Neohormone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
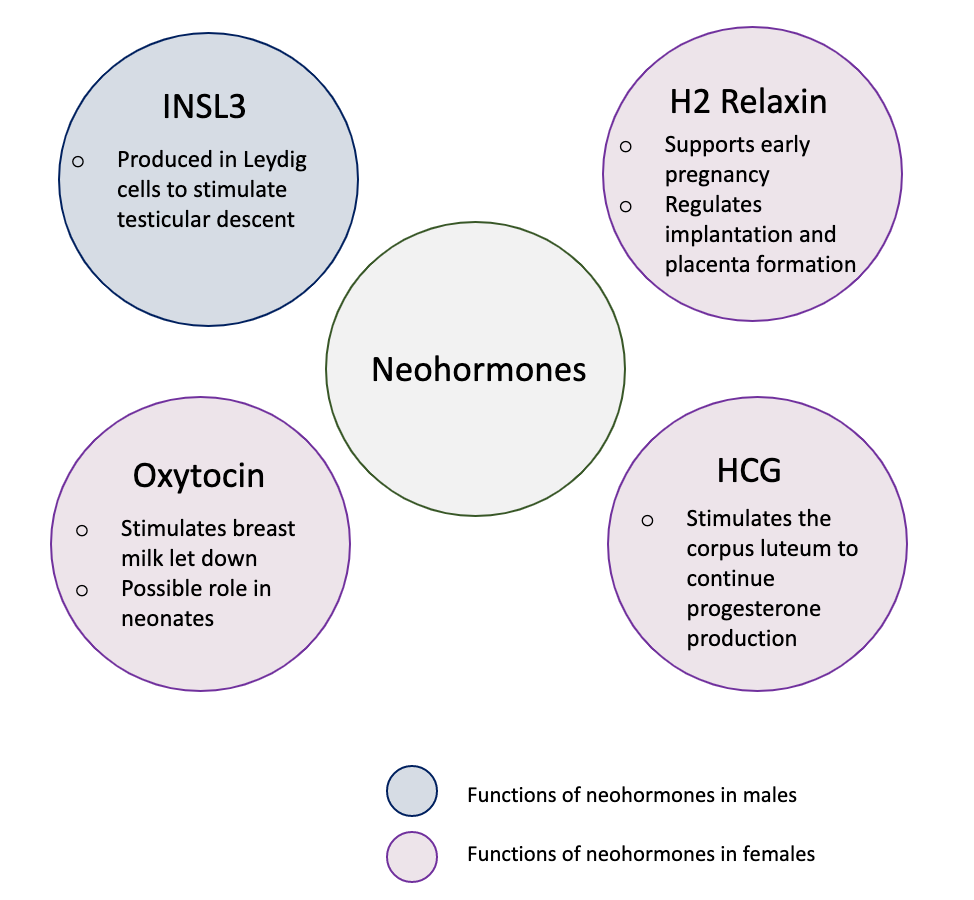 Neohormones are a group of recently evolved
Neohormones are a group of recently evolved
 In the human
In the human
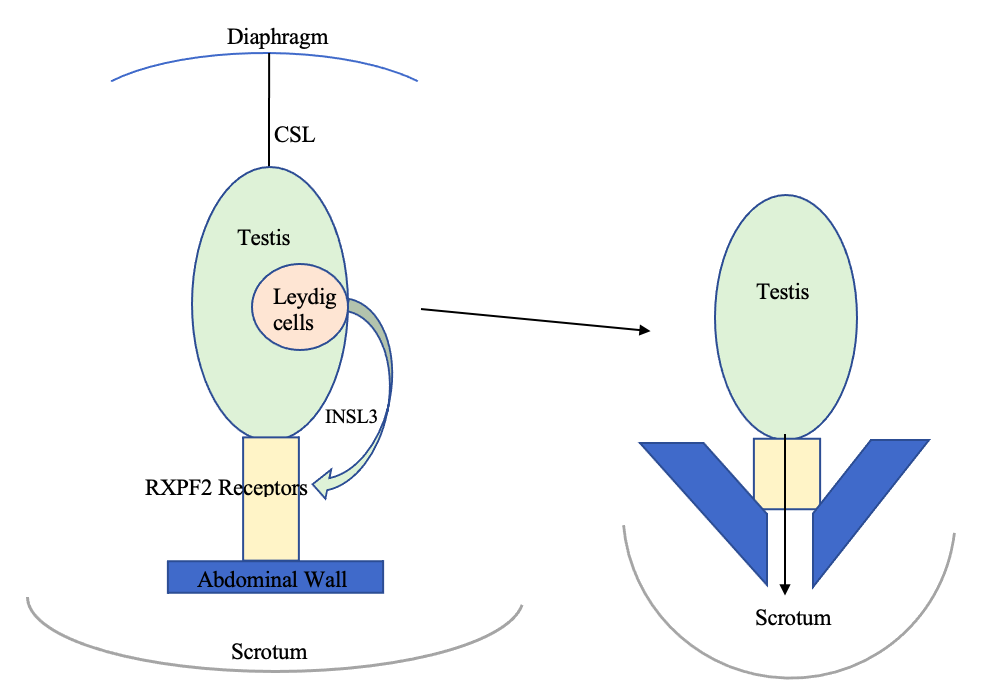
 Neohormones are a group of recently evolved
Neohormones are a group of recently evolved hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
primarily associated to the success of mammalian
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
development. These hormones are specific to mammals and are not found in other vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
—this is because neohormones are evolved to enhance specific mammalian functions. In males, neohormones play important roles in regulating testicular descent
The development of the gonads is part of the prenatal development of the reproductive system and ultimately forms the testicles in males and the ovaries in females. The immature ova originate from cells from the dorsal endoderm of the yolk sac. ...
(the testes descend into the scrotum during foetal development) and preparing the sperm for internal fertilisation
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For intern ...
(the sperm fertilizes the egg within the female). In females, neohormones are essential for regulating early pregnancy, mammary gland development lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process ...
(secretion of milk from the mammary gland), and viviparity
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juv ...
(allowing the fertilized egg to grow inside the female until they can exist independently). Neohormones superimpose their actions on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (a hormone system which regulates key reproductive functions in animals) and are not associated with other core bodily functions.
Pre-natal functions of neohormones
Prenatally, neohormones play a role in the development of the embryo as well as supporting early pregnancy.H2 Relaxin
 In the human
In the human ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
, H2 relaxin is produced by the corpus luteum
The corpus luteum (Latin for "yellow body"; : corpora lutea) is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone, and moderate levels of estradiol, and inhibin A. It is the ...
and by Granulosa cells from large antral follicles. Research has shown that the relaxin gene is expressed once the Granulosa cells have reached a certain luteinised status, by which Granulosa cells differentiate into Luteal cells. Therefore, it can act as a good biomarker in relation to Granulosa cell differentiation status.
Relaxin is produced to support early pregnancy until the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
can take over. Relaxin plays a key role in implantation and placenta formation.
The relaxin receptor RXFP1 is found on myometrial cells. In rats, it has been linked playing a role in the spacing between embryos in the uterus. RXFP1 is also located on endometrial stromal cells where it can induce cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine tri ...
(cAMP). cAMP is a molecule which is necessary for the functional changes in the endometrium to form the decidual lining, where the blastocyst can implant. This results in neo-angiogenesis and endometrial thickening, both linked to early pregnancy development.
Human chorionic gonadotropin

Human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantat ...
(hCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. This hormone stimulates the Corpus Luteum to produce progesterone to maintain pregnancy. Therefore, hCG plays a role in human maternal recognition of pregnancy.
Insulin-like peptide 3
Insulin-Like Peptide 3 (INSL3) is produced by the interstitial Leydig cells located in the adult testes. Leydig cells are responsible for steroidogenesis, the fetal Leydig cells differentiate during the development of the embryo. They produce necessary androgens for the masculinisation of organs. They also produce INSL3, which is required for the first transabdominal phase of testicular descent. INSL3 acts on RXFP2 receptors which link the testis to the inguinal abdominal wall. As a result, the testes move from the inguinal canal into the scrotum. Only mammals have a scrotum and descended testes. INSL3 measured in amniotic fluid can therefore be a biomarker for testis development, although this period differs between species.Post-natal functions of neohormones
After birth, neohormones play a major role in development of mammary glands and their function. Alongside, neohormones have also been measured to be a significant component of breast milk. The so-called lactocrine hypothesis dictates that breast milk does not simply fulfil nutritional requirements but also plays an important role in signaling and development in the neonate. Neohormones are theorised to have specific effects on target organs in the neonate, but more research is needed in this area, and effects have been observed to different extents in different species.Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, ...
is responsible for the milk let-down reflex as a response to neonate suckling. It is released from the posterior pituitary gland in a pulsatile manner, via stimulation of the vagus nerve. This causes myoepithelial cells, which surround the mammary alveoli, to contract. Oxytocin injections have been found to increase milk yield in cows. The role of oxytocin in the neonate is yet quite unclear, however we know that oxytocin has an important role in empathy and bonding between pairs.
Relaxin
There are three relaxin genes in humans. One type, H2, is made and secreted in the ovaries, as well as in the mammary glands. Relaxin acts via locally expressed specific receptors located on parenchyma and myoepithelial cells. It reaches peak concentrations 24-48 hours after birth and then declines.Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Like relaxin, hCG may be measured, although the effects on the neonate are not well understood. It is posited that it may act as an LH paralogue to affect the development of neonatal gonads, although further research is required.Biomarkers of reproductive health
The main neohormones that can be used as biomarkers of reproductive health are relaxin, oxytocin, hCG, INSL3, and INSL5 and INSL6. Relaxin (Specifically Ovarian H2-relaxin) aids in the implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall after fertilisation, as well as establishing the placenta. The levels of relaxin are altered in cases of early miscarriage and hence can be used as a biomarker during early pregnancy. Oxytocin has a range of functions in the reproductive systems of both males and females. It has a major role in the production of breast milk and lactation. It is responsible for muscle contractions in the uterus to facilitate birth. It also assists in ovarian steroid production and ovum release. In men, oxytocin has a role in erections and ejaculation. It also participates in gonadal development in both males and females. Despite being tricky to measure, measuring oxytocin can help build a clinical picture of reproductive health in the above mechanisms. hCG has a vital role in early pregnancy. Higher levels of hCG is a good indication for the survival and viability of the embryo. β-hCG can be monitored to test for an ectopic pregnancy. INSL3 is responsible for the first phase of testicular descent in males and may be disrupted in cases of cryptorchidism. It also acts as a measure of Leydig cell function, particularly in older males. INSL5 and INSL6 may have a role in spermatogenesis. There are currently no ways to measure these hormones but there is some evidence that with altered INSL5, there is reduced fertility and impaired spermatogenesis.Therapeutic uses of neohormones
Relaxin has been shown to repair and reverse the symptoms associated with scleroderma (an autoimmune condition affecting connective tissues, blood vessels and internal organs) and fibrosis (thickening, hardening or build up of scar tissue). It also aids in the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). This is also beneficial in wound management and healing. Other potential targets include the use of relaxin within human reproduction, such as in the preparation of the cervix for labour and birth and also as a drug target for breast cancer treatment although much more research is required in this area. Oxytocin is important for many different biological processes including social, maternal and sexual behaviours, pregnancy, milk production, and ejaculation. Agonists and antagonists of oxytocin – development of drugs that can utilise the receptor binding activity of oxytocin is an important therapeutic target as this could be applied to a range of conditions. Oxytocin plays a role in cell proliferation and differentiation in different ways depending on where it is in the body. Understanding the underlying pathways for different localities could help with development of cancer therapies.References