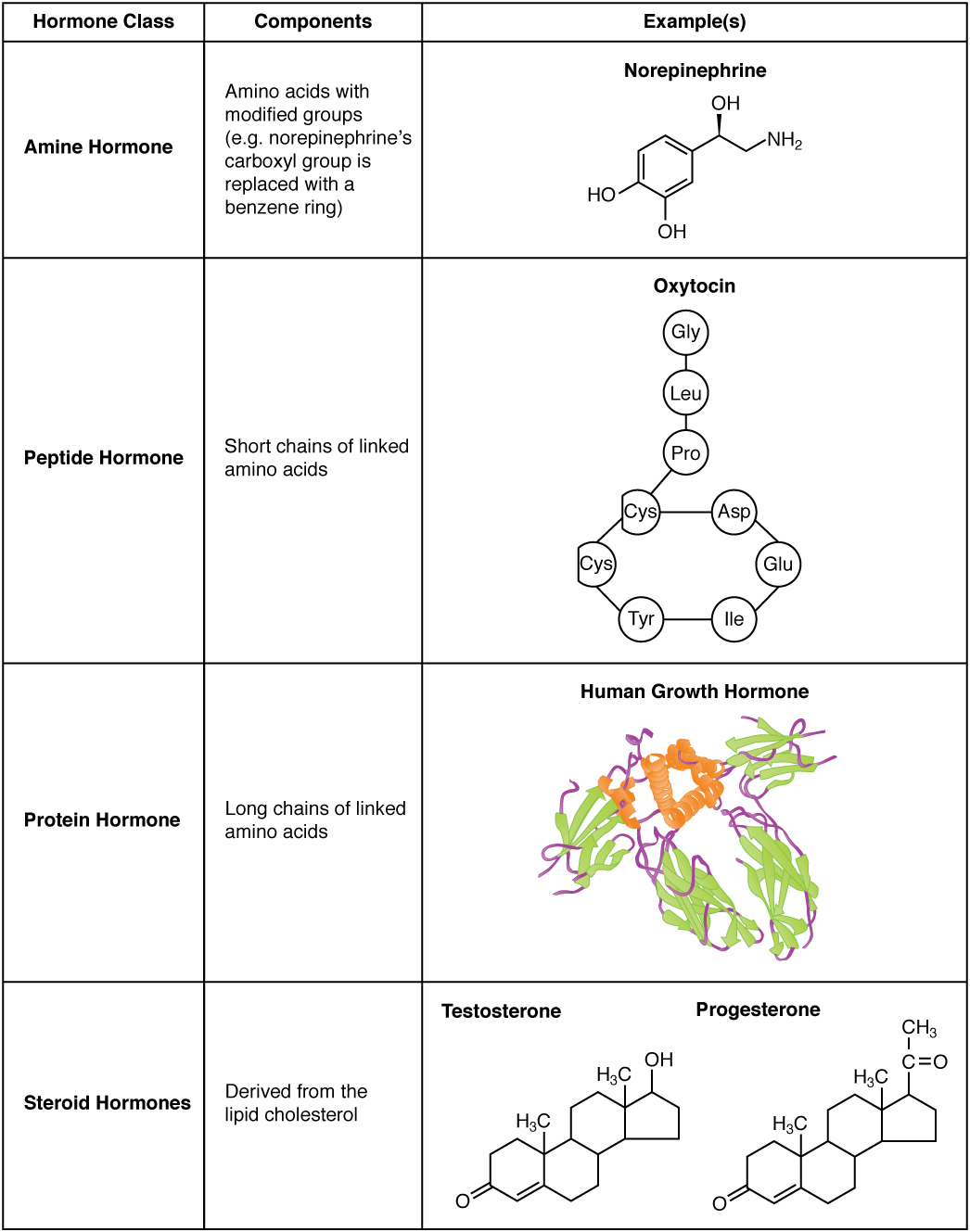
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. Estrogen, oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a wide range of processes including both physiological pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, social bonding, love, reproduction, childbirth, and the Postpartum period, period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to Human sexual activity, sexual activity and during childbirth. It is also available in Oxytocin (medication), pharmaceutical form. In either form, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions to speed up the process of childbirth. In its natural form, it also plays a role in maternal bonding and lactation, milk production. Production and secretion of oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism, where its initial release stimulates production and release of further oxytocin. For example, when oxytocin is released during a contraction of the uterus at the start of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests (HCG pregnancy strip tests). Some cancerous tumors produce this hormone; therefore, elevated levels measured when the patient is not pregnant may lead to a cancer diagnosis and, if high enough, paraneoplastic syndromes, however, it is unknown whether this production is a contributing cause or an effect of carcinogenesis. The pituitary analog of hCG, known as luteinizing hormone (LH), is produced in the pituitary gland of males and females of all ages. Beta-hCG is initially secreted by the syncytiotrophoblast. Structure Human chorionic gonadotropin is a glycoprotein composed of 237 amino acids with a molecular mass of 36.7 kDa, approximately 14.5kDa αhCG and 22.2kDa βhCG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSL3
Insulin-like 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''INSL3'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is an insulin like hormone produced mainly in gonadal tissues in males and females. Studies of the mouse counterpart suggest that this gene may be involved in the development of urogenital tract and female fertility. INSL-3 initiates meiotic progression in follicle-enclosed oocytes by mediating a reduction in intra-oocyte cAMP concentration by activating leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 8 (LGR8). It may also act as a hormone to regulate growth and differentiation of gubernaculum, and thus mediating intra-abdominal testicular descent. The mutation In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...s in this gene may lead to, but not a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual ( endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Luteum
The corpus luteum (Latin for "yellow body"; : corpora lutea) is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone, and moderate levels of estradiol, and inhibin A. It is the remains of the ovarian follicle that has released a mature ovum during a previous ovulation. The corpus luteum is colored as a result of concentrating carotenoids (including lutein) from the diet and secretes a moderate amount of estrogen that inhibits further release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and thus secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). A new corpus luteum develops with each menstrual cycle. Development and structure The corpus luteum develops from an ovarian follicle during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle or oestrous cycle, following the release of a secondary oocyte from the follicle during ovulation. The follicle first forms a corpus hemorrhagicum before it beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxin
Relaxin is a protein hormone of about 6000 Da, first described in 1926 by Frederick Hisaw. The relaxin family peptide hormones belong to the insulin superfamily and consists of seven peptides of high structural but low sequence similarity; relaxin-1 (RLN1), 2 (RLN2) and 3 ( RLN3), and the insulin-like (INSL) peptides, INSL3, INSL4, INSL5 and INSL6. The functions of relaxin-3, INSL4, INSL5, and INSL6 remain uncharacterised. Synthesis In the female, relaxin is produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary, the breast and, during pregnancy, also by the placenta, chorion, and decidua. In the male, it is produced in the prostate and is present in human semen. Structure Structurally, relaxin is a heterodimer of two peptide chains of 24 and 29 amino acids linked by three disulfide bridges, and it appears related to insulin. Relaxin is produced from its prohormone, "prorelaxin", by post-translational proteolytic cleavage of its signal peptide and C domain peptide. Function in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |